Use the following procedure to check for ground loops:
- Remove the pH sensor from the process liquid.
- Calibrate the sensor in buffers. Be sure there is no direct electrical connection between the container holding the buffer and the process liquid or piping.
- Strip back the ends of a heavy gauge wire.
- Connect one end of the wire to the process piping or, better, place it in the process liquid. ...
- Set your volt meter to the most sensitive AC setting.
- Disconnect the camera you want to test.
- Place one contact on any exposed metal of the chassis. ...
- Place the other contact on the outside of the connector on the coax from the camera.
- Any value above 0 indicates a ground loop.
What is a ground loop?
Ground loops occur whenever the ground conductor of an electrical system is connected to the ground plane at multiple points. Not only can ground loops induce noise in instrument signal cables, but in severe cases it can even overheat the instrument signal cable and thus present a fire hazard!
Is it good to fix a ground loop?
A ground cable can create a wide variety of problems, including the notorious hum that annoys everyone. And yes, it is very good that you are interested in fixing the ground loop, which we will now look at. Cable problems can be very diverse: from a banal weak connection to a hum of the ground loop that takes time to fix.
How do I know if my PC has a ground loop?
With the PC connected, the speakers put out a low level, annoying, 60-Hz hum—a clear indication of a ground loop. All my audio and video (AV) devices are fairly new, quality, brand-name products equipped with two-prong power cords, so even though the PC has a three-prong plug, there should not be multiple signal returns causing the ground loop.
How does a ground loop affect a sensor?
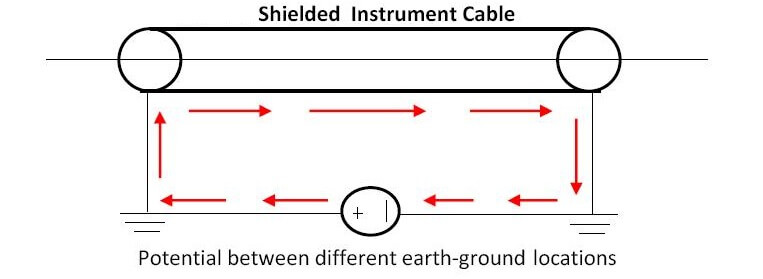
Unwanted ground loops can cause inaccurate sensor readings by negatively affecting instrumentation signals. A ground loop exists when a circuit is connected to earth ground at two or more points. Because the potential of the earth varies from point to point, two or more connections to the ground cause currents to flow.

How do you troubleshoot a ground loop?
To troubleshoot for ground loops: On a (floating) controller, measure the VAC from the phase terminal to an earth ground and repeat from the common terminal to an earth ground. No voltage (or only reactive voltage) should be read. If 24 VAC is read, there is a ground in the system.
What problems do ground loops cause?
Ground loops can result in signal noise, communications errors, or a damaging flow of ground current on long cables. Most often, ground loops do not have drastic negative effects and may be unavoidable.
What does a ground loop sound like?
Ground loops can appear when there are two or more devices connected to a common ground and can sound like a low frequency hum, similar to touching the end of an instrument cable connected an amplifier. This typically happens when you are using a stereo guitar rig with two grounded amplifiers.
How does a ground loop occur?
A ground loop is formed when there is more than one conductive path between the “ground” terminals on two or more pieces of equipment. The conductive loop forms a large loop antenna that picks up interference currents easily.
How do you get rid of ground hum?
The simple, inexpensive way to fix the ground hum is to plug the piece of equipment into a different outlet that is on a different circuit. Once you can identify which piece of equipment is causing the problem, this is the easiest fix.
How do you fix a ground loop sound?
Power inter-connected equipment from different AC outlets is likely to create a ground loop: The ground will travel through the shielding of the signal cables. Anything that breaks the loop will remove the noise, and the easiest way to do it is to power everything through a single AC socket.
How do I stop ground loops in audio?
The ground loop can be eliminated in one of two ways: Remove one of the ground paths, thus converting the system to a single point ground. Isolate one of the ground paths with an isolation transformer, common mode choke, optical coupler, balanced circuitry, or frequency selective grounding.
