
Explore
Method 1 Method 1 of 3: Increasing Amniotic Fluid with Medicine Download Article
- Understand that treatment is based on how far along you are in your pregnancy. ...
- Get an injection of amniotic fluid. In this process, your doctor will inject the leaking amniotic fluids back into the amniotic sac with a needle.
- Get fluid intravenously. ...
- Use a catheter to increase fluid levels. ...
What are some ways to increase amniotic fluid?
- Fetal breathing (continuous movement of the fetal diaphragm for at least 30 seconds)
- Fetal movement (at least three discrete movements of the fetal body or limbs)
- Fetal tone (at least one active extension of a fetal limb with return to flexion, or opening and closing of the fetal hand)
- Amniotic fluid volume (single deepest pocket of at least 2 cm)
How to measure the amniotic fluid?
Other treatments that may be used include:
- Amnio-infusion during labor through an intrauterine catheter. ...
- Injection of fluid prior to delivery through amniocentesis. ...
- Maternal re-hydration with oral fluids or IV fluids has shown to help increase amniotic fluid levels.
How to increase amniotic fluid in second trimester?
How often does your body replace amniotic fluid? The amount of amniotic fluid increases until about 36 weeks of pregnancy. At that time, it makes up about 1 quart. After that, the amount of amniotic fluid usually begins to decrease. Sometimes you can have too little or too much amniotic fluid.
How often does amniotic fluid replenish?
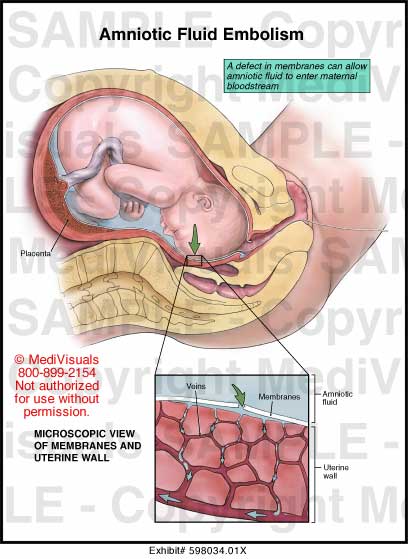
Can you prevent amniotic fluid embolism?
To prevent amniotic fluid embolism, trauma to the uterus must be avoided during maneuvers such as insertion of a pressure catheter or rupture of membranes. Incision of the placenta during caesarean delivery should also be avoided if possible.
Should I be worried about amniotic fluid embolism?
An amniotic fluid embolism can cause potentially life-threatening breathing and heart issues, as well as uncontrolled bleeding. It is an often fatal emergency that requires immediate medical care for both the pregnant person and the baby.
How fast does amniotic fluid embolism happen?
Amniotic fluid embolism is thought to occur in labor or within 30 minutes of delivery. There are several signs and phases of amniotic fluid embolism.
How many people survive amniotic fluid embolism?
Treatment is mainly supportive, but exchange transfusion, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, and uterine artery embolization have been tried from time to time. The maternal prognosis after amniotic fluid embolism is very poor though infant survival rate is around 70%.
How do you diagnose amniotic fluid embolism?
DiagnosisBlood tests, including those that evaluate clotting, heart enzymes, electrolytes and blood type, as well as a complete blood count (CBC)Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) to evaluate your heart's rhythm.Pulse oximetry to check the amount of oxygen in your blood.Chest X-ray to look for fluid around your heart.More items...•
How do you control amniotic fluid embolism?
Treatment is supportive and includes the following:Administer oxygen to maintain normal saturation. ... Initiate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) if the patient arrests. ... Treat hypotension with crystalloid and blood products. ... Avoid excessive fluid administration.More items...•
How can you tell the difference between amniotic fluid embolism and pulmonary embolism?
Symptoms of pulmonary embolism include tachycardia, tachypnea, and shortness of breath, all of which are common complaints in pregnancy. Heightened awareness leads to rapid diagnosis and institution of therapy. Amniotic fluid embolism is associated with maternal collapse.
What is an AFE Survivor?
AFE is a life-threatening and unexpected birth complication that can affect both mother and baby. It is characterized by acute and rapid collapse of the mother and/or baby because of an allergic reaction to amniotic fluid entering the maternal circulatory system.
Can you have another baby after amniotic fluid embolism?
Conclusion: This case of a 29-year-old woman with successful subsequent pregnancy after amniotic fluid embolism and a limited number of case reports in the literature suggest that AFE is a sporadic event.
Who is at risk for amniotic fluid embolism?
Age: Women ages 35 or older at the time of delivery may be at increased risk of amniotic fluid embolism. Delivery via operation: Operations like a cesarean section, forceps delivery, or vacuum extraction disturb the barriers between the mother and baby.
Is amniotic fluid embolism more common with C-section?
The incidence of amniotic fluid embolism was higher with cesarean section, 5,000 of 22,937,000 (22/100,000) than with vaginal delivery, 7,000 of 89,775,000 (8/100,000) (relative risk 2.80, 95% CI 2.70-2.90) (p < 0.0001).
