What is intergalactic space?
(Error Code: 241403) Intergalactic space is the physical space between galaxies. Generally free of dust and debris, intergalactic space is very close to a vacuum. The average density of the Universe is less than one atom per cubic meter.
What is the mass of the intergalactic star population?
Although the precise mass of the intergalactic star population cannot be known exactly, it is estimated that locally they make up 10 percent of the mass of the Virgo cluster of galaxies (and most likely, this total outweighs any of its 2500 galaxies).
How dark does it get in space?
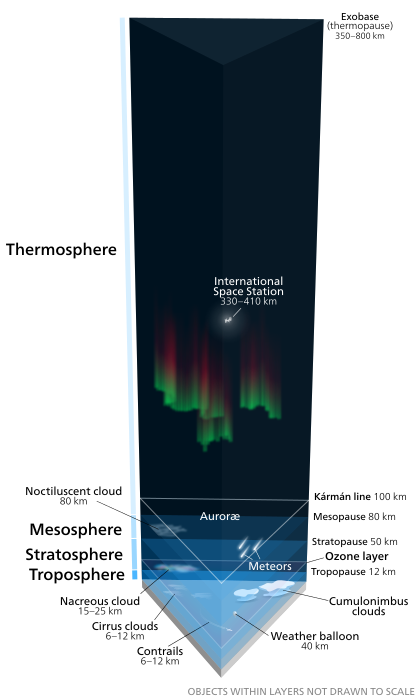
How dark does space get? If you get away from city lights and look up, the sky between the stars appears very dark indeed. Above the Earth’s atmosphere, outer space dims even further, fading to an inky pitch-black. And yet even there, space isn’t absolutely black.
Where do intergalactic stars come from?
Collisions between galaxies are commonly thought to be a source of intergalactic stars. Proposed mechanisms for the ejection of intergalactic stars by supermassive black holes The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible hypotheses have been suggested and published by astrophysicists.

Is there dark matter in intergalactic space?
The new research concludes that galaxies have no definite “edges.” Instead galaxies have long outskirts of dark matter that extend to nearby galaxies and the intergalactic space is not empty but filled with dark matter. The surface mass density as a function of distance (in units of a hundred thousand light-years).
What would intergalactic space be like?
Intergalactic space is as close as you can get to an absolute vacuum. There's very little dust and debris, and scientists have calculated that there's probably only one hydrogen atom per cubic meter. The density of material is higher near galaxies, and lower in the midpoint between galaxies.
How dark is it in deep space?
How dark does space get? If you get away from city lights and look up, the sky between the stars appears very dark indeed. Above the Earth's atmosphere, outer space dims even further, fading to an inky pitch-black. And yet even there, space isn't absolutely black.
Can you see stars in intergalactic space?
You would not see any stars, as all the stars we see on our sky are from our galaxy. You might be able to see some Active Galactic Nuclea, which are far away galaxies that look like stars (point sources), and are extremely luminous, so we are able to see them even though they are really far away.
Are there black holes in intergalactic space?
How 'volcanic' black holes and cosmic bubbles are sculpting intergalactic space. Supermassive black holes are the most powerful dynamos in the known universe, but a new study reveals how they not only shape the galaxies they inhabit but the shape of intergalactic space itself.
What lies in intergalactic space?
intergalactic medium, material found between galaxies and that mostly consists of hot, tenuous hydrogen gas. At one time it was thought that large amounts of mass might exist in the form of gas clouds in the spaces between galaxies.
Why is there no sound in space?
No, you cannot hear any sounds in near-empty regions of space. Sound travels through the vibration of atoms and molecules in a medium (such as air or water). In space, where there is no air, sound has no way to travel.
Is space completely silent?
Sound does not travel at all in space. The vacuum of outer space has essentially zero air. Because sound is just vibrating air, space has no air to vibrate and therefore no sound.
What does outer space smell like?
A succession of astronauts have described the smell as '… a rather pleasant metallic sensation ... [like] ... sweet-smelling welding fumes', 'burning metal', 'a distinct odour of ozone, an acrid smell', 'walnuts and brake pads', 'gunpowder' and even 'burnt almond cookie'.
What is beyond the universe?
The trite answer is that both space and time were created at the big bang about 14 billion years ago, so there is nothing beyond the universe. However, much of the universe exists beyond the observable universe, which is maybe about 90 billion light years across.
Are there planets in intergalactic space?
Astronomers think they've found a Saturn-sized planet in the Whirlpool Galaxy, around 30 million light-years from Earth. If confirmed, this would be the first intergalactic exoplanet, beyond our own Milky Way, and would extend the search for new worlds to greater distances than ever before.
