The methods or techniques for the evaluation of alternatives are:-
- Marginal Analysis : To evaluate alternatives, a manager may use the marginal analysis technique. The marginal analysis technique helps to compare additional revenues with additional costs. ...
- Cost Effectiveness Analysis : This technique is an improvement of the traditional marginal analysis. In this case, the manager considers the cost-benefit analysis. ...
What is the process of analyzing and evaluating alternatives?
The process of analyzing and evaluating alternatives applies evaluation criteria to alternatives or options in a way that facilitates decision making. This may be a one-step or multi-step process, depending on the complexity of the alternatives and the decision.
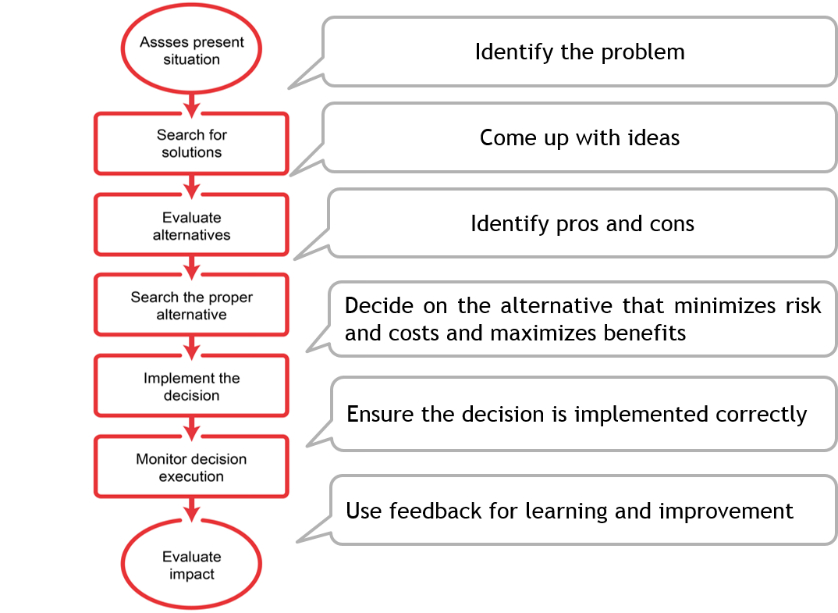
How do you evaluate alternatives in a group?
Before evaluating alternatives, the group needs to first establish criteria for judging solutions. The criteria should define general characteristics that a solution should have. One way to help members develop criteria is to ask them to complete sentences that naturally lead to identifying criteria.
Why is it important to solve a problem before evaluating alternatives?
It is important at this stage to solve a problem that requires some very creative thinking and innovative ideas. Before evaluating alternatives, the group needs to first establish criteria for judging solutions. The criteria should define general characteristics that a solution should have.
Do you need to evaluate alternatives to make a decision?
But if you need a decision, then you first need to find a valid way of comparing your alternatives. Note that evaluating alternatives is another opportunity to engage with your stakeholders. While this could be formal meetings, it could also be over a coffee with some of the stakeholders to gain their insight.

Why we should evaluate alternatives?
Why? Frequently, unimplementable or extreme alternatives are evaluated along with workable alternatives to show why they won't work and to find some component or compromise that will work. In our search for the most desirable alternative, an analysis of trade-offs among competing needs and solutions is essential.
How do consumers evaluate alternatives?
Generally, consumers evaluate the alternatives based on a number of attributes of the product. Looks, durability, quality, price, service, popularity, brand, social media reviews are some of the factors that consumers consider. The market offers many products that can solve the problem of a consumer.
How do you identify alternatives?
The obvious way to identify alternatives is brainstorming. This can be the classic 'get everyone in a room' method, or it could be a simple chat with a colleague. The usual brainstorming is to be completely open, or it can be bounded towards the alternatives required.
What does it mean to evaluate an alternative?
Evaluate alternatives by examining the benefits and drawbacks of each alternative. During the evaluation of alternatives, careful consideration is given to social, economic, and ecological factors that influence the predicted outcome. Encourage discussion and use visual aids to help explain alternatives.
