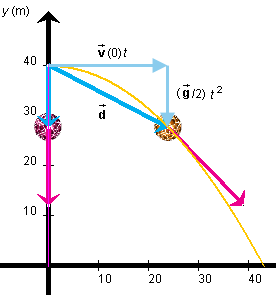
Perhaps the simplest model for modelling projectile motion that includes air resistance is what is known as the linearly resisted model or the linear drag model. Here the resistance to the motion of the projectile as it moves through air is considered to be proportional to its velocity. For some accessible accounts of this model, see, for example:
Full Answer
How do you find the air resistance of a projectile?
If wind is in the direction of motion at 3 m/s and the projectile is moving at 10 m/s then the air resistance term uses 7 m/s. The air resistance is − c ∗ v 2 or − c ∗ v like normal. This made sense for an approximate answer.
How do you calculate how far a projectile will go?
The math to do actually calculate how far a projectile would go was almost impossible and was impractical to do before numeric integration on a computer. The air resistance is dependent on the shape and velocity of the projectile. Air density - dependent on temperature, humidity and altitude- will also make a difference.
What is the formula for projectile motion analysis?
Projectile motion analysis. Three vectors - v, vx and vy - form a right triangle. Write down the equations of motion. Horizontal distance traveled can be expressed as x = vx * t, where t is the time. Vertical distance from the ground is described by the formula y = vy * t – g * t^2 / 2, where g is the gravity acceleration.
How do you calculate vertical and horizontal velocity in projectile motion?
Projectile motion analysis 1 The horizontal velocity component Vx is equal to V * cos (α). 2 The vertical velocity component Vy is equal to V * sin (α). 3 Three vectors - V, Vx and Vy - form a right triangle.
How do you model projectile motion with air resistance?
2:3925:08Projectile Motion with Air Resistance - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo any points that's motion whichever way it's moving at that that second in time the air resistanceMoreSo any points that's motion whichever way it's moving at that that second in time the air resistance will always be in the opposite direction and that means it's going to affect both the horizontal.
How do you calculate the distance a projectile will travel with air resistance?
Horizontal distance traveled can be expressed as x = Vx * t , where t is the time. Vertical distance from the ground is described by the formula y = h + Vy * t – g * t² / 2 , where g is the gravity acceleration.
How does air resistance affect projectile motion?
As a projectile moves through the air it is slowed down by air resistance. Air resistance will decrease the horizontal component of a projectile. The effect of air resistance is very small, but needs to be considered if you want to increase the horizontal component of a projectile.
What is the formula for calculating projectile motion?
h = v 0 y 2 2 g . This equation defines the maximum height of a projectile above its launch position and it depends only on the vertical component of the initial velocity.
How do you calculate air resistance?
Air resistance can be calculated by taking air density times the drag coefficient times area all over two, and then multiply by velocity squared.
How do you find distance in projectile motion?
Horizontal projectile motion equations Horizontal distance can be expressed as x = V * t . Vertical distance from the ground is described by the formula y = – g * t² / 2 , where g is the gravity acceleration and h is an elevation.
Is projectile motion air resistance?
Properties of Projectile Motion As an object travels through the air, it encounters a frictional force that slows its motion called air resistance. Air resistance does significantly alter trajectory motion, but due to the difficulty in calculation, it is ignored in introductory physics.
How does air resistance affect the maximum height of a projectile?
Solution : In the presence of air resistance, the range, maximum height, speed at which the projectile strikes the ground will decreases whereas the angles at which the projectile strikes the ground will increases.
Is air resistance ignored in projectile motion?
Thus, in the projectile motion, if air resistance is ignored, the horizontal motion is at constant velocity. Hence, option C is the right answer.
How do you solve a projectile motion problem?
0:0128:19How To Solve Projectile Motion Problems In Physics - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the final velocity is equal to the initial velocity plus the acceleration multiplied by the time.MoreSo the final velocity is equal to the initial velocity plus the acceleration multiplied by the time. Also the square of the final velocity is equal to the square of the initial velocity.
What is the maximum range of a projectile with air resistance?
For ideal projectile motion, which starts and ends at the same height, maximum range is achieved when the firing angle is 45°. If air resistance is taken into account, the optimal angle is somewhat less than 45° and this is often considered obvious.
Does a projectile experience air resistance?
A projectile is a free-falling object. A projectile experiences negligible or no air resistance. A projectile must be moving in the downward direction. A projectile must be accelerating in the downward direction.
When there is air resistance, does the projectile feel an extra force?
When there is air resistance the projectile feels an extra force other than the gravitational force (as the friction acts downwards upward motion) which may be considered as a certain amount of increment in ‘g’ . From the above result for t, you can see that as g increases t assumes a decreased value.
How does a projectile travel?
