Main Difference between Reducing and Non-Reducing Sugar
- Reducing sugars tend to act as reducing agents whereas non-reducing sugars cannot act as a reducing agent.
- Reducing sugars tend to contain aldehyde or ketone groups whereas non-reducing sugars do not contain either aldehyde or...
- Reducing sugars have more sweet tastings while non-reducing sugars have less...
Which sugar is not a reducing sugar?
The main non-reducing sugar is sucrose, or more commonly known as table sugar. Sucrose is a glucose carbon connected at the anomeric carbon to an anomeric carbon on a fructose. Since both anomeric carbons are involved in the bond, neither one has an OH group, so it is not a reducing sugar.
How do you test for non - reducing sugars?
Then you must:
- Add 2cm3 of the food sample to an equal amount of Hydrochloric Acid in a test tube.
- Place the test tube in a water bath for 5 minutes. ...
- Remove the test tube and then add some Sodium Hydrocarbonate solution to the test tube to neutralise the acid. ...
Do all non reducing sugars have glucose and fructose?
The common dietary monosaccharides galactose, glucose and fructose are all reducing sugars. Disaccharides are formed from two monosaccharides and can be classified as either reducing or nonreducing. Nonreducing disaccharides like sucrose and trehalose have glycosidic bonds between their anomeric carbons and thus cannot convert to an open-chain form with an aldehyde group; they are stuck in the cyclic form.
Is starch reducing or non reducing?
Starch is a polysaccharide composed of multiple monomeric units of glucose linked together by α-1,4 linkages. Starch is a non-reducing sugar as it doesn’t have a free aldehyde or ketone group present in the structure.

What is the difference between a reducing and non reducing sugar a level biology?
Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of Benedict's or Fehling solution to cuprous ions. Non reducing sugar fail to reduce the cupric ions of Benedict's solution to cuprous ions.
Which test is used to differentiate between reducing and non reducing sugars?
The Benedict's testThe Benedict's test identifies reducing sugars (monosaccharide's and some disaccharides), which have free ketone or aldehyde functional groups. Benedict's solution can be used to test for the presence of glucose in urine.
How do you tell if a sugar is reducing or nonreducing?
3:365:11Reducing Sugar vs Non-reducing Sugar (Acetal Hemiacetal ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt's a hemiacetal. So whenever the anomeric carbon is a hemiacetal. It's reducing sugar. However ifMoreIt's a hemiacetal. So whenever the anomeric carbon is a hemiacetal. It's reducing sugar. However if the anomeric carbon is an acetal.
What is the difference between reducing end and non reducing end?
The end of the molecule containing the free anomeric carbon is called the reducing end, and the other end is called the nonreducing end. So non-reducing sugars that cannot reduce oxidizing agents.
What are reducing and non reducing sugars give examples?
Ex : Glucose, fructose, maltose, lactose.
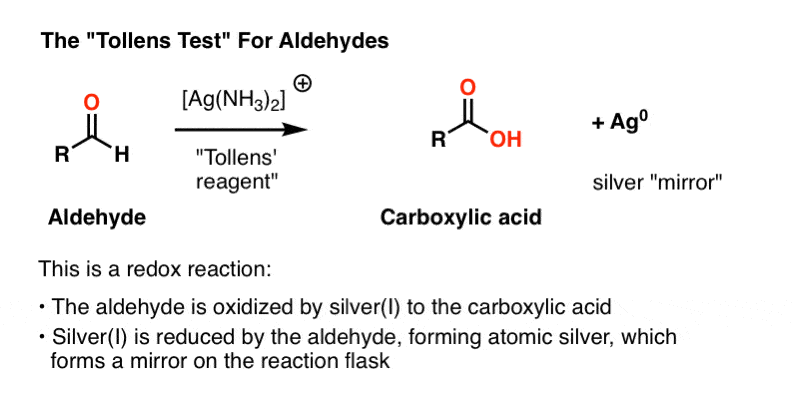
Sugars which does not reduce Fehlings solution and Tollen's reagent are called non- reducing sugars. Ex : Sucrose.
What is the defining characteristic of a reducing sugar?
The defining characteristic of a reducing sugar is that it can mutarotate through the open chain form to produce an aldehyde. Monosaccharides are reducing compounds, but methylated derivatives are not because they become locked in acetal structure which does not allow them to mutarotate.
What makes sugars non reducing?
A nonreducing sugar is a carbohydrate that is not oxidized by a weak oxidizing agent (an oxidizing agent that oxidizes aldehydes but not alcohols, such as the Tollen's reagent) in basic aqueous solution.
What is the difference between reducing and non reducing end of glycogen?
The single reducing end has the C1 carbon of the glucose residue free from the ring and able to react. A nonreducing end of a sugar is one that contains an acetal group, whereas a reducing sugar end is either an aldehyde or a hemiacetal group (Fig. 7.10).