What is the amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic Fluid Embolism (Anaphylactic Syndrome of Pregnancy) A very rare condition, the exact cause of amniotic fluid embolism is unknown. This condition is a dangerous and fatal complication that can happen during labor or soon after childbirth.
Why is it so difficult to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism?
Diagnosing amniotic fluid embolism is difficult because many of the symptoms can overlap with other serious medical conditions. Your doctor will rule out other possible causes while working to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism. Amniotic fluid embolism is thought to occur in labor or within 30 minutes of delivery.
What happens when a baby floats in amniotic fluid?
When this fluid mixes with a mother’s blood, it can cause an allergic-like reaction that can be fatal. This is a medical emergency requiring expert medical care. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center.
Can amniotic fluid embolism occur after birth?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a very rare condition that can happen during childbirth or soon after birth. It’s unknown what causes amniotic fluid embolism, but some experts think it may be related to amniotic fluid entering the mother’s blood stream (circulatory system).
Can amniotic fluid be prevented?
Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent amniotic fluid embolism. Healthcare providers are still unsure why this happens and what exactly causes this condition. One way to prepare for any kind of medical emergency is to develop a plan with your family and healthcare providers.
What are the symptoms of an amniotic fluid embolism?
Signs and symptoms. Amniotic fluid embolism is suspected when a woman giving birth experiences very sudden insufficient oxygen to body tissues, low blood pressure, and profuse bleeding due to defects in blood coagulation. Though symptoms and signs can be profound, they also can be entirely absent. There is much variation in how each instance ...
What is AFE in obstetrics?
Obstetrics. Pathophysiology of the amniotic fluid embolism. An amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a very uncommon childbirth ( obstetric) emergency in which amniotic fluid enters the blood stream of the mother to trigger a serious reaction.
How does AFE occur?
The disorder occurs during the last stages of labor when amniotic fluid enters the circulatory system of the mother via tears in the placental membrane or uterine vein rupture. Upon later analysis, fetal cells are found in the maternal circulation. When the fetal cells and amniotic fluid enter the bloodstream, reactions occur that cause severe changes in the mechanisms that affect blood clotting. Disseminated intravascular coagulation occurs and results in serious bleeding. The condition can also develop after elective abortion, amniocentesis, cesarean delivery or trauma. Small lacerations in the lower reproductive tract are associated with AFE.
What is AFE diagnosis?
Diagnosis. AFE is diagnosed when all other causes have been excluded. The presence of fetal squamous cells or other fetal tissues, including meconium, have been found in the maternal circulation after the event. Diagnosis is also based upon the signs and symptoms observed during the birth or procedures.
What age is associated with AFE?
According to one study, induction of labor may double the risk of AFE. However, other studies have refuted this claim. A maternal age of 35 years or older is associated with AFE.
How many times has the complication of a syringe been recorded?
This rare complication has been recorded seventeen times prior to 1950. The complication was originally described in 1926 by J. R. Meyer at the University of Sao Paulo. A 1941 case study of eight autopsies of pregnant women who died suddenly during childbirth by Clarence Lushbaugh and Paul Steiner enabled widespread recognition of the diagnosis within the medical community, and was eventually republished as a landmark paper in the Journal of the American Medical Association.
Why is amniotic fluid embolism a condition?
Amniotic fluid embolism is a condition that occurs because there is systemic reaction similar to that found in an allergic response to amniotic fluid or fetal cells or fetal tissue debris by the pregnant mother.
How to tell if you have amniotic fluid embolism?
Other common initial symptoms include difficulty breathing or shortness of breath (dyspnea), abnormally rapid breathing (tachypnea), low blood pressure (hypotension), an abnormally rapid heartbeat (tachycardia), bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to a lack of oxygen (cyanosis) in the blood, and a deficiency in the amount of oxygen reaching the tissues of the body (hypoxia). There may be rapidly high blood pressure in the blood vessels of the lungs (pulmonary hypertension) and sudden narrowing of blood vessels (vasospasm).
What is the diagnosis of amniotic fluid embolism?
A diagnosis of amniotic fluid embolism is based upon identification of characteristic clinical symptoms only. To date, there are no diagnostic assays, imaging studies or pathologic markers that have been validated for the diagnosis of AFE. Prompt diagnosis and early, aggressive advanced life support techniques are essential in assuring the best possible outcomes in amniotic fluid embolism. There is a lack of internal consensus in the medical community as to diagnostic criteria for this disorder, although there have been proposed diagnostic criteria for the research reporting of AFE (Clark SL, 2016). The diagnosis is made by identifying characteristic symptoms and excluding other possible causes of the signs and symptoms (diagnosis of exclusion).
What is AFE in pregnancy?
Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is an extremely rare, but life-threatening complication that affects pregnant women shortly before, during, or immediately following labor and childbirth. Most instances occur during labor. In this disorder, it is hypothesized that a pregnant woman has a severe, allergic reaction to amniotic fluid or other fetal ...