What are the 3 techniques in selecting alternative?
Experience, experimentation, and research and analysis are the three common tools or approaches for choosing the best alternative in decision making.
What is the key to a good assessment of alternative solutions?
The key to a good assessment of the alternatives is to define he opportunity or threat exactly and then specify the criteria that should influence the selection of alternatives for responding to the problem or opportunity.
How do you evaluate alternatives in a case study?
Evaluation of Alternatives Each alternative must be compared to each criteria and its suitability ranked in some way, such as met/not met, or in relation to the other alternatives, such as better than, or highest. This will be important to selecting an alternative.
How do you analyze alternatives examples?
Alternatives analysis is the process of achieving the same outcome through different means or ways. For example, if we re-deploy resources from a task with float to another task with zero float to crash that task, there is a possibility of controlling delays. At the same time, there are risks associated with it.
How do you write an alternative analysis?
Step 1 Plan: Determine the goals, schedule, stakeholders, funding, team, and deliverables. Step 2 Establish analysis foundation: Determine the problem and scope being addressed and the ground rules and assumptions. Step 3 Identify and Define Alternatives: Identify the alternatives to the problem set.
How do customers evaluate goods?
Search Attributes Physical goods tend to emphasize those attributes that allow customers to evaluate a product before purchasing it. Features like style, color, texture, taste, and sound allow prospective consumers to try out, taste test, or "test drive" the product prior to purchase.
What does evaluation of alternatives mean in marketing?
the stage in the buying decision process in which the buyer uses information gathered to make a final choice between the products in the evoked set.
How do you offer alternatives to customers?
There are many ways you can say no to clients and still hope to retain their benevolence.Understand the Root Cause of Problems.Listen First and Then Reply.Explain Things in Detail.Frame Your Response Carefully.Be Empathetic.Offer the Alternatives.Avoid Standard Responses.Seek Customer Feedback.More items...•
How do you analyze alternative decision making?
Analyze alternatives: Assess each option against the criteria set up. Compare alternatives: Decide what the relative advantages of the various solutions are as revealed by the analysis. Report results: Record the results that are supportive of the needs of the decision-maker or stakeholder.
How can mind mapping help evaluate alternatives?
Start by writing the alternative in the center of the page. In this example it’s buying a new piece of equipment. The next level of branches is each category to consider. It could be a budget, or a list of requirements, ROI, daily operation, and so on.
How do you go about choosing the right solution?
It’s a good idea to look at the same idea in different ways — visually, quantifiably, even checking in with your gut instinct — this helps you evaluate alternatives. Consider using all styles, not just one. Using a variety of tools helps engage different parts of the brain and see alternatives in different ways to get a holistic view.
How to get out of irrational behavior?
The way out of this irrational behaviour is to take a more scientific approach, and try to be more objective.
What does "cut back the options" mean?
Cut back the options. More options means more attention, more short-term memory usage and more multitasking between different evaluation methods. Attention and will power are both exhaustible resources, and too many options can be quite draining – possibly leading to analysis paralysis.
Can you prove causation with quantitative data?
Quantitative data can prove correlation, but it can rarely prove causation.
Is qualitative data always disputable?
Qualitative data will always be disputable as it isn’t ‘hard data’ but it is often necessary in small sample sizes or when people are directly involved.
Is quantitative data compelling?
While quantitative data can be compelling, it won’t be the whole answer.
Is it better to find misunderstandings early?
It is better to find any misunderstandings early. Decisions are limited by assumptions. Without proper attention, humans tend to make poor assumptions, if we even realise we make them at all. Call out the assumptions to the team or in the document.
Can you compare apples with apples?
Comparisons can be complicated, as you are rarely comparing apples with apples. You will need to find ways to compare your alternatives. This can be done in a few different ways, and the choice of comparison can be as complicated as the original list of alternatives. But if you need a decision, then you first need to find a valid way ...
Why is it important to remember that evaluation matrices and voting by dots are simple tools to help the group make?
It is important to remember that evaluation matrices and voting by dots are simple tools to help the group make better decisions and to make collective judgment about the selected solution or idea.
