Where do sister chromatids separate during anaphase?
During anaphase, sister chromatids are separated at the centromere and are pulled towards opposite poles of the cell by the mitotic spindle. Do sister chromatids separate during mitosis? The two sister chromatids are separated from each other into two different cells during mitosis or during the second division of meiosis.
What is the significance of sister chromatid separation?
Sister chromatid separation ensures that each daughter cell gets the appropriate number of chromosomes after division. In humans, each mitotic daughter cell would be a diploid cell containing 46 chromosomes. Each meiotic daughter cell would be haploid containing 23 chromosomes.
How are sister chromatids formed in meiosis?
A full set of sister chromatids is created during the synthesis (S) phase of interphase, when all the chromosomes in a cell are replicated. The two sister chromatids are separated from each other into two different cells during mitosis or during the second division of meiosis.
What is a separated chromatid called?
In telophase and cytokinesis, separated sister chromatids are divided into two separate daughter cells. Each separated chromatid is referred to as a daughter chromosome . Meiosis is a two-part cell division process that is similar to mitosis.

Do sister chromatids separate during anaphase in plant cells?
In anaphase I, the homologues are pulled apart and move apart to opposite ends of the cell. The sister chromatids of each chromosome, however, remain attached to one another and don't come apart.
What phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate?
anaphaseSister chromatids separate during anaphase in a three-stage program as directed by interaxis bridges.
Do sister chromatids separate in anaphase 1 or 2?
In anaphase I, the homologous chromosomes are separated. In prometaphase II, microtubules attach to the kinetochores of sister chromatids, and the sister chromatids are arranged at the midpoint of the cells in metaphase II. In anaphase II, the sister chromatids are separated.
Do sister chromatids separate in meiosis or mitosis?
During mitosis the sister chromatids separate and go to opposite ends of the dividing cell. Mitosis ends with 2 identical cells, each with 2N chromosomes and 2X DNA content. All eukaryotic cells replicate via mitosis, except germline cells that undergo meiosis (see below) to produce gametes (eggs and sperm).
In which process is chromatids separated from each other?
Metaphase leads to anaphase, during which each chromosome's sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
Which step play primary role in separation of sister chromatids?
Separation and segregation of sister chromatids in growing cells occurs in the cell cycle stage called `anaphase'.
What separated during anaphase 2?
Anaphase II involves separation of the sister chromatids.
What happened to Sister chromatid in meiosis 2?
During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes, and in meiosis II, sister chromatids are segregated into daughter cells.
Are sister chromatids pulled apart in meiosis?
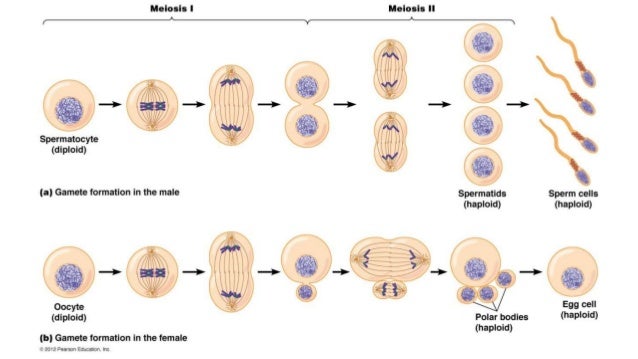
During interphase, the DNA of the chromosomes is replicated (during S phase). After DNA replication, each chromosome becomes composed of two identical copies (called sister chromatids) that are held together at the centromere until they are pulled apart during meiosis II (Figure 1).
How are the chromosome copies called sister chromatids separated from each other?
The two “sister” chromatids are joined at a constricted region of the chromosome called the centromere. During cell division, spindle fibers attach to the centromere and pull each of the sister chromatids to opposite sides of the cell. Soon after, the cell divides in two, resulting in daughter cells with identical DNA.
What separates during meiosis?
During anaphase II, microtubules from each spindle attach to each sister chromatid at the kinetochore. The sister chromatids then separate, and the microtubules pull them to opposite poles of the cell. As in mitosis, each chromatid is now considered a separate chromosome (Figure 6).
How do chromosomes split apart during anaphase?
During anaphase of mitosis, the sister chromatids separate and move to opposite ends of the cell. This occurs via the action of spindle fibers and microtubules that pull each chromosome apart at the centromere.
Do sister chromatids separate in meiosis 2?
During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes, and in meiosis II, sister chromatids are segregated into daughter cells.
Where are the sister chromatids separated in meiosis?
In Anaphase II the centromere of each chromosome divides into two. The two centromeres along with their chromatids separate and move towards the opposite poles of the spindle as in mitosis.
How does sister chromatid separation work?
Sister chromatid separation ensures that each daughter cell gets the appropriate number of chromosomes after division.
Where do sister chromatids move in mitosis?