Can a planet exist outside a galaxy?
Using information from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and a planet detection technique called microlensing to study a distant quasar galaxy , scientists at the University of Oklahoma found evidence that there are approximately 2,000 extragalactic planets for every one star beyond the Milky Way.
How hot is intergalactic space?
Intergalactic space is admittedly pretty cold, at -455°F (-270°C). But parts of the Boomerang have it beat, clocking in at -457.7°F (-272°C).
Is intergalactic travel possible?
The technology required to travel between galaxies is far beyond humanity's present capabilities, and currently only the subject of speculation, hypothesis, and science fiction. However, theoretically speaking, there is nothing to conclusively indicate that intergalactic travel is impossible.
Are there planets in intergalactic space?
Astronomers think they've found a Saturn-sized planet in the Whirlpool Galaxy, around 30 million light-years from Earth. If confirmed, this would be the first intergalactic exoplanet, beyond our own Milky Way, and would extend the search for new worlds to greater distances than ever before.
How dense is intergalactic space?
The average density of the intergalactic medium (IGM) is about one atom per cubic meter: less than a billionth of a billionth of the density of air on Earth. Despite that, astronomers have measured some properties of the IGM, enough to learn that its temperature is millions of degrees.
What is the cosmic optical background?
The cosmic optical background that the team sought to measure is the visible-light equivalent of the more well-known cosmic microwave background – the weak afterglow of the big bang itself , before stars ever existed.
How many galaxies are there in the universe?
An estimate of the total number of galaxies has been extrapolated from very deep sky observations by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope and suggested there are about two trillion galaxies in the cosmos. It relied on mathematical models to estimate how many galaxies were too small and faint for Hubble to see. That team concluded that 90% of the galaxies in the universe were beyond Hubble’s ability to detect in visible light. That study also estimated the combined light from those two trillion galaxies. The new findings, which relied on measurements from NASA’s distant New Horizons mission, finds only about half as much light as that earlier Hubble study but still twice as much light as existing catalogs of observed galaxies can account for.
How did the team correct the New Horizons image?
The team analyzed existing images from the New Horizons archives. To tease out the feeble background glow, they had to correct for a number of other factors. For example, they subtracted the light from the galaxies expected to exist that are too faint to be identifiable. The most challenging correction was removing light from Milky Way stars that was reflected off interstellar dust and into the camera.
How many galaxies were too small for Hubble to see?
That study also estimated the combined light from those two trillion galaxies.
What is the band in the background of the New Horizons spacecraft?
This artist’s illustration shows NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft in the outer solar system. In the background lies the Sun and a glowing band representing zodiacal light, caused by sunlight reflecting off of dust.
What telescope can detect faint galaxies?
NASA’s upcoming James Webb Space Telescope may be able to help solve the mystery. If faint, individual galaxies are the cause, then Webb ultra-deep field observations should be able to detect them. This study is accepted for publication in the Astrophysical Journal.
Do New Horizons observations have a constraint on the total number of galaxies?
The New Horizons observations do not place a constraint on the total number of galaxies but rather do constrain the total amount of light all galaxies emit at ultraviolet and optical wavelengths. How dark does space get? If you get away from city lights and look up, the sky between the stars appears very dark indeed.
What is the matter between galaxies called?
The matter between galaxies — often called the intergalactic medium, or IGM for short — is mostly hot, ionized hydrogen (hydrogen that has lost its electron) with bits of heavier elements such as carbon, oxygen and silicon thrown in.
How does IGM affect the galaxy?
The IGM under the influence of a galaxy's gravitational pull slowly accumulates onto the galaxy at a rate of about one solar mass (equal to the mass of the sun) per year , which is about the rate of star formation in the disk of the Milky Way. "IGM is the gas that feeds star formation in galaxies," Shull said.
What was the gas of the IGM?
In the 1960s, astronomers first discovered quasars — incredibly bright and active galaxies in the distant universe — and shortly thereafter, they noticed that the light from the quasars had missing pieces. These pieces had been absorbed by something in between the quasar and the astronomers' telescopes — this was the gas of the IGM. In the decades since, astronomers have discovered vast webs and filaments of gas and heavy elements that collectively contain more matter than all the galaxies combined. Some of this gas was likely left over from the Big Bang, but the heavier elements hint that some of it comes from old stardust, spewed out by galaxies.
How to study IGM?
To probe the IGM, astronomers also have started looking at fast radio bursts that come from distant galaxies. Using both this technique and by examining quasar light, astronomers continue to study the characteristics of the IGM to determine its varying temperatures and densities.
Is intergalactic space empty?
