How did the Weimar government ratify the Treaty of Versailles?
The treaty was widely opposed within Germany, the government briefly considered refusing to sign and ratify. 4. Faced with a resumption of the war and an Allied invasion, the Weimar government reluctantly ordered the signing of the Treaty of Versailles and organised its ratification by the Reichstag.
How did the terms of the Treaty of Versailles affect Germany?
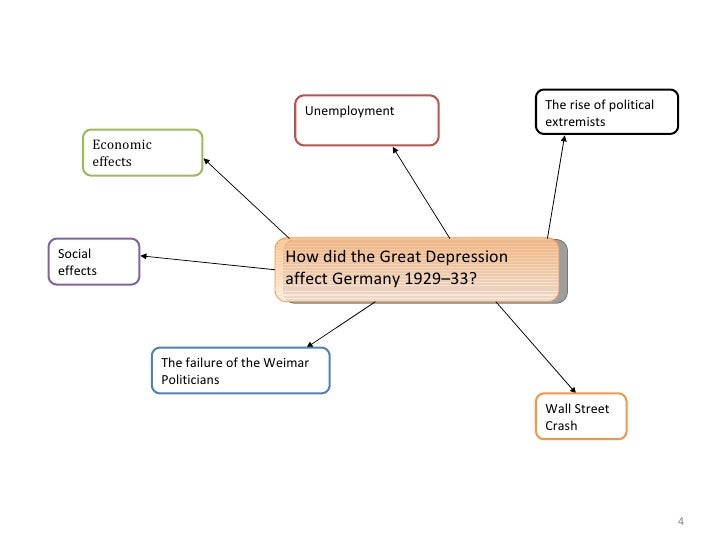
The terms of the Treaty were very damaging to Germany for a number of reasons: Territory was taken from Germany, depriving it of valuable industrial income. Germany had to accept responsibility for starting the war, leading to feelings of humiliation and anger.
What was the economic impact of the Weimar Republic on Germany?
Germany had to pay reparations of £6.6 billion, which would ensure that the economy would not recover. Germany’s armed forces were severely reduced. For example, there was no air force, a maximum 100,000 soldiers and a reduced navy. The link to the armistice and Treaty of Versailles had serious repercussions for the Weimar Government.
How did the Weimar Republic feel about the war guilt clause?
- It was felt by the Germany people that when the Weimar Republic agreed to sign the treaty it agreed to the alleged truth of the War Guilt Clause. The German people found it extremely difficult to support a government that agreed to accept such a horrible stain upon the honor of Germany and the German people.
See more
How did the Treaty of Versailles affect Germany government?
The treaty gave some German territories to neighbouring countries and placed other German territories under international supervision. In addition, Germany was stripped of its overseas colonies, its military capabilities were severely restricted, and it was required to pay war reparations to the Allied countries.
What were 3 major impacts of the Treaty of Versailles on Germany?
The treaty forced Germany to surrender colonies in Africa, Asia and the Pacific; cede territory to other nations like France and Poland; reduce the size of its military; pay war reparations to the Allied countries; and accept guilt for the war.
What happened to Germany as a result of the Treaty of Versailles?
The Versailles Treaty forced Germany to give up territory to Belgium, Czechoslovakia and Poland, return Alsace and Lorraine to France and cede all of its overseas colonies in China, Pacific and Africa to the Allied nations.
What was the problem facing the Weimar Republic?
