How many layers of Phospholipids make up the plasma membrane?
it has a "sandwich" structure, with two phospholipid layers The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, meaning that Multiple choice question. only some substances can cross the membrane. Which of the following applies to the formation of the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane?
What are phospholipids and why should you care?
Properties Of Phospholipids
- They are signal mediators.
- They are amphipathic molecules.
- They anchor proteins within the cell membranes.
- They are the major constituents of cell membranes.
- They are the components of bile and lipoproteins.
Does plasma membrane consist of phospholipds?
Unsaturated fatty acids result in kinks in the hydrophobic tails. The plasma membrane consists of two adjacent layers of phospholipids. The lipid tails of one layer face the lipid tails of the other layer, meeting at the interface of the two layers.
What are the four components of phospholipids?
What are the 4 main phospholipids?
- Phosphatidic acid (phosphatidate) (PA)
- Phosphatidylethanolamine (cephalin) (PE)
- Phosphatidylcholine (lecithin) (PC)
- Phosphatidylserine (PS)
- Phosphoinositides: Phosphatidylinositol (PI) Phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP) Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) and.

How are the phospholipids arranged to form the plasma membrane quizlet?
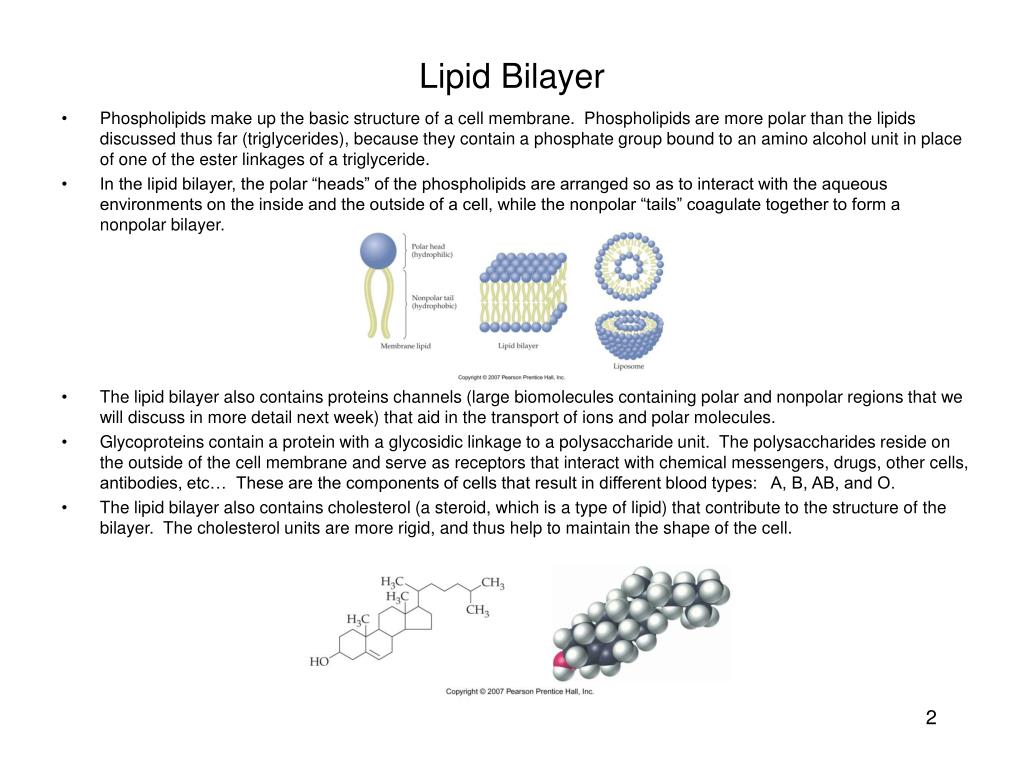
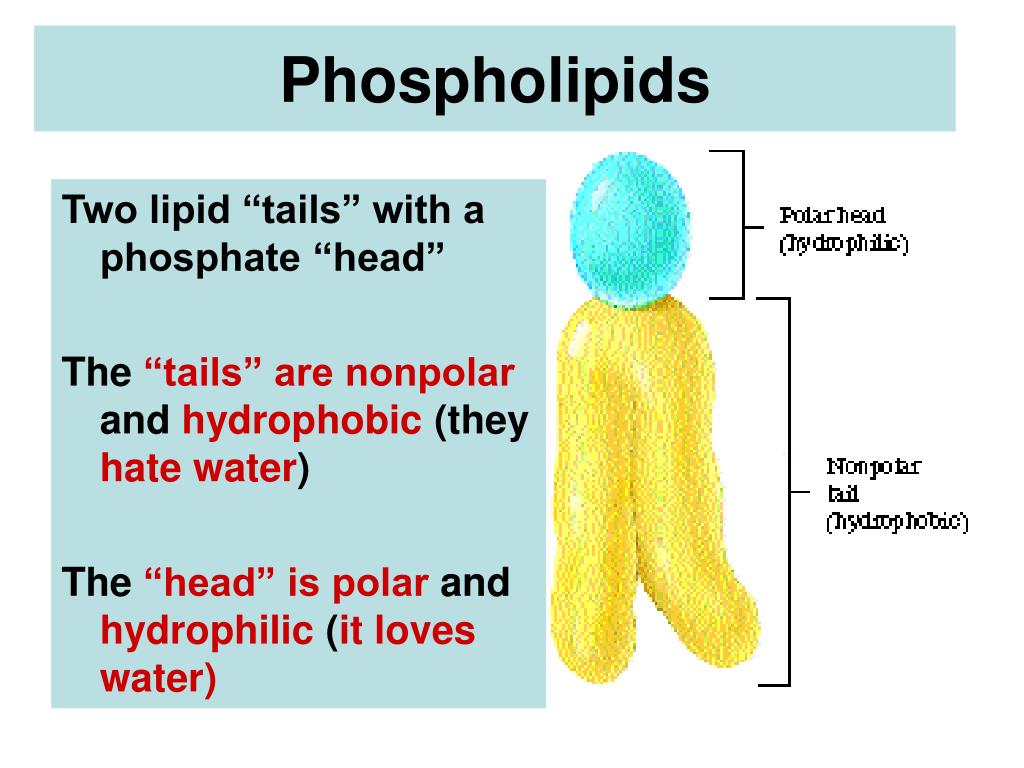
How are phospholipids arranged in the membrane? The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer. ach phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The head "loves" water (hydrophilic) and the tails "hate" water (hydrophobic).
How do they arrange themselves to form the plasma membrane?
The membrane is partially made up of molecules called phospholipids, which spontaneously arrange themselves into a double layer with hydrophilic (“water loving”) heads on the outside and hydrophobic (“water hating”) tails on the inside. These interactions with water are what allow plasma membranes to form.
How are phospholipids arranged to form a lipid bilayer?