In prophase of mitosis, sister chromatids begin to move toward the cell center. In metaphase, sister chromatids align along the metaphase plate at right angles to the cell poles. In anaphase, sister chromatids separate and begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell.
What is the process of meiosis?
Meiosis is a two-part cell division process that is similar to mitosis. In prophase I and metaphase I of meiosis, events are similar with regard to sister chromatid movement as in mitosis. In anaphase I of meiosis, however, sister chromatids remain attached after homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. Sister chromatids do not separate until anaphase II. Meiosis results in the production of four daughter cells, each with one half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Sex cells are produced by meiosis.
Why is DNA synthesized during the S phase?
DNA is synthesized during the S phase or synthesis phase of interphase to ensure that each cell ends up with the correct number of chromosomes after cell division. The paired chromatids are held together at the centromere region by a special protein ring and remain joined until a later stage in the cell cycle.
What is sister chromatid?
Updated January 23, 2019. Definition: Sister chromatids are two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome that are connected by a centromere. Chromosome replication takes place during interphase of the cell cycle. DNA is synthesized during the S phase or synthesis phase of interphase to ensure that each cell ends up with ...
How many daughter cells are produced in meiosis?
Meiosis results in the production of four daughter cells, each with one half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Sex cells are produced by meiosis. Chromatid - one-half of two identical copies of a replicated chromosome. Chromatin - DNA and protein complex that forms chromosomes.
What is the name of the DNA strands that contain genes that code for the production of proteins?
Chromatin - DNA and protein complex that forms chromosomes. Chromosomes - DNA strands containing genes that code for the production of proteins. Daughter Chromosome - single-stranded chromosome resulting from the separation of sister chromatids. Cite this Article.
When DNA is transferred to the daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of?
Then during mitosis, when the DNA is transferred to the two daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of the two cells .
What is a chromatid in mitosis?
Then during mitosis, when the DNA is transferred to the two daughter cells, one of each of those chromatids is transferred to each of the two cells. So a chromatid is one copy of a chromosome after DNA replication.
What is a chromatid?
Chromatid. Chromatid. =. A chromatid is one of two identical halves of a replicated chromosome. During cell division, the chromosomes first replicate so that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Following DNA replication, the chromosome consists of two identical structures called sister chromatids, ...
What is the structure that pulls chromosomes away during cell division?
During cell division (anaphase) the chromosomes are pulled away by structures called microtubule's which are formed by centrioles , just before this the centrioles line up on two opposite sides of the cell . in plant cells microtubules are made by the Golgi bodies.
Where are mitotic spindles organized?
There are many different ways to make a spindle in plant cells: Mitotic spindles may be organized at centriolar centrosomes (only in final divisions of spermatogenesis), polar organizers (POs), plastid MTOCs, or nuclear envelope MTOCs (NE-MTOCs).
What do plants without centrioles do?
Plant cells without centrioles build special vesicles from their Golgi apparatus which are important for cell division.
Why do plants have spindles?
Spindle formation in plants is very different from most other eukaryotes owing to the fact that plant cells lack centrosomes or spindle pole bodies, which act as the microtubule organizing centers in animal cells. The evolutionary advantage that animal cells gain due to the presence of centrosomes is the ability to direct drastic changes in their ...
What is a biology stack exchange?
Biology Stack Exchange is a question and answer site for biology researchers, academics, and students. It only takes a minute to sign up.
What are the two phases of cell division?
Animal cells under go cell division in two phases karyo-kinesis and cyto-kinesis. During cell division (anaphase) the chromosomes are pulled away by structures called microtubule's which are formed by centrioles , just before this the centrioles line up on two opposite sides of the cell . in plant cells microtubules are made by the Golgi bodies. Animal cells are much evolved than plant cells that's why they have centrioles . Spindle formation is very much different in plant cells than in animal cells due to the absence of centrioles .
Do plants have centrioles?
Most plants do not have centrioles, so what organelle enables them to multiply?
Chromosomes
Sister chromatids in Mitosis
- In prophase of mitosis, sister chromatids begin to move toward the cell center. In metaphase, sister chromatids align along the metaphase plate at right angles to the cell poles. In anaphase, sister chromatids separate and begin moving toward opposite ends of the cell. Once the paired sister chromatids separate from one another, each chromatidis co...
Sister chromatids in Meiosis
- Meiosis is a two-part cell division process that is similar to mitosis. In prophase I and metaphase I of meiosis, events are similar with regard to sister chromatid movement as in mitosis. In anaphase I of meiosis, however, sister chromatids remain attached after homologous chromosomes move to opposite poles. Sister chromatids do not separate until anaphase II. Mei…
Related Terms
- Chromatid- one-half of two identical copies of a replicated chromosome.
- Chromatin- DNA and protein complex that forms chromosomes.
- Chromosomes - DNA strands containing genes that code for the production of proteins.
- Daughter Chromosome- single-stranded chromosome resulting from the separation of sister chromatids.