Why sucrose is called non reducing sugar?
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar because The two monosaccharide units are held together by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of α-glucose and C2 of β-fructose. Since the reducing groups of glucose and fructose are involved in glycosidic bond formation, sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
Which test is used to identify reducing sugar?
Benedict's testBenedict's test is a chemical test that can be used to check for the presence of reducing sugars in a given analyte. Therefore, simple carbohydrates containing a free ketone or aldehyde functional group can be identified with this test.
What is Benedict's test for reducing sugars?
Test for sugars Sugars classed as reducing sugars will react with Benedict's solution on heating for a few minutes. Glucose is an example of a reducing sugar. Reducing sugars give a red/brown precipitate with Benedict's solution. The precipitate takes a while to settle in the tube.
What are the tests for reducing sugars?
Most commonly used tests for detection of reducing sugars are Fehling's Test, Benedict's Test and Barfoed's Test. a) Fehling's Test: Fehling's Solution (deep blue colored) is used to determine the presence of reducing sugars and aldehydes. Perform this test with fructose, glucose, maltose and sucrose.
What happens in Fehling's test?
In this test the presence of aldehydes but not ketones is detected by reduction of the deep blue solution of copper(II) to a red precipitate of insoluble copper oxide. The test is commonly used for reducing sugars but is known to be NOT specific for aldehydes.
Which sugar is non reducing agent?
The most common non-reducing sugar is sucrose, which is commonly known as "table sugar." It is non-reducing because it has no OH group attached to...
What is the difference between a reducing and a non-reducing end of a chain?
The anomeric carbon in reducing sugars has an OH group attached that can reduce other compounds. Because the anomeric carbon in non-reducing sugars...
What are five reducing sugars?
All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars. Among the many reducing sugars are glucose, galactose, fructose, and lactose, which...
What are non reducing and reducing sugars?
Reducing sugars contain free aldehyde or ketone groups and are capable of reducing other compounds. On the other hand, non-reducing sugars do not c...
What Are Non-reducing Sugars?
Non-reducing sugars are carbohydrates which are unable to be oxidized and do not reduce other substances. Non-reducing sugars do not have an OH group attached to the anomeric carbon and therefore they cannot reduce other compounds.
What is the difference between reducing and non-reducing sugars?
Difference Between Reducing And Non-reducing Sugars In Tabular Form. A reducing sugar has a free aldehyde (-CHO) or ketone (-C=O) group that can act as a reducing agent. A non-reducing sugar does not have a free aldehyde or ketone and therefore it cannot act as a reducing agent.
What are the characteristics of reducing sugars?
The main characteristic of reducing sugars is that in aqueous medium, they generate one or more compounds containing an aldehyde group. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars along with some disaccharides, some oligosaccharides and some polysaccharides.
What is the function of aldehyde?
The aldehyde functional group allows the sugar to act as a reducing agent. The presence of reducing sugars is determined chemically by test methods such as dinitrosallicillic (quantitative) and qualitative methods using Benedict’s reagent, Fehling’s solution and Tollen’s reagent.
How to identify reducing sugars?
Identification. Presence or absence of reducing sugars can be identified by carrying out different tests. The presence or absence of non-reducing sugars cannot be identified by different tests. Classification. Most of the reducing sugars are monosaccharides. Most of non-reducing sugars are polysaccharides whereas others are disaccharides.
What color does non-reducing sugar give?
Non-reducing sugars do not give a red color but remains green in color when it reacts with Benedict’s solution. Non-reducing sugars have a less sweet taste. The molecular weight of reducing sugars is relatively high when compared to that of reducing sugars.
Do reducing sugars have a sweet taste?
Reducing sugars have a sweet taste. Molecular weight of reducing sugars is relatively low. Reducing sugars give a positive reaction towards the Fehling’s test. Reducing sugars have the ability to reduce cupric ions of Benedict’s or Fehling solution to cuprous ions. Reducing sugars give positive result with Tollen’s test.
What are the two groups of monosaccharides?
Reducing monosaccharides can further be classified into two groups; aldoses and ketose . Aldoses are sugars consisting of an aldehyde group as the reducing component, whereas ketoses are sugars consisting of a ketone group as the reducing component.
What is reducing sugar?
Reducing sugar is a type of sugar that consists of a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group, allowing the molecule to act as a reducing agent.
Which monomers are involved in the formation of glycosidic bonds?
The aldehyde and ketone present on the monomers are involved in the formation of the glycosidic bond in the case of most disaccharides and all polysaccharides.
What is the cyclic form of glucose?
The cyclic form of glucose is formed when the hydroxyl group on carbon 5 binds to the aldehyde group on carbon 1.
What is starch used for?
