You can read the direction/azimuth on the outer edge of the chart. North is 000, East is 90°, South is 180°, West is 270° and then of course you get every 10 dgerees in between. To find the azimuth of the sun, draw a line from the center to the outer edge of the chart, going directly through the sun position you marked.
Full Answer
How do you measure the azimuth of the sun?
3:144:41HOW TO MEASURE SOLAR ANGLES | DEFINITIONS - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe azimuth angle is like a compass direction with North equals zero degrees and South equals 180MoreThe azimuth angle is like a compass direction with North equals zero degrees and South equals 180 degrees the angle practically is measured clockwise from due north.
What is the azimuth of the sun?
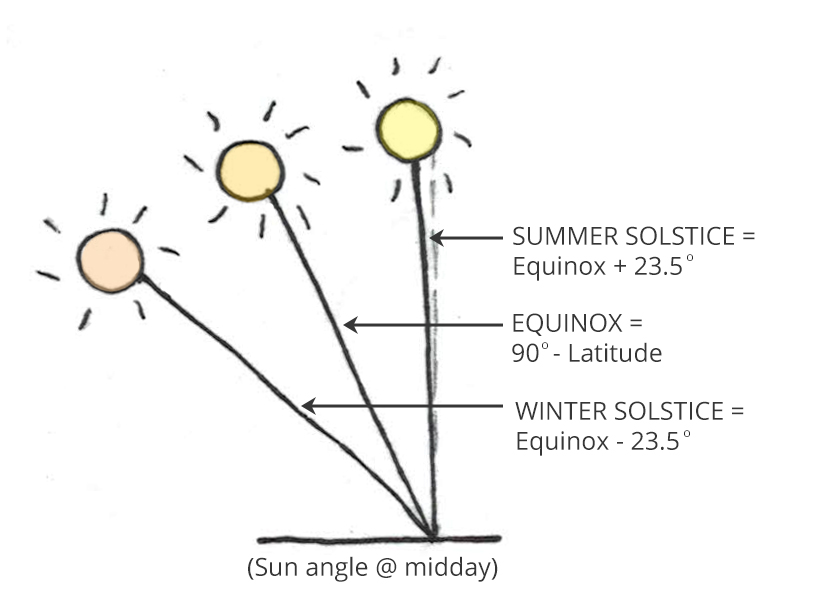
At the equinoxes, the sun rises directly east and sets directly west regardless of the latitude, thus making the azimuth angles 90° at sunrise and 270° at sunset.
What is the formula of azimuth?
Most noteworthy, one must make use of the following formula for the purpose of azimuth calculation to the west: Z = 360 – d, where “Z” is the azimuth one intends to find, and “d” is the distance in the form of degrees from due north.
What is sun elevation and azimuth?
The solar azimuth angle is the azimuth angle of the Sun's position. This horizontal coordinate defines the Sun's relative direction along the local horizon, whereas the solar zenith angle (or its complementary angle solar elevation) defines the Sun's apparent altitude.
What is an example of an azimuth?
What's the azimuth? The azimuth is the angle between North, measured clockwise around the observer's horizon, and a celestial body (sun, moon). It determines the direction of the celestial body. For example, a celestial body due North has an azimuth of 0º, one due East 90º, one due South 180º and one due West 270º.
Why does the azimuth of the sun change?
Why does the azimuth of the sunrise position change over the course of the year? The reason is the tilt of Earth's axis of rotation with respect to the orbital plane. As you know, the axis of rotation is tilted by an angle of 23.5 degrees with respect to the plane in which all the planets go around the Sun.
How do you find the azimuth of a star?
10:3511:44Celestial Navigation: How to find the azimuth of a star - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo you do 180 degrees minus the angle and South something West would be a hundred and eighty twoMoreSo you do 180 degrees minus the angle and South something West would be a hundred and eighty two degrees plus the angle.
How do you find the coordinates of azimuth?
You can calculate the azimuth between the points (ϕ₁, λ₁) and (ϕ₂ λ₂), where ϕ is the latitude and λ longitude, as follows: Compute x = sinΔλ × cosϕ₂, where Δλ = λ₂ - λ₁ is the difference in longitudes.
How do you convert an azimuth?
4:317:24SMCT: Convert Azimuths and Compute Back Azimuths - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSubtract an easterly GM angle from the original grid asmath to convert to a magnetic asmath. Add aMoreSubtract an easterly GM angle from the original grid asmath to convert to a magnetic asmath. Add a westerly GM angle to the original grid asmath to convert to a magnetic azimuth. In this example the
What is the another name of azimuth?
the angle of the imaginary line between the position of a plane, ship etc and the position of another object. Synonyms and related words. Angles. acute angle. adjacent angles.