Lets imagine that you fire a projectile horizontally, from some distance from the ground. Assuming flat ground, it travels horizontally, being slowed by air resistance. It also travels vertically, toward the ground, due to the pull of gravity. The time it takes for it to hit the ground is almost exactly the same as if the projectile were simply dropped from the firing point. The travel distance is limited only by the height of the firing point.
Why is it better to fire a projectile horizontally or vertically?
Firing straight up will cause it to come straight back down on you, while firing horizontally wont work because the projectile hits the ground to soon. The optimum solution is to allow gravity and air resistance to stack slightly (by firing up at an angle) while also maximising travel distance.
What happens if you launch a projectile vertically?
If you launched the projectile vertically next to a mountain then the projectile would deviate very slightly towards the mountain - again not symmetrical.
What happens to the horizontal component of a projectile as time increases?
This creates a perfect parabola. As time increases, the object “falls” faster and faster but the speed across the ground remains unchanged.
What happens to an object when it is inertia?
So once the horizontal inertia is spent, the object stops moving across the ground, and once the air resistance matches the gravitational force the object will fall at a constant velocity. Straight down.
What is the optimum firing angle?
Withn no air resistance, the optimum firing angle is 45 degrees, every time. With air resistance, the optimum firing angle is a little under 45 degrees, to balance mimimising the interaction of gravity and air resistance while still maximising travel distance.
What happens if a projectile stays in the air longer than a time of order?
It thus follows, from Equations ( 180) and ( 183 ), that if the projectile stays in the air much longer than a time of order then it ends up falling vertically downward at the terminal velocity, , irrespective of its initial launch angle.
What is terminal velocity?
Here, is the terminal velocity: i.e., the velocity at which the drag force balances the gravitational force (for a projectile falling vertically downward).
Does air drag cause horizontal velocity?
It is clear, from the above equation, that air drag causes the projectile's horizontal velocity, which would otherwise be constant, to decay exponentially on a time-scale of order .
What is projectile motion calculator?
Our projectile motion calculator is a tool that helps you analyze the parabolic projectile motion. It can find the time of flight, but also the components of velocity, the range of the projectile, and the maximum height of flight. Continue reading if you want to understand what is projectile motion, get familiar with the projectile motion definition, and determine the abovementioned values using the projectile motion equations.
How to find the range of a projectile?
The range of the projectile is the total horizontal distance traveled during the flight time. Again, if we're launching the object from the ground (initial height = 0), then we can write the formula as R = Vx * t = Vx * 2 * Vy / g. It may be also transformed into the form: R = V² * sin (2α) / g
Why does an object follow a parabola?
An object follows a parabola because of how its two components of motion - the horizontal and vertical - are affected by gravity. The horizontal component is not affected by gravity at all, and so changes in a constant, linear fashion. The vertical part, however, is constantly affected by gravity, and so it will increase in height, and then decrease, accelerating due to gravity.
How does initial velocity affect a projectile?
Initial velocity, the initial height the projectile is being launched from, and gravity will all affect a projectile launched horizontally. Air resistance will also have an effect in real life, but for most theoretical calculations it is negligible and is therefore ignored. If the projectile has wings, this will also impact its motion, as it will glide.
What objects have projectile motion?
Objects with projectile motion include: keys being thrown, a 300 kg projectile being thrown 90 m by a trebuchet, a football being kicked so that it no longer touches the ground, a diver jumping from a diving board, an artillery shell the moment it leaves the barrel, and a car trying to jump a bridge.
How to find the greatest distance traveled by a projectile?
The equation for the distance traveled by a projectile being affected by gravity is sin (2θ)v2/g , where θ is the angle, v is the initial velocity and g is acceleration due to gravity. Assuming that v 2 /g is constant, the greatest distance will be when sin (2θ) is at its maximum, which is when 2θ = 90 degrees. This means θ = 45 degrees.
What happens when a projectile reaches its maximum height?
When the projectile reaches the maximum height, it stops moving up and starts falling. It means that its vertical velocity component changes from positive to negative – in other words, it is equal to 0 for a brief moment at time t (Vy=0).
What happens to the effective footprint of a projectile if the wind direction changes?
Also worth noting is the fact that if the wind direction changes, the effective footprint of your projectile will change, thus changing D and therefore the force due to drag. If you are willing to make a reasonable approximation for the average footprint of your projectile, however, this will likely yield a result that is accurate enough for your purposes.
Does wind affect velocities?
Oh, and in the scenario of the wind, it can blow from any angle, which means it will affect the x and y velocities and either augment them or lessen them depending on the angle at which it blows. So I guess another request is an explanation of how to obtain the set of equations (position, velocity, acceleration) for the x direction based on whether the wind angle is helpful or hurtful, and how to obtain the set of equations for the y direction, based again on whether the wind is helpful or hurtful.