Intergalactic space is more than just an empty void. (Image credit: Shutterstock) The vast voids between galaxies can stretch millions of light-years across and may appear empty. But these spaces actually contain more matter than the galaxies themselves.
What is intergalactic travel?
Intergalactic travel is the hypothetical crewed or uncrewed travel between galaxies. Due to the enormous distances between the Milky Way and even its closest neighbors —tens of thousands to millions of light-years —any such venture would be far more technologically demanding than even interstellar travel. Intergalactic distances are roughly a hundred-thousandfold (five orders of magnitude) greater than their interstellar counterparts.
How long does it take light to travel through space?
While it takes light approximately 2.54 million years to traverse the gulf of space between Earth and, for instance, the Andromeda Galaxy, it would take a much shorter amount of time from the point of view of a traveler at close to the speed of light due to the effects of time dilation; the time experienced by the traveler depending both on velocity (anything less than the speed of light) and distance traveled ( length contraction ). Intergalactic travel for humans is therefore possible, in theory, from the point of view of the traveler.
How long would it take to travel to the Andromeda Galaxy?
Traveling to the Andromeda Galaxy, 2.54 million light years away, would take 28 years on-ship time with a constant acceleration of 1g and a deceleration of 1g after reaching half way, to be able to stop.
Can humans travel intergalactic?
Intergalactic travel for humans is therefore possible, in theory, from the point of view of the traveler. Accelerating to speeds closer to the speed of light with a relativistic rocket would allow the on-ship travel time to be drastically lower, but would require very large amounts of energy.
Is intergalactic travel possible?
However, theoretically speaking, there is nothing to conclusively indicate that intergalactic travel is impossible. There are several hypothesized methods of carrying out such a journey, and to date several academics have studied intergalactic travel in a serious manner.
Is the technology required to travel between galaxies beyond humanity's present capabilities?
The technology required to travel between galaxies is far beyond humanity's present capabilities , and currently only the subject of speculation, hypothesis, and science fiction .
Why do intergalactic stars exist?
It is commonly believed that intergalactic stars may primarily have originated from extremely small galaxies, since it is easier for stars to escape a smaller galaxy's gravitational pull, than that of a large galaxy. However, when large galaxies collide, some of the gravitational disturbances might also expel stars.
What is the source of intergalactic stars?
Formation. Collisions between galaxies are commonly thought to be a source of intergalactic stars. Proposed mechanisms for the ejection of intergalactic stars by supermassive black holes. The way these stars arise is still a mystery, but several scientifically credible hypotheses have been suggested and published by astrophysicists.
How are intergalactic stars ejected from the galaxy?
Another hypothesis, that is not mutually exclusive to the galactic collisions hypothesis, is that intergalactic stars were ejected from their galaxy of origin by a close encounter with the supermassive black hole in the galaxy center, should there be one. In such a scenario, it is likely that the intergalactic star (s) was originally part of a multiple star system where the other stars were pulled into the supermassive black hole and the soon-to-be intergalactic star was accelerated and ejected away at very high speeds. Such an event could theoretically accelerate a star to such high speeds that it becomes a hypervelocity star, thereby escaping the gravitational well of the entire galaxy. In this respect, model calculations (from 1988) predicts the supermassive black hole in the center of our Milky Way galaxy to expel one star every 100,000 years on average.
How do stars get expelled from galaxies?
Although stars normally reside within galaxies, they can be expelled by gravitational forces when galaxies collide . It is commonly believed that intergalactic stars may primarily have originated from extremely small galaxies, since it is easier for stars to escape a smaller galaxy's gravitational pull, than that of a large galaxy. However, when large galaxies collide, some of the gravitational disturbances might also expel stars. In 2015, a study of supernovae in intergalactic space suggested that the progenitor stars had been expelled from their host galaxies during a galactic collision between two giant ellipticals, as their supermassive black hole centres merged.
How many stars are there in the Milky Way?
Some Vanderbilt astronomers report that they have identified more than 675 stars at the edge of the Milky Way, between the Andromeda Galaxy and the Milky Way. They argue that these stars are hypervelocity (intergalactic) stars that were ejected from the Milky Way's galactic center. These stars are red giants with a high metallicity (a measure of the proportion of chemical elements other than hydrogen and helium within a star) indicating an inner galactic origin, since stars outside the disks of galaxies tend to have low metallicity and are older.
How fast is Ursa Major moving?
"One of the newfound exiles is moving in the direction of the constellation Ursa Major at about 1.25 million mph with respect to the galaxy. It is 240,000 light-years away.
Where are supernovae found?
Most intergalactic star candidates found in the neighborhood of the Milky Way seem not to have an origin in the Galactic Center but in the Milky Way disk or elsewhere.