What is the azimuth of the moon?
82.8°PositionAzimuth82.8° (E)Right ascension7h 2m 39sDeclination26° 53' 52"Range404,540 km2 more rows
Is azimuth the same as longitude?
For the equivalent of longitude, the Horizontal System uses azimuth. Azimuth is the East to West Coordinate, with 0 degrees of azimuth at North, 180 degree at South, etc. The latitude equivalent is altitude. The horizon and the observer's zenith define 0 degrees and 90 degrees of altitude, respectively.
What is the best azimuth for solar panels?
Since solar panels are more productive when the sun's rays are perpendicular to their surfaces, the certainly best orientation is the one directly true SOUTH (azimuth angle = 180 °).
What is true azimuth?
The angle at the zenith measured clock-wise from true north to the vertical circle passing through the body.
What is azimuth in astronomy?
Azimuth is the number of degrees clockwise from due north (usually) to the object's vertical circle (i.e., a great circle through the object and the zenith).
What is the another name of azimuth?
the angle of the imaginary line between the position of a plane, ship etc and the position of another object. Synonyms and related words. Angles. acute angle. adjacent angles.
What is azimuth in math?
The azimuth is the angle between the spot where that line crosses the horizon and the reference direction. If true north is used as reference, it is represented by an azimuth of 0°, and angle values increase towards the east. This means, for example, that an azimuth of 180° means due south.
What is the azimuth of a reference?
Imagine a vertical line connecting the object with the horizon. The azimuth is the angle between the spot where that line crosses the horizon and the reference direction. If true north is used as reference, it is represented by an azimuth of 0°, and angle values increase towards the east. This means, for example, that an azimuth of 180° means due south.
What coordinate system is used to find objects in the sky?
Just as the geographic coordinate system uses latitude and longitude to define any location on Earth, the horizontal coordinate system provides altitude and azimuth angles to locate objects in the sky.
What is the invisible part of the sky called?
In effect, the system also includes the invisible half of the sky that is below the horizon. The dome above you is called the upper hemisphere and the invisible part of the sky below you is the lower hemisphere. Together, they form the celestial sphere, an imaginary globe surrounding you, with you at its center.
What is the horizontal coordinate system?
The horizontal coordinate system, also known as the Alt/Az system, is a method for describing the exact position of objects in the sky, such as planets, the Sun, or the Moon. Illustration 1: The upper hemisphere of the celestial sphere. This system is also used by timeanddate.com to describe the positions of the Sun, the Moon, ...
What is azimuth in illustration 3?
Illustration 3: The azimuth refers to the object's cardinal direction.
What is the angle of an object that touches the horizon?
Altitude or elevation: The angle the object makes with the horizon. Objects that seem to touch the horizon have an altitude of 0° , while those straight above you are at 90° (see illustration 2). Anything below the horizon has a negative angle, with -90° describing a location straight down.

Distance Irrelevant
The Celestial Sphere
- Imagine the sky as a dome towering above you, its edges resting on the horizon. This is the backdrop the horizontal coordinate system uses to map the sky and describe the positions of its objects. To compare, the geographic coordinate systemuses the Earth's surface as a backdrop to determine a position. In effect, the system also includes the invisible half of the sky that is belo…
The Celestial Horizon
- The horizontal line separating the two hemispheres is called the celestial horizon. It is a continuation into space of the imaginary plane created between you and the horizon around you. If the Earth were flat, the celestial horizon would follow the terrestrial plane. However, since we are living on a globe, it is defined as the imaginary plane perpendicular to the direction of gravity …
Altitude and Azimuth
- Just as the geographic coordinate system uses latitude and longitude to define any location on Earth, the horizontal coordinate system provides altitude and azimuth angles to locate objects in the sky. 1. Altitude or elevation: The angle the object makes with the horizon. Objects that seem to touch the horizon have an altitude of 0°, while those st...
Depends on Location and Time
- The horizontal coordinate system owes its name to the fact that it is based upon the observer's horizon. As the horizon's limits – and, therefore, the portion of the sky you see – depends on your location, an object's altitude and azimuth angles shift as you move to a different spot on the Earth's surface. What's more, most celestial objects move across the sky, so their coordinates c…
Doesn't Work at The Poles
- While the horizontal coordinate system provides an easy way to define a location in the sky at almost any location on Earth, it is not possible to define an azimuth at the North Pole or the South Pole, rendering the system useless there. At the North Pole, for example, it is easy to find the Polaris, the North Star. It is very close to the zenith position, so you have to look straight up to se…