What are the R groups in a protein?
Jan 10, 2020 · In this regard, how do R groups affect the tertiary structure of a protein? R group interactions that contribute to tertiary structure include hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces – basically, the whole gamut of non-covalent bonds. These include hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, and disulfide …
What determines the structure of a protein?
Feb 08, 2022 · How do R groups affect protein structure? The R group determines the characteristics (size, polarity, and pH) for each type of amino acid. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another through dehydration synthesis. A chain of amino acids is a polypeptide.
What are the R groups of amino acids in a β-pleated sheet?
Nov 10, 2021 · How do R groups affect protein structure and function? The R group determines the characteristics (size, polarity, and pH) for each type of amino acid. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another through dehydration synthesis. A chain of amino acids is a polypeptide.
How does the shape of a protein affect its function?
Apr 08, 2021 · *The structure of the R-group affects the chemical reactivity and solubility of the amino acid. *In proteins, amino acids are joined bu a peptide bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. the combination of polypeptides represents the protein’s quarternary structure.

How do R groups affect the tertiary structure of a protein?
R group interactions that contribute to tertiary structure include hydrogen bonding, ionic bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces – basically, the whole gamut of non-covalent bonds.
How do R groups affect protein structure quizlet?
*The structure of the R-group affects the chemical reactivity and solubility of the amino acid. *In proteins, amino acids are joined bu a peptide bond between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
How do amino acid R groups affect the function of a protein?
The R group determines the characteristics (size, polarity, and pH) for each type of amino acid. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another through dehydration synthesis. A chain of amino acids is a polypeptide.
What do R groups do in proteins?
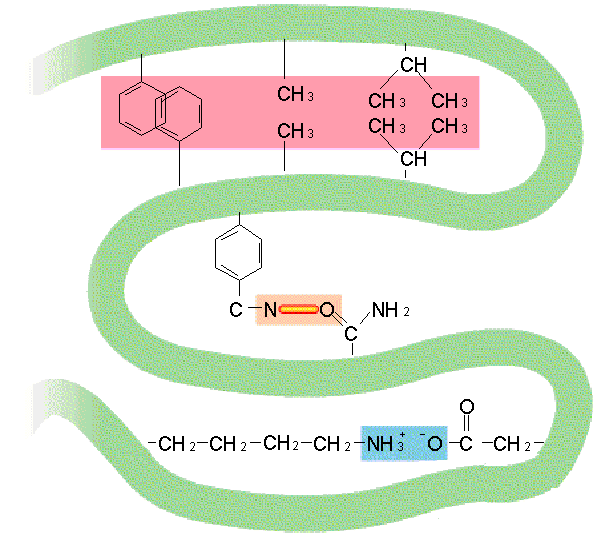
Each of the 20 amino acids has a specific side chain, known as an R group, that is also attached to the α carbon. The R groups have a variety of shapes, sizes, charges, and reactivities. This allows amino acids to be grouped according to the chemical properties of their side chains.
How do the R groups of amino acids contribute to protein structure quizlet?
Because the amino acid R-groups affect a polypeptide's properties and function, just a single amino acid change can radically alter protein function. Hydrogen bonds between the carbonyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another form a protein's secondary structure.
Why is protein structure important for protein function quizlet?
Primary structure is fundamental to protein function, because the order of the amino acids in a protein determine the other levels of its structure and ultimately its function.
How does the R group affect amino acids?
The R group determines the characteristics (size, polarity, and pH) for each type of amino acid. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another through dehydration synthesis.
What is the effect of temperature on protein shape?
It is determined that the protein molecule expands slightly (0.4% per 100 K) with increasing temperature and that this expansion is linear. The expansion is due primarily to subtle repacking of the molecule, with exposed and mobile loop regions exhibiting the largest movements.
Why are R groups important in amino acids?
R-group chemistry It is useful to classify amino acids based on their R-groups, because it is these side chains that give each amino acid its characteristic properties. Thus, amino acids with (chemically) similar side groups can be expected to function in similar ways, for example, during protein folding.Mar 6, 2021
What is the R in protein structure?
The amino acids present in proteins differ from each other in the structure of their side (R) chains. The simplest amino acid is glycine, in which R is a hydrogen atom. In a number of amino acids, R represents straight or branched carbon chains.
What is R in amino acid structure?
General structure. In the structure shown at the top of the page R represents a side chain specific to each amino acid. The carbon atom next to the carboxyl group is called the α–carbon. Amino acids containing an amino group bonded directly to the α-carbon are referred to as α-amino acids.
How do peptide bonds affect protein structure?
When connected together by a series of peptide bonds, amino acids form a polypeptide, another word for protein. The polypeptide will then fold into a specific conformation depending on the interactions (dashed lines) between its amino acid side chains.