The lipid bilayer is arranged in two layers of phospholipids with the hydrophilic heads forming the outer edges and the tails forming the interior. In this arrangement, the bilayer has a hydrophobic core that prevents the passage of polar molecules while allowing the relatively free diffusion of non-polar molecules.
Why do phospholipids arrange themselves the way they do?
Because phospholipids have both polar and hydrophobic parts, when they are in water they will spontaneously arrange themselves into ordered structures.
Why do phospholipids self assemble into a bilayer?
When cellular membranes form, phospholipids assemble into two layers because of these hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. The phosphate heads in each layer face the aqueous or watery environment on either side, and the tails hide away from the water between the layers of heads, because they are hydrophobic.
How many layers of phospholipids form the plasma membrane?
Phospholipids are made up of two layers, the outer and inner layers. The inside layer is made of hydrophobic fatty acid tails, while the outer layer is made up of hydrophilic polar heads that are pointed toward the water.
How is a phospholipid formed?
Phospholipids are mostly made from glycerides by substituting one of the three fatty acids by a phosphate group with some other molecule attached to its end. The other form of phospholipids is sphingomyelin, which is derived from sphingosine instead of glycerol.
Which of the following best describes how phospholipids are arranged in the bilayer structure?
So, the correct answer is 'Two layers of phospholipids where the outer layer has the hydrophilic heads facing toward the outside of the cell and the inner layer have the hydrophobic tails facing toward the inside of the cell.
Which component of the plasma membrane is arranged as a bilayer?
PhospholipidsPhospholipids. Phospholipids, arranged in a bilayer, make up the basic fabric of the plasma membrane. They are well-suited for this role because they are amphipathic, meaning that they have both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions. Chemical structure of a phospholipid, showing the hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tails ...
How does the arrangement of different structural components the cell membrane contributes to its fluidity?