Can ground loop damage speakers?
Major Contributor. If you can only hear it with your ear against the 'speaker then there really is nothing to worry about, or even think about. Many unbalanced systems have some degree of ground loopery, it's only an issue if it's audible at normal listening distances.
What is a ground loop and why is it bad?
Ground loops are a potential cause of noise interference on the PCB. If one component on the loop is noisy and the return current flows through shared ground connectors, this noisy component is then the source for an introduction of noise to other components on the loop.
What does improper grounding cause?
A poor electrical ground can cause the lights in a home to dim. When this symptom is present, it is often made worse by turning on larger appliances, such as a stove or heater. This will usually cause the lights to dim even more or even turn off and the appliance likely will not have enough power to operate properly.
How to eliminate ground loop problems?
You can eliminate most ground loop problems by just plugging your devices into one AC source with the same ground. By doing so, you reduce the difference in electrical potential between grounds of the devices.
What is a ground lift switch?
Most audio devices nowadays have a ground lift switch, so that one can easily cut a ground path from one device. If ground lift switches are not available, you can simply break or disconnect the ground shield at one end of the cables used between devices. 3. Audio Isolation Transformer. This device is inserted along the audio path.
What happens when two devices are connected to ground?
A ground loop is basically what happens when two separate devices (A and B) are connected to ground via different paths and then also connected to each other by another path, creating a loop. When a ground loop is created, current may flow in unanticipated directions.
What is a 1:1 transformer?
A 1:1 transformer is usually used but other transformers could also be used to boost the level of the output.
What is an electronics engineer?
An Electronics Engineer and is currently working as a Research and Development Engineer at an audio electronics company for guitars and some related accessories. Loves music, audio gears, and electronics. Some fields of interests are amplification designs, analog circuits, digital circuits, and embedded electronics.
Can a laptop make a buzzing sound?
One example where a ground loop can happen is in a simple setup of a laptop computer and an AC powered speaker. When the speaker is used by the laptop, connected through an audio cable, while both the laptop and speaker are plugged into the AC mains, the speaker may produce a buzzing sound. This issue may be solved by unplugging the laptop charger from the mains, which breaks the ground loop. This scenario may or may not happen depending on the grounding of one's home or establishment.
Why does current flow to ground?
The current may flow to ground via the device’s own ground path or it may flow first to the other device before going to ground due to the difference of electrical potential between devices. This unintended current flow causes system noise or interference to be transmitted to nearby devices.
What is stakeless in grounding?
Stakeless measurement only measures individual ground rod resistances in parallel to earth grounding systems. If the ground system is not parallel to earth, then you'll either have an open circuit or be measuring ground loop resistance.
What is earth ground measurement?
Normal earth ground measurement involves disconnecting parallel grounding rods, "planting" several auxiliary grounding stakes , and using a earth ground tester to calculate the resistance of grounding system electrodes. Sometimes, though, there isn't anywhere to plant the grounding stakes - such as inside a building, at a cell phone substation, or on power pylons. What then?
What is the RMS of Fluke 1630?
The Fluke 1630 measures ground resistance from 0.025 to 1500 ohms and True RMS current flow from 0.02 to 35 A; and enables non-intrusive leakage current measurements from 0.2 to 1000 mA. It features a HI/LO alarm function to help users quickly compare the measured value against upper and lower limits, a display-HOLD function, a recording function that allows storage of measured values, and automatic self-calibration.
Is the net resistance of all the parallel return path resistances zero?
So, the net resistance of all the parallel return path resistances is effectively zero. Stakeless measurement only measures individual ground rod resistances in parallel to earth grounding systems. If the ground system is not parallel to earth, then you'll either have an open circuit or be measuring ground loop resistance.
Do you need earth stakes for stakeless testing?
With the Stakeless testing method, earth ground stakes aren't necessary. Place an earth ground clamp like the Fluke 1630 around the earth ground rod or the connecting cable. One half of the clamp will induce a known voltage while the other half measures current.
