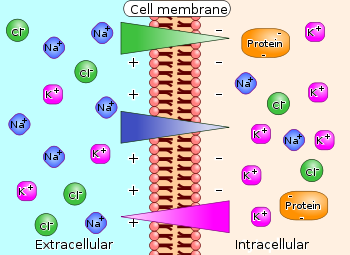
How are sodium and potassium ions move across the membrane?
The sodium-potassium pump system moves sodium and potassium ions against large concentration gradients. It moves two potassium ions into the cell where potassium levels are high, and pumps three sodium ions out of the cell and into the extracellular fluid.
Is sodium ions moving into the cell active transport?
Secondary active transport brings sodium ions, and possibly other compounds, into the cell. As sodium ion concentrations build outside of the plasma membrane because of the action of the primary active transport process, an electrochemical gradient is created.
What type of transport is sodium ions?
The sodium-potassium pump carries out a form of active transport—that is, its pumping of ions against their gradients requires the addition of energy from an outside source.
What membrane transport transports sodium ions?
Answer and Explanation: The type of membrane transport used to transport these sodium ions is d. facilitated diffusion. Facilitated diffusion is the process by which the ion moves with the concentration gradient (i.e. from areas of high to low concentrations) through a protein channel.
Which ions are moved by active transport?
These three types of carrier proteins are also found in facilitated diffusion, but they do not require ATP to work in that process. Some examples of pumps for active transport are Na+–K+ ATPase, which carries sodium and potassium ions, and H+–K+ ATPase, which carries hydrogen and potassium ions.
Is the transport of ions active or passive?
active transportThe transport of ion species can be passive (facilitated) or active. Facilitated transport is mainly mediated through ion channels whereas active transport can be either conveyed by primary active (ion pumps) transporters and secondary active (ion cotransporters and exchangers) transporters.
What is moving in active transport?
In the active transport, substances (e.g. ions, glucose, and amino acids) move across a membrane from a region of their lower concentration to a region of their higher concentration. Thus, they move against the direction of their concentration gradient.
How do ions move?
Ions move in predictable ways. Concentration and electrical gradients drive ion movement. Ions will diffuse from regions of high concentration to regions of low concentration. Diffusion is a passive process, meaning it does not require energy.
Why do ion channels control ion movement across the cell membrane?
Ion channels control ion movement across the cell membrane because the phospholipid bilayer is impermeable to the charged atoms. When the channels are closed, no ions can move into or out of the cell. When ion channels open, however, then ions can move across the cell membrane. Video Player.
How do ions move in equilibrium?
The ions continue to move across the membrane through open channels, but the ion flow into and out of the cell is equal . In this animation, the membrane starts and ends with seven positive ions on each side even though the ions move through the open channels. ‘Ion Equilibrium’ by Casey Henley is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial (CC-BY-NC) 4.0 International License. View static image of animation.
What are ion channels?
Ion channels are proteins that span the width of the cell membrane and allow charged ions to move across the membrane. Ions cannot pass through the phospholipid bilayer without a channel. Channels can be opened in a number of different ways.
What is the neuronal membrane made of?
The neuronal membrane is composed of two layers of phospholipid molecules that form a barrier to water and water-soluble molecule due to the organization of the hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic ends of the molecules.
What is the summation of the two individual gradients and provides a single direction for ion movement?
Sometimes the concentration and electrical gradients driving ion movement can be in the same direction; sometimes the direction is opposite. The electrochemical gradient is the summation of the two individual gradients and provides a single direction for ion movement.
How do ions move down the concentration gradient?
As long as a pathway exists (like through open ion channels), the ions will move down the concentration gradient. In addition to concentration gradients, electrical gradients can also drive ion movement. Ions are attracted to and will move toward regions of opposite charge.
Which pump transports sodium and potassium across the cell membrane?
Illustration showing active transport of sodium and potassium across the cell membrane via the sodium-potassium ATPase pump.
How do molecules move across the membrane?
There are two major ways that molecules can be moved across a membrane, and the distinction has to do with whether or not cell energy is used. Passive mechanisms like diffusion use no energy, while active transport requires energy to get done.
Why is sodium pump important?
This is one major explanation for why the sodium/potassium pump is so important – that one molecule helps set up the needed gradient to allow for the movement of many chemicals into and out of the cell. In fact, this relationship is taken advantage of in certain heart disease medications.
What is the energy released by ATP?
This protein uses the energy released from hydrolysis of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) to pump three sodium ions out of and two potassium ions into the cell. ATP is an energy molecule, and when hydrolysis happens, it gets broken down to release the energy that was stored in its chemical bonds.
Why is simple diffusion disrupted?
Simple diffusion can be disrupted if the diffusion distance is increased. If the alveoli in our lungs fill with fluid (pulmonary edema), the distance the gases must travel increases, and their transport decreases.
What is diffusion in biology?
Diffusion is the movement of particles down their gradient. A gradient is any imbalance in concentration, and moving down a gradient just means that the particle is trying to be evenly distributed everywhere, like dropping food coloring in water. This is what happened when we made our granola - a bunch of separate ingredients came together and spread out across the whole mixture. We call this evening-out moving “downhill”, and it doesn’t require energy. The molecule most likely to be involved in simple diffusion is water - it can easily pass through cell membranes. When water undergoes simple diffusion, it is known as osmosis.
What is the most likely molecule to be involved in simple diffusion?
The molecule most likely to be involved in simple diffusion is water - it can easily pass through cell membranes. When water undergoes simple diffusion, it is known as osmosis. Image showing purple ink diffuse from a tiny drop into a beaker of water . "Simple diffusion.".