How do different R groups affect protein structure?
The tertiary structure is primarily due to interactions between the R groups of the amino acids that make up the protein. For example, R groups with like charges repel one another, while those with opposite charges can form an ionic bond.
How do R groups affect protein structure and function?
The R group determines the characteristics (size, polarity, and pH) for each type of amino acid. Peptide bonds form between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another through dehydration synthesis. A chain of amino acids is a polypeptide.
How do R groups stabilize protein structure?
There are about 5 amino acids that are either acidic or basic, and their R-groups ionize at various pHs to produce a chemical structure that has either a positive or negative charge. These types of R-groups are strongly hydrophilic and are stabilized when surrounded by water.
How does temperature affect protein structure?
It is determined that the protein molecule expands slightly (0.4% per 100 K) with increasing temperature and that this expansion is linear. The expansion is due primarily to subtle repacking of the molecule, with exposed and mobile loop regions exhibiting the largest movements.
What is the R group in a protein?
Each of the 20 amino acids has a specific side chain, known as an R group, that is also attached to the α carbon. The R groups have a variety of shapes, sizes, charges, and reactivities. This allows amino acids to be grouped according to the chemical properties of their side chains.
How does the structure of the R group affect the properties of a particular amino acid?
How does the structure of the R group affect the properties of a particular amino acid? The R group differs with each amino acid. The physical and chemical properties of the R group determine the unique characteristics of a particular amino acid, thus affecting its functional role in a polypeptide.
What causes changes in protein structure?
Proteins change their shape when exposed to different pH or temperatures. The body strictly regulates pH and temperature to prevent proteins such as enzymes from denaturing. Some proteins can refold after denaturation while others cannot. Chaperone proteins help some proteins fold into the correct shape.
How to determine the structure of a protein?
How to Determine Protein Structure Type. The three-dimensional shape of a protein is determined by its primary structure. The order of amino acids establishes a protein's structure and specific function. The distinct instructions for the order of amino acids are designated by the genes in a cell.
What type of interactions are involved in the folding and shaping of proteins?
There are several types of bonds and forces that hold a protein in its tertiary structure. Hydrophobic interactions greatly contribute to the folding and shaping of a protein. The "R" group of the amino acid is either hydrophobic or hydrophilic.
How many different types of protein are there?
Four Protein Structure Types. The four levels of protein structure are distinguished from one another by the degree of complexity in the polypeptide chain. A single protein molecule may contain one or more of the protein structure types: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure. 1.
What is the amino acid sequence?
All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and an amino group. The "R" group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers. The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code.
What type of bonding is used to hold proteins together?
Folding in proteins happens spontaneously. Chemical bonding between portions of the polypeptide chain aid in holding the protein together and giving it its shape. There are two general classes of protein molecules: globular proteins and fibrous proteins.
How are amino acids determined?
The amino acid sequence of a protein is determined by the information found in the cellular genetic code. The order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is unique and specific to a particular protein. Altering a single amino acid causes a gene mutation, which most often results in a non-functioning protein. 2.
What type of bonding occurs when proteins fold?
Due to protein folding, ionic bonding can occur between the positively and negatively charged "R" groups that come in close contact with one another. Folding can also result in covalent bonding between the "R" groups of cysteine amino acids. This type of bonding forms what is called a disulfide bridge.
What is the role of protein structure?
Protein structure plays a key role in its function; if a protein loses its shape at any structural level, it may no longer be functional. Primary structure is the amino acid sequence. Secondary structure is local interactions between stretches of a polypeptide chain and includes α-helix and β-pleated sheet structures.
What is the overall three-dimension folding driven largely by interactions between R groups?
Tertiary structure is the overall the three-dimension folding driven largely by interactions between R groups. Quarternary structures is the orientation and arrangement of subunits in a multi-subunit protein.
Why are amino acids held in pleated sheets?
The stretches of amino acids in β-pleated sheets are held in their pleated sheet structure because hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen atom in a polypeptide backbone carbonyl group of one β-pleated sheet and the hydrogen atom in a polypeptide backbone amino group of another β-pleated sheet.
How many amino acids are in the A and B chain of insulin?
