- Choose a DKIM selector.
- Generate a public-private key pair.
- Publish the selector and public key by creating a DKIM TXT record.
- Attach the token to each outgoing email.
How do I add DKIM to my domain?
List all of your sending domains. List all domains and subdomains from which you send email messages. ... Install a DKIM package. ... Create the public & private DKIM key pair. ... Publish your public DKIM key. ... Hide your private DKIM key. ... Configure your email server. ... Test your DKIM setup.
How do I find my DKIM key?
How can I find my DKIM Selector?When you open the email, view the “original message” (some email clients might call this view “raw” or “full headers”) of the email. ... Search the headers for “DKIM-signature” to find the DKIM signature applied to the message.
How do I get a DKIM key from Google?
Step 1: Get your DKIM key in your Admin consoleSign in to your Google Admin console. ... In the Admin console, go to Menu Apps Google Workspace. ... Click Authenticate email.In the Selected domain menu, select the domain where you want to set up DKIM.Click the Generate New Record button.More items...
How do I create a DKIM record in Office 365?
Select the app launcher icon in the upper-left and choose Admin. In the lower-left navigation, expand Admin and choose Exchange. Go to Protection > dkim. Select the domain for which you want to enable DKIM and then, for Sign messages for this domain with DKIM signatures, choose Enable.
How do I know if a domain has DKIM?
You can check/validate your DKIM record by using our DKIM record Checker.Enter 'Google' as the Selector. As an example, we're using a generated domain key from Google Apps.The DKIM record is correctly configured when the DKIM Checker shows 'This is a valid DKIM key record'. ... If the selector is not valid.
Does Gmail have DKIM?
Business Gmail users (Google Workspace) can set up the DKIM for their Gmail account if it's not set. However, they need to have access to the admin console of that Google Workspace account and access to the DNS manager of the domain they wish to set up the DKIM for.
How is DKIM signature created?
The DKIM signature will be generated in a unique textual string, the 'hash value'. Before sending the email, the hash value is encrypted with a private key, the DKIM signature. Only the sender has access to this private key. When the email is encrypted the email is sent with this DKIM signature.
How do I set up SPF and DKIM records?
How to setup SPF and DKIM TXT records for your domainAdd your sender domain.Copy the SPF and DKIM TXT records from your Zoho Campaigns account.Add the SPF and DKIM TXT records to the DNS server.Verify your domain in your Zoho Campaigns account after adding the SPF and DKIM TXT records to the DNS server.
What is a public key for DKIM?
DKIM authentication uses public-key cryptography to sign email with a responsible party's private key as it leaves a sending server; recipient servers then use a public key published to the DKIM's domain to verify the source of the message, and that the parts of the message included in the DKIM signature haven't ...
Where is DKIM private key stored?
Key Components of DKIM: The private key is placed on the sender's server and used to generate the appropriate DKIM headers for all outgoing client mail. The public key is placed by the domain owner in his DNS zone file in the form of a special TXT record, and it becomes available to everyone.
How do I find my DKIM key in Office 365?
In the Microsoft 365 Defender portal at https://security.microsoft.com, go to Email & Collaboration > Policies & Rules > Threat policies > Email Authentication Settings in the Rules section >DKIM. To go directly to the DKIM page, use https://security.microsoft.com/dkimv2.
How do I manually check DKIM?
How do I manually verify DKIM?First, you need to calculate the email body's hash value.Then, compare the calculated hash to the email's DKIM-Signature header's bh value.After that, create the hashed_header using the DKIM-Signature header's parameter h .Finally, verify the signature.
How do I fix my DKIM email?
Verify messages pass DKIM authentication. ... Verify your DKIM key is correct at your domain provider. ... Check message forwarding. ... Contact admins for servers rejecting DKIM-signed messages. ... Verify your domain providers TXT record character limits. ... Review your email sending practices.
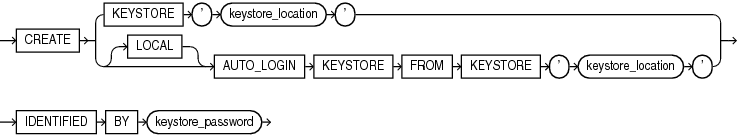
How do I create a DKIM record for a domain?
1 – Create a list of all domains and sending services (such as marketing campaign platforms or invoice generators, also referred to as ESPs) that are authorized to send email on your behalf. Contact them and request DKIM to be configured and that you need a copy of the public key.
How do I add a DKIM record?
1 – Publish your public key to your DNS record as a text (TXT) record. Check with your DNS provider to see if they allow more than 255 characters in the input field or not, as you may have to work with your provider to increase the size or to create the TXT record itself.
What is DKIM inspector?
Feel free to use our DKIM Inspector, a free diagnostic tool that you can use to test your DKIM settings if you’ve already started implementing DKIM for your domain (s). Our free DKIM Validator can help you verify that your DKIM record is correctly formatted.
What is DKIM in email?
Like SPF, DKIM is an open standard for email authentication that is used for DMARC alignment and exists in the DNS record of the domain, but it is a bit more complicated than SPF. DKIM gives emails a signature header that is added to the email and secured with a public/private key pair and a certificate. This DKIM signing acts like a watermark ...
How long is a DMARC trial?
If you haven’t begun your DMARC project, you can register for a free 14-day trial.
Where is the public key in an email?
The public key exists in the DKIM record in your domain’s DNS as a text file.
Does an organization have a DKIM server?
If your organization has its own email server, it may have native DKIM functionality. Check the available documentation for the public/private key generation and policy record creation (or check in with your IT staff who are responsible for the server).
What records are used for domain keys?
Be sure to include DKIM records for all of your applicable sending domains. These records will be included in your public facing DNS record for each sending domain. There are basically two types of DNS records used by Domain Keys; policy records and public key records. Policy records: A domain name using Domain Keys should have a single policy ...
How to send outbound mail on a domain?
Step 1: Determine which domains are allowed to send outbound mail on its behalf. Step 2: Create the DKIM public/private keys and the policy record . The ‘public’ key will be used in your public-facing DNS TXT record along with what’s called a policy record. The ‘private’ key will be used on your sending MTA. When an outbound message is sent ...
What is DKIM in email?
DKIM is a process to validate sending domain names associated to email messages through cryptographic authentication. It achieves this by inserting a digital signature into the message header which is later verified by the receiving host to validate the authenticity of the sending domain.
What is a private key in MTA?
When an outbound message is sent from the sending MTA, it will add the private key to the message header for identification and validation by the receiving domain by way of the public key. This uses a new domain name identifier to digitally sign the message.
How to create a DKIM keypair?
The best way to create a DKIM keypair is to use the openssl utility. In my case, I used it on an Ubuntu machine.
What is domainkey in DKIM?
The _domainkey part is a standard keyword for identifying the DKIM records.
What is a selector in a txt file?
The selector is a combination of any alphanumeric characters which you use to let the mail providers know which public key should they use when validating the authenticity of your email.
Where is the private key saved?
The private key will be saved to a key.private file and the public key will be saved to the key.public file.
