Phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities—their phylogeny—based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. The taxa joined together in the tree are implied to have descended from a common ancestor.
What is a phylogenetic tree and how to construct it?
What is the Phylogenetic Tree?
- Construction of the Phylogenetic tree. There are two different methods based on which the phylogenetic tree is constructed. ...
- Steps for preparing the Phylogenetic Tree
- Types of Phylogenetic Trees. Make the inference about the most common ancestor of the leaves or branches of the tree. ...
- Importance of Phylogenetic Tree. ...
What is the history behind phylogenetic trees?
History. The idea of a "tree of life" arose from ancient notions of a ladder-like progression from lower into higher forms of life (such as in the Great Chain of Being).Early representations of "branching" phylogenetic trees include a "paleontological chart" showing the geological relationships among plants and animals in the book Elementary Geology, by Edward Hitchcock (first edition: 1840).
What does a phylogenetic tree represent?
A phylogenetic tree is a visual representation of the relationship between different organisms, showing the path through evolutionary time from a common ancestor to different descendants. Trees can represent relationships ranging from the entire history of life on earth, down to individuals in a population. The diagram below shows a tree of 3 ...
Which is the best definition of a phylogenetic tree?
What is a Phylogenetic Tree?
- Phylogenetic Tree Definition. ...
- History of Phylogenetic Trees. ...
- Parts of a Phylogenetic Tree. ...
- Strengths and Limitations of a Phylogenetic Tree. ...
- Types of Phylogenetic Trees. ...
- Examples for Phylogenetic Tree of Life. ...
What do phylogenetic relationships show?
Evolutionary trees or phylogenetic trees are used to represent the relationships between different species. Typically, they are drawn in multiple V-like shapes. The bottom of the tree, or the root, represents the common ancestors of all species listed on the higher parts of the trees.
What can phylogenetic trees tell us?
A phylogenetic tree can help trace a species back through evolutionary history, down the branches of the tree, and locate their common ancestry along the way. Over time, a lineage may retain some of their ancestral features but will also be modified to adapt to the changing environment.
How do you determine evolutionary relationships?
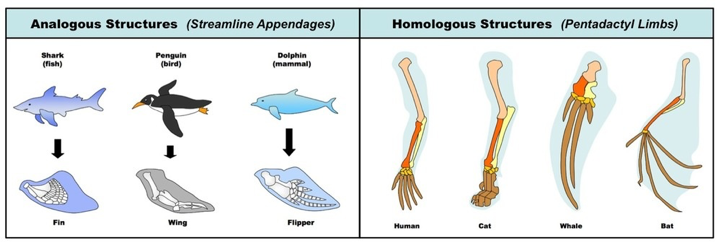
Using morphologic and molecular data, scientists work to identify homologous characteristics and genes. Similarities between organisms can stem either from shared evolutionary history (homologies) or from separate evolutionary paths (analogies).
What does the phylogenetic tree tell about the evolutionary relationships of animals?
The pattern of branching in a phylogenetic tree reflects how species or other groups evolved from a series of common ancestors. In trees, two species are more related if they have a more recent common ancestor and less related if they have a less recent common ancestor.
Does the phylogenetic tree make sense in terms of evolutionary biology?
Scientists use a tool called a phylogenetic tree to show the evolutionary pathways and connections among organisms. A phylogenetic tree is a diagram used to reflect evolutionary relationships among organisms or groups of organisms.
What is the most accurate way to determine evolutionary relationships?
Presently, the most accepted method for constructing phylogenetic trees is a method called cladistics. This method sorts organisms into clades, groups of organisms that are most closely related to each other and the ancestor from which they descended.
Why are evolutionary relationships often referred to as a tree?
Just like your family tree, an evolutionary tree indicates which ancestors gave rise to which descendants. The root of a phylogeny represents the common ancestor of all the descendants in the tree.
What is meant by evolutionary relationships?
A. Relationship between different species on the basis of their evolutionary or ancestral history. B. Relationship between different species on the basis of their reproductive nature.
Phylogenetic Tree Definition
A phylogenetic tree (commonly known as an evolutionary tree or a phylogeny) is a diagram with branches that displays the evolutionary relationships between different biological species.
History of Phylogenetic Trees
Since a phylogenetic tree is known as the " tree of life ," it's an upgraded understanding of an old conception that says that life progresses from lower to higher tiers like a ladder, referring to it be like the Great Chain of Being.
Parts of a Phylogenetic Tree
A simple phylogenetic tree contains several parts that are mentioned below:
Strengths and Limitations of a Phylogenetic Tree
Like every systematic model, a phylogenetic tree paradigm has some strengths and limitations which are mentioned below.
Types of Phylogenetic Trees
A tree is generally known as the Dendrogram. It is not necessarily a Phylogenetic tree and is used to represent and demonstrate something diagrammatically.
How to Read a Phylogenetic Tree?