How to eliminate ground loop
Of all the options available, the most affordable way to remove the ground loop hum is to replace the socket. This means that you need to connect the devices to a different outlet in a different circuit. Once you understand which part of the circuit is malfunctioning, it will be easy to fix.
Silencer as a way out of the situation
You can use a device that resembles a muffler in principle. It’s called the Hum Eliminator. It is designed to destroy ground loops. The method of working with it is also quite simple: Hum Eliminator is installed between inoperative components of the circuit, and thus, it breaks the ground loop, removing unnecessary noise.
Adding a direct box
A direct box can be added to the system, which will help remove unnecessary problems. It has a built-in grounding hoist that is designed to break the ground loop. As a result, it will allow you to enjoy great sound without lags and unnecessary hum.
Why is induction reduced?
Electromagnetic induction is reduced because when the wires are twisted so as to create a series of loops instead of one large loop, the inductive effects of the external magnetic field tend to cancel out thereby reducing the induced noise voltage on the instrument signal wires due to the external magnetic field.
What is inductive coupling?
Inductive Coupling. When a wire carries an electrical current it produces a magnetic field; if this wire is in the vicinity of another wire also carrying electrical current or signal, the magnetic field they produce interact with one another resulting in noise voltage being induced in the wires. This is the principle through which inductive ...
How is inductance stored?
As we already know, Inductance is a property intrinsic to any conductor, whereby energy is stored in the magnetic field formed by current through the wire. Mutual inductance existing between parallel wires forms a bridge. whereby an AC current through one wire is able to induce an AC voltage along the length of another wire.
What is single point grounding?
Single point grounding involves grounding the instrumentation installation at a single point. This approach significantly reduces the noise voltage generated due to ground loops from multiple grounding points.
Why use differential inputs?
Differential inputs are used to cancel out the noise voltage that may appear in the instrumentation circuit. One very effective way to completely isolate an instrumentation system from ground loops is to use battery powered instruments. However because of the limited life of a battery, they are seldom used.
Why does the error voltage in a circuit occur?
The error voltage is due to the impedance in the return wire.
How to reduce impedance coupling?
One way to reduce the effects of impedance coupling is to minimize the impedance of the return wire. The second solution is to avoid any contact between the circuits and to use separate returns for each individual circuit.
What causes a guitar to hum?
Since the ground signal travels from pot to pot over both the wire connecting them and also over the shielding connecting them, it causes a ground loop. Ground loops can cause hum.
What is ground loop?
A ground loop occurs when a signal ground has two or more paths to the (-) terminal of the output jack. This is most obvious when the guitar has the pots touching the shielding (a metal plate or metallic foil) and the pots are connected together with a wire soldered to the backs of the pot cases.
Do Jazzmasters have a ground wire?
Usually in Jazzmasters, the switch is not shielded (or touching shielding) but there should be a ground wire from the switch to the back of one of the pots, effectively grounding it. (it sounds like you did that already… good!) It’s tough to give advice without actually seeing the wiring but, if you can send us a picture of the wiring, we’ll be happy to help guide you to getting it grounded properly with no ground loops. Send it to my attention at [email protected] Thanks for the question! Heywood @ HOAGLAND CUSTOM
Can telecasters touch shielding?
Which is fine. The metal control plate grounds the pots together. The problem comes into play when the pots are connected together with an additional piece of wire soldered between the cases. That creates a ground loop. Not good.
Do rewiring guitars cause buzzing?
Do they ALWAYS cause humming and buzzing in your guitar. No, not 100% of the time. But wouldn’t you rather eliminate the possibility if you are rewiring your guitar?
Why is grounding important in circuit design?
In many circuits, large currents may exist through the ground plane, leading to voltage differences of the ground reference in different parts of the circuit, leading to hum and other problems. Several techniques should be used to avoid ground loops, and otherwise, guarantee good grounding:
What causes ground loops?