What are the complications of amniotic fluid?
Breathing problems, cardiac arrest, and excessive bleeding are some of the life-threatening complications that can occur. Researchers and physicians do not fully understand why amniotic fluid or fetal cells entering the mother’s bloodstream causes this reaction in some women.
Why does amniotic fluid enter the bloodstream?
The amniotic fluid and other material enters the mother’s bloodstream, most likely due to small tears in the lower part of the uterus, the part of the cervix that forms a canal connecting the vagina to the uterus (endocervix), or because of damage or abnormality affecting the placenta.
How many women have a fluid embolism?
Rare disorders often go unrecognized or misdiagnosed, making it difficult to determine their true frequency in the general population. Estimates have ranged from 1 in 8,000 to 1 in 80,000 pregnancies.
Signs
The signs and symptoms of amniotic fluid embolism can sometimes overlap with other childbirth complications, making it difficult to recognize.
Causes
The exact causes of amniotic fluid embolism are still unknown because it is so rare.
Diagnosis
It is hard for doctors to diagnose amniotic fluid embolism because the symptoms are similar to other childbirth-related complications. Additionally, there is no specific test to diagnose the condition, which means that other conditions will need to be ruled out first.
Treatment
If your doctor suspects you could have an amniotic fluid embolism, you’ll need immediate emergency treatment to prevent potentially life-threatening complications.
Complications
Amniotic fluid embolism can cause serious complications for a pregnant person and their baby. These life-threatening complications can include:
Risk Factors
Experts do not know for sure why amniotic fluid embolism happens. Research points to a few factors that might be linked to an increased risk of experiencing the condition.
Coping
Experiencing a life-threatening condition during childbirth is frightening. Survivors of amniotic fluid embolism experience lasting medical and emotional effects from the traumatic event.
What is an amniotic fluid embolism?
Amniotic Fluid Embolism. Amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a rare but serious complication that can happen during delivery or shortly after birth. AFE only affects an estimated 1 in 40,000 deliveries but is still a leading cause of maternal death during labor. This condition occurs when the baby's amniotic fluid ...
What are the factors that increase the risk of amniotic fluid embolism?
These factors include: Advanced maternal age: Mothers who are 35 years and older are at a much higher risk of pregnancy and labor complications, including AFE.
What is the condition where fetal cells make their way into the mother's bloodstream?
This condition occurs when the baby's amniotic fluid (the fluid that surrounds the baby in the placenta), fetal cells, or hair makes its way into the mother's bloodstream. AFE can rapidly develop into a life-threatening situation that puts both the baby and mother's life at risk. Emergency medical intervention is needed to stabilize ...
When does AFE occur?
AFE occurs when the amniotic fluid or fetal material passes the placental barrier, enters the mother's bloodstream and starts moving throughout the circulatory system.
What happens if a baby is deprived of oxygen for too long?
Infant death: If the baby is deprived of oxygen for too long or is not delivered quickly enough, the baby can die during delivery. Sudden cardiac arrest: The effects of AFE can develop so rapidly that the blood clots in the lungs send the mother into cardiac arrest.
How many mothers die from AFE?
The effects of AFE can be devastating. The maternal mortality rate for this condition can be as high as 80%, with 50% of mothers dying within the first hour of symptom onset. For patients that do survive the embolism, the majority of them will experience long-term neurological deficits.
What happens if you have an AFE?
Still, there are several complications that can occur from AFE: Brain injury to mother: The blood clots in the lungs from the embolism can reduce the amount of oxygen traveling to the mother's brain, which can result in permanent brain damage.

Overview
Signs and symptoms
Causes
- It's estimated that there are between one and 12 cases of amniotic fluid embolism for every 100,000 deliveries. Because amniotic fluid embolisms are rare, it's difficult to identify risk factors. Research suggests that several factors might be linked to an increased risk of amniotic fluid em…
Diagnosis
Treatment
An amniotic fluid embolism (AFE) is a very uncommon childbirth (obstetric) emergency in which amniotic fluid enters the blood stream of the mother to trigger a serious reaction. This reaction then results in cardiorespiratory (heart and lung) collapse and massive bleeding (coagulopathy). The rate at which it occurs is 1 instance per 20,000 births and it comprises 10% of all maternal de…
Epidemiology
Amniotic fluid embolism is suspected when a woman giving birth experiences very sudden insufficient oxygen to body tissues, low blood pressure, and profuse bleeding due to defects in blood coagulation. Though symptoms and signs can be profound, they also can be entirely absent. There is much variation in how each instance progresses.
History
AFE is very rare and complex. The disorder occurs during the last stages of labor when amniotic fluid enters the circulatory system of the mother via tears in the placental membrane or uterine vein rupture. Upon later analysis, fetal cells are found in the maternal circulation. When the fetal cells and amniotic fluid enter the bloodstream, reactions occur that cause severe changes in the mechanisms that affect blood clotting. Disseminated intravascular coagulation occurs and result…