Starch is an essential polysaccharide that is used in different industries as well as a source of nutrients in plants. Plants often store starch as a form of glucose storage.
What are some examples of non-reducing sugars?
Some of the examples of non-reducing sugars include sucrose, trehalose, starch, etc.
How to differentiate non-reducing sugar from reducing sugar?
Non-reducing sugar can be differentiated from reducing sugars through tests like Benedict’s test and Fehling’s test.
What Are Sugars?
What do toast, browned steak, and caramel have in common? Besides all tasting delicious, they're all possible because of science. Who'd have thought there could by more to sugar than just tasting good?
Why is Benedict's reagent more alkaline than Barfoed's reagent?
Because Benedict's reagent is more alkaline, it more rapidly oxidizes reducing sugars than Barfoed's reagent. Monosaccharides will be oxidized by both reagents (resulting in a color change), while disaccharides will only be oxidized by Benedict's reagent. The following is a table of results obtained by the biochemist.
What is the difference between Barfoed's oxidation and Benedict's oxidation?
Both are based on the oxidation of Cu (II) to Cu (I) resulting in the formation of Cu {eq}_2 {/eq}O. Benedict's reagent is basic, while Barfoed's reagent is weakly acidic. Because Benedict's reagent is more alkaline, it more rapidly oxidizes reducing sugars than Barfoed's reagent. Monosaccharides will be oxidized by both reagents (resulting in a color change), while disaccharides will only be oxidized by Benedict's reagent.
How to identify sugars?
You can identify a sugar by looking for the anomeric carbon. An anomeric carbon is the first stereocenter of the molecule. If that stereocenter has an OH group coming off of it then it is a reducing sugar. This is because when the sugar is in the open configuration, that alcohol becomes a ketone or aldehyde which is able to reduce other compounds.
What are the two monosaccharides?
Disaccharides are two monosaccharides combined. Common disacccharides are maltose, lactose, and sucrose. These can either be reducing or non-reducing sugars. Maltose is a combination of two glucose molecules.
What is a negative control?
1. A negative control (such as water) demonstrates the colour of the reaction when no sugars are present. A positive control demonstrates the colour of the reaction when reducing sugars are present. The first is a positive control for monosaccharides (such as glucose).
Why is it important to know that there are reducing and non-reducing sugars?
One way is to help diagnose if a person is diabetic. It is important to measure how much glucose is in the urine to diagnose diabetes. The Fehling's Test uses the reducing nature of glucose to help determine how much glucose is present. By seeing how much of the Fehling's reagent (a copper-based solution) is able to reduce, we can deduce how much glucose is in the sample.
What is the difference between reducing sugar and non-reducing sugar?
Difference between Reducing and Non-reducing sugars. Any carbohydrate which is capable of being oxidized and causes the reduction of other substances without having to be hydrolysed first is known as reducing sugar, but those which are unable to be oxidised and do not reduce other substances are known as non-reducing sugars.
Which monosaccharide is oxidized?
Generally, all the free monosaccharides having free aldehyde or hydroxyl ketonic group are capable of being oxidised. After being oxidised they cause the reduction of the other substances and so known as reducing sugars.
What are non-reducing sugars?
Non-reducing Sugars. 1. Such sugar bear a free aldehyde. (-CHO) or ketonic (-CO) group. These sugars do not have such groups. 2. Reducing sugars have the capacity to reduce cupric ions of Benedict’s or Fehling solution to cuprous ions.

Reducing Sugar Definition
non-reducing Sugar Definition
- Non-reducing sugar is a type of sugar that doesn’t have a free aldehyde or ketone group, as a result of which the sugar cannot act as a reducing agent. 1. All polysaccharides are non-reducing sugars, and so are most disaccharides and oligosaccharides. 2. Non-reducing sugars are either dimers, trimers, or polymers, which are formed of many reducing ...
Examples of Reducing Sugar
- Glucose
1. Glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide on the plant, which is primarily produced by green algae and plants. 2. Glucose is a hexose with six carbon atoms and the molecular formula of C6H12O6. 3. It is an aldose consisting of a free aldehyde group at one of the ends, making it …
Examples of non-reducing Sugar
- Starch
1. Starch is a polysaccharide composed of multiple monomeric units of glucose linked together by α-1,4 linkages. 2. Starch is a non-reducing sugar as it doesn’t have a free aldehyde or ketone group present in the structure. 3. The aldehyde or ketone groups on the monosaccharides are in…
References
- Gautum SD, Pant M and Adhikari NR (2016). Comprehensive Chemistry, Part 2. Sixth Edition. Heritage Publishers and Distributors Pvt. Ltd.
- https://pediaa.com/difference-between-reducing-and-nonreducing-sugar/
- https://vivadifferences.com/difference-between-reducing-sugar-and-non-reducing-sugar-with-examples/