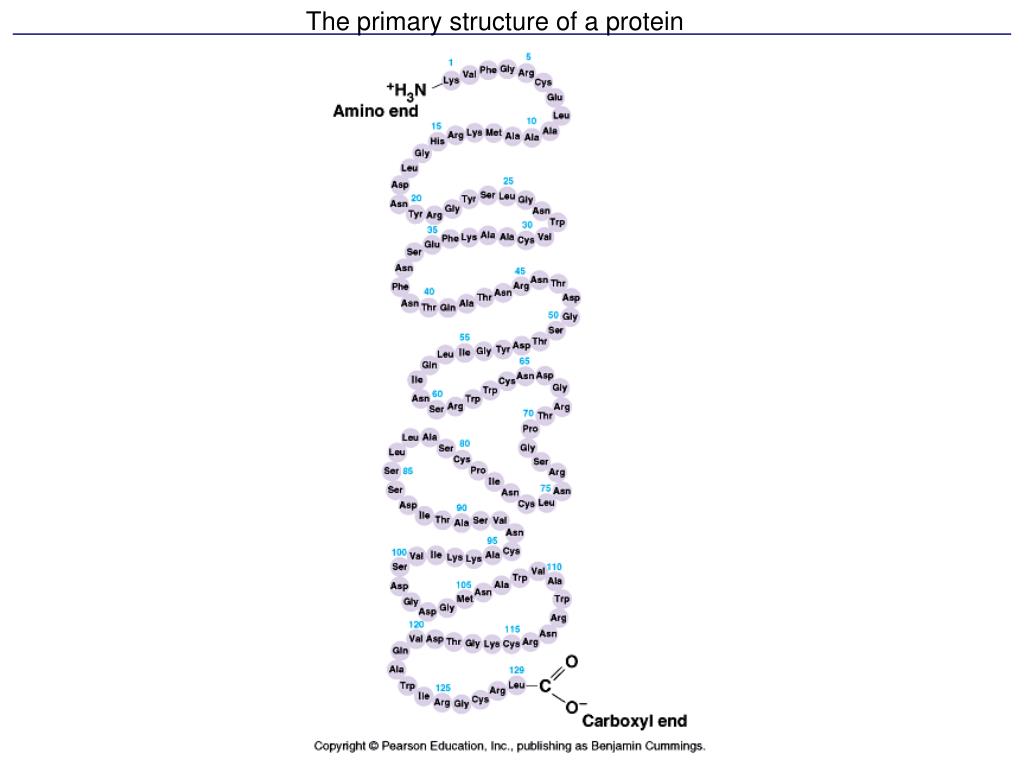
For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B. Primary structure: The A chain of insulin is 21 amino acids long and the B chain is 30 amino acids long, and each sequence is unique to the insulin protein. The gene, or sequence of DNA, ultimately determines the unique sequence of amino acids in each peptide chain.
Why do amino acids form a helix?
Secondary structure: The α-helix and β-pleated sheet form because of hydrogen bonding between carbonyl and amino groups in the peptide backbone. Certain amino acids have a propensity to form an α-helix, while others have a propensity to form a β-pleated sheet.
Why do amino acids zig zag?
In β-pleated sheets, stretches of amino acids are held in an almost fully-extended conformation that “pleats” or zig-zags due to the non-linear nature of single C-C and C-N covalent bonds. β-pleated sheets never occur alone. They have to held in place by other β-pleated sheets.
What is the difference between a disulfide and a antiparallel bond?
antiparallel: The nature of the opposite orientations of the two strands of DNA or two beta strands that comprise a protein’s secondary structure. disulfide bond: A bond, consisting of a covalent bond between two sulfur atoms, formed by the reaction of two thiol groups, especially between the thiol groups of two proteins.
What are the structural properties of amino acids?
Generally, amino acids have the following structural properties: All amino acids have the alpha carbon bonded to a hydrogen atom, carboxyl group, and amino group. The "R" group varies among amino acids and determines the differences between these protein monomers.
How many amino acids are in proteins?
Although there are hundreds of amino acids found in nature, proteins are constructed from a set of 20 amino acids.
How many amino acids are there in the human body?
While amino acids are necessary for life, not all of them can be produced naturally in the body. Of the 20 amino acids, 11 can be produced naturally. These nonessential amino acids are alanine, arginine, asparagine, aspartate, cysteine, glutamate, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine, and tyrosine. With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino ...
What are nonessential amino acids?
With the exception of tyrosine, nonessential amino acids are synthesized from products or intermediates of crucial metabolic pathways. For example, alanine and aspartate are derived from substances produced during cellular respiration. Alanine is synthesized from pyruvate, a product of glycolysis.
How are amino acids joined together?
The resulting amino acids are joined together through dehydration synthesis, a process in which a peptide bond is formed between the amino acids. A polypeptide chain is formed when a number of amino acids are linked together by peptide bonds.
Why are amino acids important to life?
Amino acids are essential to life because the proteins they form are involved in virtually all cell functions. Some proteins function as enzymes, some as antibodies, while others provide structural support.
What are the four categories of amino acids?
Based on the variable group, amino acids can be classified into four categories: nonpolar, polar, negatively charged, and positively charged.