A common type of ground loop is due to faulty interconnections between electronic components, such as laboratory or recording studio equipment, or home component audio, video, and computer systems. This creates inadvertent closed loops in the ground wiring circuit, which can allow stray 50/60 Hz AC current to flow through the ground conductors of signal cables. The voltage drops in the ground system caused by these currents are added to the signal path, introducing noise and hum into the output. The loops can include the building's utility wiring ground system when more than one component is grounded through the protective earth (third wire) in their power cords.
What causes currents in signal cable ground?
Such loops in the ground path can cause currents in signal cable grounds by two main mechanisms: Ground loop current induced by stray AC magnetic fields (B, green). Ground loop currents can be induced by stray AC magnetic fields (B, green) which are always present around AC electrical wiring.
What is a ground loop?
In an electrical system, a ground loop or earth loop occurs when two points of a circuit are intended to have the same ground reference potential but instead have a different potential between them. This can be caused, for example, in a signal circuit referenced to ground, if enough current is flowing in the ground to produce a voltage drop ...
How does a ground loop affect electrical current?
These ambient magnetic fields passing through the ground loop will induce a current in the loop by electromagnetic induction. In effect, the ground loop acts as a single-turn secondary winding of a transformer, the primary being the summation of all current carrying conductors nearby. The amount of current induced will depend on the magnitude of nearby utility currents and their proximity. The presence of high power equipment such as industrial motors or transformers can increase the interference. Since the wire ground loop usually has very low resistance, often below one ohm, even weak magnetic fields can induce significant currents.
What happens when a current flows through a ground conductor?
If a current I from a separate source is flowing through the ground conductor, the resistance R of the conductor will create a voltage drop along the cable ground of IR, so the destination end of the ground conductor will be at a different potential than the source end
How does ground noise affect a signal?
A more comprehensive solution is to use equipment that employs balanced signal lines. Ground noise can only get into the signal path in an unbalanced line, in which the ground or shield conductor serves as one side of the signal path. In a balanced cable, the signal is usually sent as a differential signal along a pair of wires, neither of which are connected to ground. Any noise from the ground system induced in the signal lines is a common-mode signal, identical in both wires. Since the line receiver at the destination end only responds to differential signals, a difference in voltage between the two lines, the common-mode noise is cancelled out. Thus these systems are very immune to electrical noise, including ground noise. Professional and scientific equipment often uses balanced cabling.
How to tell if a receptacle is properly grounded?
You will know that the receptacle is properly grounded if your voltage reading is the same now as it was when the probe was in the larger slot.
What happens if a voltage tester is not working?
If the tester reads no voltage, then either the circuit breaker is tripped or turned off (or the fuse blown) or else , the tester could be faulty. Check another receptacle (that you know is working) for voltage to rule out a bad voltage tester.
How to tell if a circuit breaker is blown?
Take one of the probes of your tester and slide it into the larger slot on the outlet, then insert the tip of the other probe into the small slot. Since you're dealing with AC voltage, it doesn't really matter which of the color-coded probe (red or black) goes into which slot or opening. If there is voltage in the circuit, it will be indicated on the tester. If the tester reads no voltage, then either the circuit breaker is tripped or turned off (or the fuse blown) or else, the tester could be faulty.
How to test for ground?
Testing for ground can be performed using either a multitester or a basic voltage tester. This test ensures that the ground on the circuit is connected to the outlet and that it is working. If you are using a multitester, set the tester to read voltage (V). If you are using a basic voltage tester, then you do not need to do anything to ...
What to do if a tester does not read proper voltage?
If the tester does not read proper voltage when you have one probe in the smaller slot and the other probe in the ground opening, then keep the probe that is inside the ground opening in place and move the other probe over to the large (neutral) slot.
What is a three prong outlet?
Three-pronged outlets feature two slots (one large and one small) and a “U” shaped hole. The small slot is the “hot” side of the receptacle and the large slot is the “neutral” side. The U-shaped hole is for the ground prong.
Is a non grounded receptacle grounded?
In either case, a non-grounded receptacle should be turned OFF until it is repaired to ensure that safety is not at risk.
