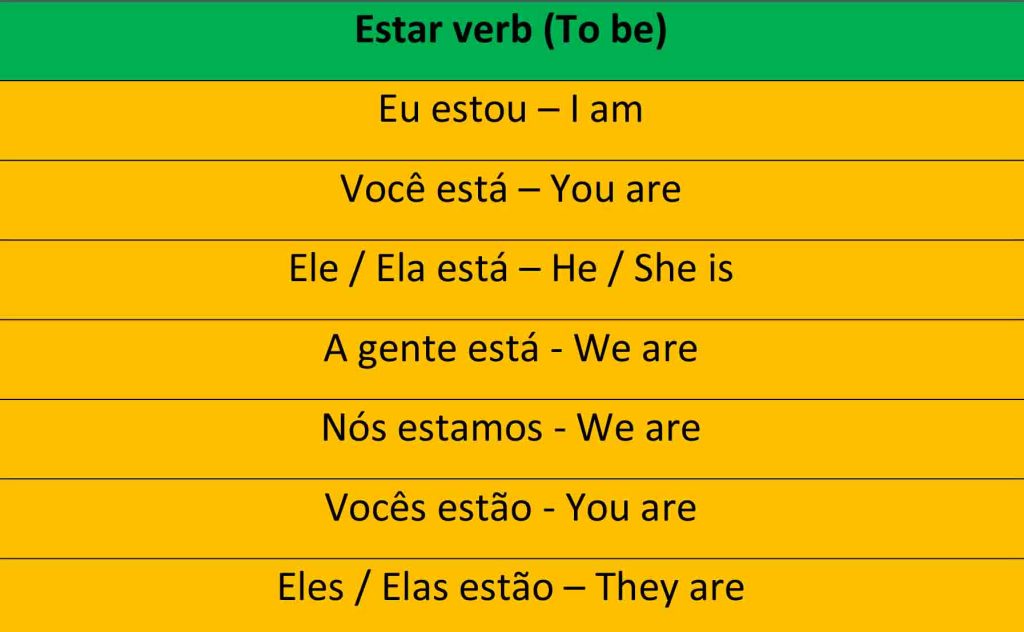
To form the preterite of regular -ar verbs, take off the -ar ending and add the endings: -é, -aste, -ó, -amos, -asteis, -aron. How do you use preterite tense? To conjugate a regular verb in the preterite tense, simply remove the infinitive ending (-ar, -er, or -ir) and add the preterite ending that matches the subject. How does the preterite work?
How do you conjugate regular preterite verbs?
There are only two sets of endings for regular preterite verbs, one for -ar verbs and one for both -er and -ir verbs. To conjugate a regular verb in the preterite tense, simply remove the infinitive ending (-ar, -er, or -ir) and add the preterite ending that matches the subject. Check out the table of regular preterite endings below.
What is the preterite form of the verb write?
The verb comer (to eat) is a regular – er verb in the preterite. Table 4, which shows the English past tense form of ate, is a good example of regular – er verb forms in the preterite tense. The verb escribir (to write) is a regular – ir verb in the preterite.
What is the imperfect tense of preterite?
In such cases, the imperfect tense is used. There are only two sets of endings for regular preterite verbs, one for -ar verbs and one for both -er and -ir verbs. To conjugate a regular verb in the preterite tense, simply remove the infinitive ending ( -ar, -er, or -ir) and add the preterite ending that matches the subject.
What are the endings of preterite verbs in Spanish?
Spanish Preterite Endings: Regular Verbs When dealing with regular verbs, there are two sets of Spanish preterite endings that you must learn. Endings for -AR verbs Endings for -ER and -IR verbs
/Getty_preterite-103772378-567a26183df78ccc154dbba2-5b50c8bdc9e77c003722f1a5.jpg)
How do you use the preterite tense?
The preterite tense is used if the past action had a definite beginning and definite end and is often used with phrases that give a specific time frame, eg: ayer (yesterday) anteayer (the day before yesterday)
How do you form preterite in Spanish?