Reading a Phylogenetic tree is the same as reading some family trees. However, we will let you know how to read a Phylogenetic tree step by step.
How to Make a Phylogenetic Tree?
You can build a Phylogenetic tree following the below-mentioned steps.
What are the relationships between phylogenetic trees?
Phylogenetic trees depict the evolutionary relationships among organisms. The relationships take the form of a tree with tips, branches, nodes, and a root. Specifically, the tips of the tree represent extant, or living, taxa and the branches denote evolutionary changes between ancestors and descendants such as the change in the DNA sequence, ...
How do phylogenetic trees work?
Phylogenetic trees come in many forms. It matters in which sequence the organisms are arranged from the bottom to the top of the tree, but the branches can rotate at their nodes without altering the information. The lines connecting individual nodes can be straight, angled, or even curved.
What is a paraphyletic group?
A paraphyletic group includes a common ancestral species and some of its descendants. For instance, all scaly animals with four legs are reptiles, with the exclusion of mammals and birds. Historically, biologists also classified some organisms as polyphyletic.
How can a scientist root a tree?
The scientist can root the tree by including an outgroup into the analysis. An outgroup is an organism that is not closely related to any of the organisms that the scientist wishes to arrange on the tree. Suggested Reading. Gregory, T. Ryan. “Understanding Evolutionary Trees.”.
What does the length of a branch mean?
The length of the branches can depict time or the relative amount of change among organisms. For instance, the branch length might indicate the number of amino acid changes in the sequence that underlies the phylogenetic tree. The exact meaning must be shown clearly on a legend accompanying the phylogenetic tree.
What is a phylogenetic tree?
Phylogenetic trees group organisms that are descendants of a common ancestor. When a group contains the most recent common ancestor and all of its descendants, it is called a clade, or a monophyletic group. For instance, all living vertebrates with feathers are considered birds.
How to construct a phylogenetic tree?
To construct accurate phylogenetic trees, scientists turned to methods such as maximum parsimony and maximum likelihood. Using maximum parsimony, one assumes the least amount of change between organisms. Consider the arrangement of elk, salmon, and whale on a phylogenetic tree. Both the salmon and whale are marine animals.
How do phylogenetic trees describe evolution?
But, a phylogenetic tree describes an evolutionary history by showing how ancestors are related to their descendants and how much those descendants have changed over time.
What do cladograms and phylogenetic trees represent?
Both phylogenetic trees and cladograms help show the relationships between different organisms, but only phylogenetic trees have branches that represent evolutionary time and amount of change . These were formerly based on physical characteristics, but are more accurately based on genetic relationships.
What are the three types of cladograms?
The three major types are: monophyletic, paraphyletic and polyphyletic. Monophyletic means one clade, paraphyletic means around one clade and polyphyletic means many clades. Lastly, we talked about how to build a cladogram based on a characteristic chart.
What is a clade?
Types of Clades. A clade is a group of species used in cladograms (and phylogenetic trees), which consists of one ancestor and all its descendants. The term clade comes from the Greek word klados, which means branch.
What does each branch or separation on a cladogram represent?
Generally, each branch or separation on a cladogram represents an evolutionary change or difference. This feature may or may not be indicated on the diagram.
Why do biologists use cladograms?
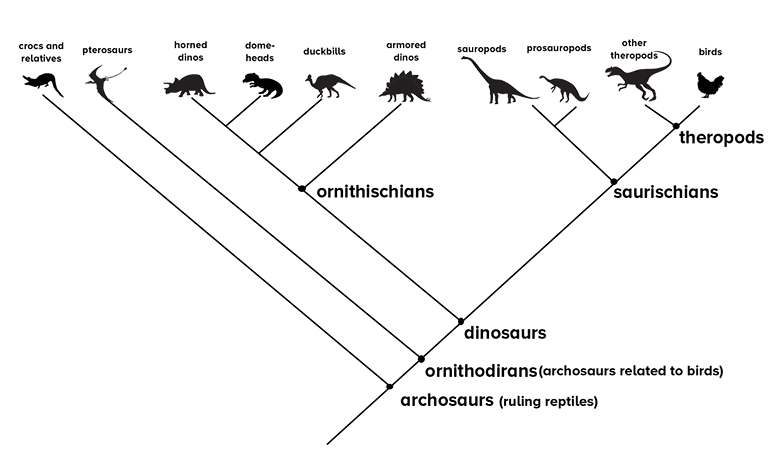
Biologists use cladograms and phylogenetic trees to illustrate relationships among organisms and evolutionary relationships for organisms with a shared common ancestor. Both cladograms and phylogenetic trees show relationships among organisms, how alike, or similar, they might be. We can see a typical cladogram and phylogenetic tree here.
Why do scientists use cladograms and phylogenetic trees?
Family trees help show how people are related to each other. Similarly, scientists use cladograms and phylogenetic trees to study the relationships between organisms. Create an account.