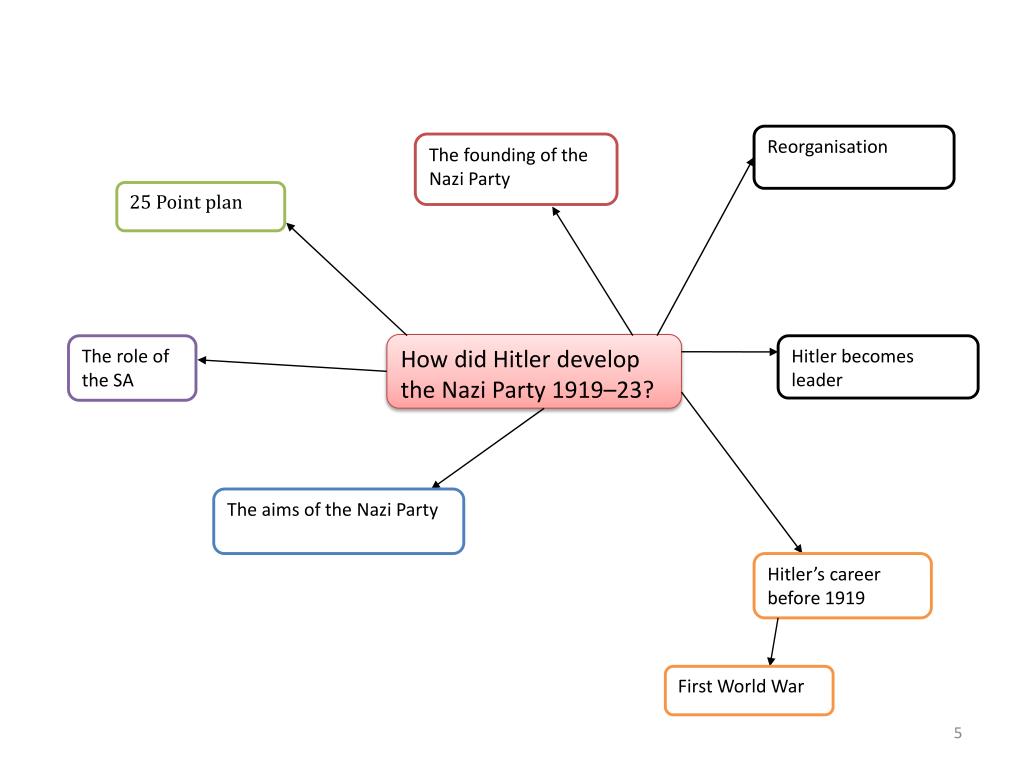
In its 14 years in existence, the Weimar Republic faced numerous problems, including hyperinflation, political extremism, and contentious relationships with the victors of the First World War, leading to its collapse during the rise of Adolf Hitler.
What is the largest result of the Treaty of Versailles?
The Treaty's required reparations amplified the state of Europe's economy in Germany, causing hyperinflation. After the Treaty was signed (reluctantly) by the German government, terrorists assassinated several government officials they held responsible for it.
Why was Germany angry about the Treaty of Versailles?
The Treaty of Versailles caused furious reactions in Germany. Germany had to pay huge sums of money to the countries it had fought in compensation for the damage. In addition, France, England, and the United States wanted to prevent Germany from becoming strong enough to start a new war.
What did Germany lose by signing the Treaty of Versailles?
In sum, Germany forfeited 13 percent of its European territory (more than 27,000 square miles) and one-tenth of its population (between 6.5 and 7 million people).
How did the Germans feel about the Treaty of Versailles?
The German Government had agreed to sign the Treaty of Versailles in June 1919 to make peace. This action was very unpopular in Germany. Enemies of the government used the treaty to claim that it had 'stabbed Germany in the back' by ending the war.
Which part of the Treaty of Versailles was the most damaging to Germany's economy?
One of the most controversial terms of the treaty was the War Guilt clause, which explicitly and directly blamed Germany for the outbreak of hostilities. The treaty forced Germany to disarm, to make territorial concessions, and to pay reparations to the Allied powers in the staggering amount of $5 billion.
What was the biggest threat to the Weimar Republic?
The main threat from the right wing was the Kapp Putsch of 1920. Due to the Treaty of Versailles, a reduction of the German army from 650,000 to 200,000 angered he right wing nationalists who rejected it and wanted to overthrow the Weimar state. The Kapp Putsch was a direct threat to Weimar's new government.
Why was the Weimar Republic weak?
Proportional representation - Each party got the same percentage of seats in parliament as the percentage of votes it received in an election. This meant there were lots of small parties in parliament making it difficult to pass laws and led to weak and often short-lived governments.
Why was Weimar Republic unpopular in Germany?
The Weimar Republic was unpopular, because they signed the Treaty of Versailles and failed to handle the economic crisis in Germany.
How did the Treaty of Versailles affect Germany quizlet?
How did the Treaty of Versailles affect Germany? Germany was forced to demilitarize the Rhineland, Germany was forced to pay reparations to the French and English, and Germany was forced to accept TOTAL guilt for the war.
What were the 5 main terms of the Treaty of Versailles?
The terms of the treaty required that Germany pay financial reparations, disarm, lose territory, and give up all of its overseas colonies. It also called for the creation of the League of Nations, an institution that President Woodrow Wilson strongly supported and had originally outlined in his Fourteen Points address.
What were the effects of WWI on Germany?
At the end of World War I, Germans could hardly recognize their country. Up to 3 million Germans, including 15 percent of its men, had been killed. Germany had been forced to become a republic instead of a monarchy, and its citizens were humiliated by their nation's bitter loss.
Which 3 countries signed the Treaty of Versailles?
The countries were split into three parties, which were led by the Principal Allied and Associated Powers of Britain, France, Italy, Japan and the United States....Signatories per country of the Treaty of Versailles, June 28, 1919.CharacteristicNumber of signatoriesUnited Kingdom5France511 more rows•Jan 7, 2020