What should a group focus on?
Group members should focus only on those criteria that are needed or desired to solve the problem. Weighing the solutions against criteria can be done with various degrees of structure. For each solution, each member assigns a score to each criterion based on the extent to which that solution meets the criterion.
How to evaluate alternatives?
The methods or techniques for the evaluation of alternatives are:- 1 Marginal Analysis : To evaluate alternatives, a manager may use the marginal analysis technique. The marginal analysis technique helps to compare additional revenues with additional costs. If the additional revenue is greater than the additional costs, more profit can be made by producing more. However, if the additional revenue is less than the additional costs, more profit can be made by producing less. 2 Cost Effectiveness Analysis : This technique is an improvement of the traditional marginal analysis. In this case, the manager considers the cost-benefit analysis. The alternative that provides the maximum benefits at the minimum cost is selected. The cost can be measured in terms of money, time, risk, goodwill, etc. The main feature of cost effectiveness analysis is that it gives importance to the results.
What are the methods of evaluation of alternatives?
Techniques for Evaluation of Alternatives. The methods or techniques for the evaluation of alternatives are:-. Marginal Analysis : To evaluate alternatives, a manager may use the marginal analysis technique. The marginal analysis technique helps to compare additional revenues with additional costs.
What is cost effectiveness analysis?
Cost Effectiveness Analysis : This technique is an improvement of the traditional marginal analysis. In this case, the manager considers the cost-benefit analysis. The alternative that provides the maximum benefits at the minimum cost is selected. The cost can be measured in terms of money, time, risk, goodwill, etc. The main feature of cost effectiveness analysis is that it gives importance to the results.
Why is evaluation required?
Evaluation is required in order to select the best alternative for implementation. Image Credits © Delios. While evaluating alternatives, the managers must compare the alternative plans or decisions. For this, the manager must consider the quantitative and qualitative factors. Quantitative Factors : The quantitative factors are those factors ...
What are quantitative factors?
Quantitative Factors : The quantitative factors are those factors that can be measured numerically. For e.g. Number of units sold, costs in rupees, etc. The quantitative factors are tangible in nature.
What is an alternative to a decision?
An alternative is a set of actions providing a comprehensive approach to the decision problem
What is value-focused alternatives?
By the time alternatives are presented to decision makers, they should be: Value-Focused, meaning that they are explicitly designed to address the fundamental values or ends of the decision – the “things that matter” or “felt needs”, as defined by the objectives and the evaluation criteria;
What is a range of creative policy or management alternatives designed to address the objectives?
A range of creative policy or management alternatives designed to address the objectives is developed. Alternatives should reflect substantially different approaches to the problem or different priorities across objectives, and should present decision makers with real options and choices. Good solutions are not possible without good alternatives.
What is the purpose of generating good alternatives?
Generating good alternatives is a source of important insights both from a technical perspective and a values perspective. Most often, an alternative is not a single action, but a set of actions – a ‘portfolio’ , “strategy”, or ‘package’ of individual elements that together provide a comprehensive approach to the decision situation.
Is it possible to have good alternatives?
Good solutions are not possible without good alternatives. Yet we often move to a single solution, without truly exploring distinct and creative alternatives. Technical teams take on the task of delivering “recommendations” to decision makers. But often these recommendations encompass value judgments that are better made by decision makers. Usually, what decision makers need is good information about a small, carefully thought out set of alternatives – their consequences, key differences (trade-offs) in their consequences, and the response of key stakeholders with respect to these trade-offs. Generating good alternatives is a source of important insights both from a technical perspective and a values perspective.
What happens when prospective buyers determine their needs?
Once prospective buyers determine their needs and complete an information search, they may have several alternative solutions they feel meet their identified needs, even if they have failed to fully define the problem. Indeed, during their information search, they probably ran across enough information about the problem itself to begin evaluating the alternatives, before they ever contact your company.
Do you have access to the same research buyers?
You have access to the same research buyers do, but you have an additional font of knowledge: Data drawn from your website analytics, completed forms, resource downloads, email analytics, and other interactions that takes place online both before and during the time you are engaged with a prospect.