If saturated fatty acids are compressed by decreasing temperatures, they press in on each other, making a dense and fairly rigid membrane. If unsaturated fatty acids are compressed, the “kinks” in their tails push adjacent phospholipid molecules away, which helps maintain fluidity in the membrane.
What is the structure of the plasma membrane quizlet?
The plasma membrane is made up of a phospholipid bilayer which has polar head and hydrophobic tails that face each other keeping water out. There are proteins embedded in the membrane to selectively facilitate the movement of particles across the membrane.
What is the structure of the plasma membrane?
Plasma Membrane Structure The plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer, which is two layers of phospholipids back-to-back. Phospholipids are lipids with a phosphate group attached to them. The phospholipids have one head and two tails. The head is polar and hydrophilic, or water-loving.
How are phospholipids arranged in the plasma membrane quizlet?
How are phospholipids arranged in the membrane? The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer. ach phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The head “loves” water (hydrophilic) and the tails “hate” water (hydrophobic).
What are the two major kinds of phospholipids?
Main phospholipids Phosphatidylinositol phosphate (PIP) Phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate (PIP2) and.
What are the folds of the plasma membrane called?
Folds of the plasma membrane that increase surface area are called A. cilia. B. microvilli. C. flagella. D. vesicles. B. microvilli. 34. Cells with large numbers of microvilli on their apical surface are probably involved in A. movement of the body. B. reabsorption of molecules during production of urine.
What is a phospholipid molecule?
This phospholipid molecule is composed of a hydrophilic head and two hydrophobic tails. The hydrophilic head group consists of a phosphate-containing group attached to a glycerol molecule. The hydrophobic tails, each containing either a saturated or an unsaturated fatty acid, are long hydrocarbon chains. Image Attribution: OpenStax Biology.
Why do phospholipids form a bilayer?
This is because, in water, phospholipids tend to become arranged with their hydrophobic tails facing each other and their hydrophilic heads facing out. In this way, they form a lipid bilayer—a barrier composed of a double layer of phospholipids that separates the water and other materials on one side of the barrier from the water and other materials on the other side.
What are phospholipids in aqueous solution?
In fact, phospholipids heated in an aqueous solution tend to spontaneously form small spheres or droplets. We refer to these spheres as micelles or liposomes. Their hydrophilic heads form the exterior and their hydrophobic tails stay on the inside ( see image above ).
What is the main fabric of the plasma membrane?
The main fabric of the membrane is composed of amphiphilic, phospholipid molecules. The hydrophilic or “water-loving” areas of these molecules look like a collection of balls in an artist’s rendition of the model. Look at the image of the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane below.
What is the backbone of a phospholipid?
A phospholipid molecule ( see image below) consists of a three-carbon glycerol backbone with two fatty acid molecules attached to carbons 1 and 2, and a phosphate-containing group attached to the third carbon. This arrangement gives the overall molecule an area described as its head (the phosphate-containing group), ...
What is the bilayer of a lipid?
In this way, they form a lipid bilayer—a barrier composed of a double layer of phospholipids that separates the water and other materials on one side of the barrier from the water and other materials on the other side. In an aqueous solution, phospholipids tend to arrange themselves with their polar heads facing outward.
Which region of the cell is hydrophilic?
The hydrophilic regions of the phospholipids tend to form hydrogen bonds with water and other polar molecules on both the exterior and interior of the cell. Thus, the membrane surfaces that face the interior and exterior of the cell are hydrophilic.
What would allow cells to selectively remove molecules from the extracellular fluid?
Receptor-mediated endocytosis would allow cells to selectively remove molecules from the extracellular fluid.
What is the structure of motile cilia?
All body cells have motile cilia with a "9+2" structure.
How are cholesterol and AIDS viruses taken into cells?
Cholesterol and AIDS viruses are taken into cells by receptor-mediated endocytosis.
How do neutrophils move through the extracellular matrix?
Neutrophils and macrophages move through the extracellular matrix by amoeboid movement.
What is the basic structural and functional unit of the body?
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit in the body.
Which type of receptor binds to molecules to be brought into the cell?
C. specific membrane receptors bind to the molecules to be brought into the cell.
Which part of the plasma membrane restricts the movement of water and fat-soluble substances through the membrane?
The hydrophobic center of the plasma membrane will restrict the movement of water and fat-soluble substances through the membrane.