2:458:42Preterite/pretérito in Spanish: how to form it & learn it! Easy ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe studied a lot but today we aren't studying at all now back to the pattern that was ar verbs ifMoreWe studied a lot but today we aren't studying at all now back to the pattern that was ar verbs if the infinitive was an ER verb. We add these endings. For example karev means to run the stem is cor
How do you identify preterite?
1:124:22Preterit vs Imperfect (How to Distinguish) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipHere. Another way we can use the preterite is if we have a series of completed. Actions. TheMoreHere. Another way we can use the preterite is if we have a series of completed. Actions. The imperfect is something where we don't know a beginning or an end and so we'll call that an ongoing. Action.
What is preterite past tense?
The simple past tense, sometimes called the preterit, describes completed actions in the past. It is formed by adding -ed to the end of the verb, if the verb is regular: I washed the floor yesterday.
How do you remember the preterite tense in Spanish?
0:411:34Songs to Remember Preterite Spanish Endings - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd eotteon again E is the EO emos nd air on. And there you have the endings e is the EO e. MostMoreAnd eotteon again E is the EO emos nd air on. And there you have the endings e is the EO e. Most Andy air on.
How do you study preterite or imperfect?
The rule of thumb for determining which tense to use is that the preterite talks about what you did, and the imperfect talks about what you were doing or what you used to do. Notice how the meaning changes for these verbs in the preterite vs the imperfect.
What are the 3 past tenses in Spanish?
As we mentioned before, there're three Spanish past tenses that you need to know as a beginner or intermediate speaker: The Spanish preterite (pretérito perfecto simple, or pretérito indefinido) The Spanish present perfect (pretérito perfecto) The Spanish imperfect (pretérito imperfecto)
Is time preterite or imperfect?
While the preterite describes actions that happened at a certain time, use the past imperfect when telling the date or time of a past event: Eran las diez de la mañana. (It was ten in the morning.) Era el 22 de junio.
How do you form the preterite tense of ER and IR verbs?
Preterite Tense Conjugation of Regular -ER and -IR Verbs He learned the lessons. To conjugate -er and -ir verbs in the preterite tense in Spanish, simply drop the -er or -ir and add the following personal endings: -í, -iste, -ió, -imos, -isteis, -ieron.
What are the 3 past tenses in Spanish?
As we mentioned before, there're three Spanish past tenses that you need to know as a beginner or intermediate speaker: The Spanish preterite (pretérito perfecto simple, or pretérito indefinido) The Spanish present perfect (pretérito perfecto) The Spanish imperfect (pretérito imperfecto)
How do you conjugate verbs in Spanish?
To conjugate a verb in the present indicative, remove the infinitive ending from the regular verb, in this case -ar , -er or -ir, and replace it with an ending indicating "the person" who performs the action of the verb.
Is the preterite tense the same as past tense?
The preterite or preterit (/ˈprɛtərɪt/; abbreviated PRET or PRT) is a grammatical tense or verb form serving to denote events that took place or were completed in the past; in some languages, such as Spanish, French, and English, it is equivalent to the simple past tense.
What is a preterite?
The preterite is used for listing past events that took place in a sequence.
What is the preterite tense in Spanish?
The Spanish preterite tense ( el pretérito o el pretérito perfecto simple) is used to describe actions completed at a point in the past. The Spanish preterite is not used to describe habitual or continuous actions in the past with no specific beginning or end. In such cases, the imperfect tense is used.
How to conjugate a regular verb in Spanish?
To conjugate a regular verb in the preterite tense, simply remove the infinitive ending ( -ar, -er, or -ir) and add the preterite ending that matches the subject.
Is Ser the same as Ir?
Note that ser and ir have the exact same forms in the preterite.
Is "ar" plural or singular?
The first person plural ( nosotros) endings for regular - ar and -ir verbs are the same for both the preterite and present tenses. Context clues, such as adverbs like siempre ( always) and ayer ( yesterday ), can help you figure out if a nosotros form refers to the past or the present.
What does "preterite" mean?
The preterite typically translates to a single past tense word in English.
What is the verb form of the past in Spanish?
Spanish has two main verb forms for talking about the past, the imperfect and the preterite. And in true Spanish style, they have totally different conjugations and distinct, nuanced meanings. So what gives? How do you know what each form means? In this post, we'll be sharing tips and tricks for using Spanish past tenses.
Why do we use imperfect in Spanish?
That's because the imperfect is used for talking about more complex situations in the past — situations spread out over time. English uses these more complex phrases to talk about these kinds of past situations, and in Spanish you'll use the imperfect!
What does the imperfect tell us?
The imperfect actually tells us something about the world — that there’s an *underlying reason* for an ongoing or repeated action in the past. We use the imperfect when there was an intention, a routine, or a circumstance that made the action ongoing.
How to conjugate a regular verb in the preterite tense?
For an – ar verb that is regular in the preterite, use the endings from Table 1. (Not all verbs that were regular in the present tense are regular in the preterite.)
What is the conjugation chart for hablar?
Table 2 is a conjugation chart for the verb hablar in the preterite tense. Since the preterite is a past tense, these forms translate to the English past tense form “spoke.”. Table 3 shows that the endings for – er verbs and – ir verbs are the same for regular verbs in the preterite tense.
Is the verb "er" or "nosotros" identical?
Notice that the nosotros/nosotras form of an – ir verb looks identical in both the present and preterite tenses, but an – er verb has a different nosotros form in the preterite. The nosotros/nosotras form in the present tense is the only form where – er and – ir verbs are different.
Is "eat" a verb?
The verb comer (to eat) is a regular – er verb in the preterite. Table 4, which shows the English past tense form of ate, is a good example of regular – er verb forms in the preterite tense.
Do regular verbs have the same nosotros form in the preterite?
Regular – ar verbs have the same nosotros form in the preterite as they do in the present tense. The only way you will know whether an – ar verb in the nosotros form is in the preterite or present tense is the context of the sentence. If you see one of these words in the sentence, you will know the verb is conjugated in the preterite tense.
When To Use The Spanish Preterite Tense
Before we explore the Spanish preterite conjugation, we need to clarify exactly when and where you can use this past tense.
Spanish Preterite Endings: Regular Verbs
When dealing with regular verbs, there are two sets of Spanish preterite endings that you must learn.
Spanish Preterite Endings: Irregular Verbs
Throughout Spanish grammar, there are some irregular verbs that must be conjugated differently – and the Spanish preterite is no different.
How To Stop Confusing Spanish Preterite vs Imperfect
A common problem for many Spanish students is knowing which past tense to use: Preterite vs Imperfect.
Spanish Preterite Practice
Now it’s time to see how well you understand the Spanish preterite tense by adding the correct conjugations to the below sentences.
Where is the verb in preterite?
In order to build these kinds of sentences, you can follow this phrase structure. Notice that the verb in preterite is always placed after the word ‘cuando’:
What is the preterite in Spanish?
Since we have other past tenses, it’s difficult for many students to know when to use preterite in Spanish. In Spanish, the preterite is the equivalent of the English simple past tense.
How to use the simple past tense in Spanish?
Just like any other tenses, in order to form the simple past in Spanish, you need to use the verb’s root and add the appropriate ending. Here is a conjugation chart that you can use when conjugating regular verbs in preterite tense:
What does the preterite tense mean in Spanish?
As mentioned earlier, the preterite Spanish tense implies that there is a clear starting or ending point for the subject at hand. As a result, this tense is commonly used when talking about or referring to specific dates or amounts of time.
What are the two past tenses in Spanish?
Even though sentences with simultaneous actions are quite common in Spanish, they might be a little more complicated since they require you to use two different past tenses: preterite and imperfect or pluscuamperfecto.
What does "pretérito" mean?
As you may have already noticed, pretérito is used to refer to specific actions, things or events in the past. For that reason, we also use this tense when talking about the frequency of an action.
When to use "pretérito"?
Another common situation where you need to use pretérito is when enlisting or referring to a sequence of events in the past. In other words, we use this tense when talking about a string of actions that we performed at some point in the past.