What are the tools used to identify the CCP?
There are at least two established ways in the food industry to identify CCPs - using a decision tree and a hazard or risk assessment matrix.
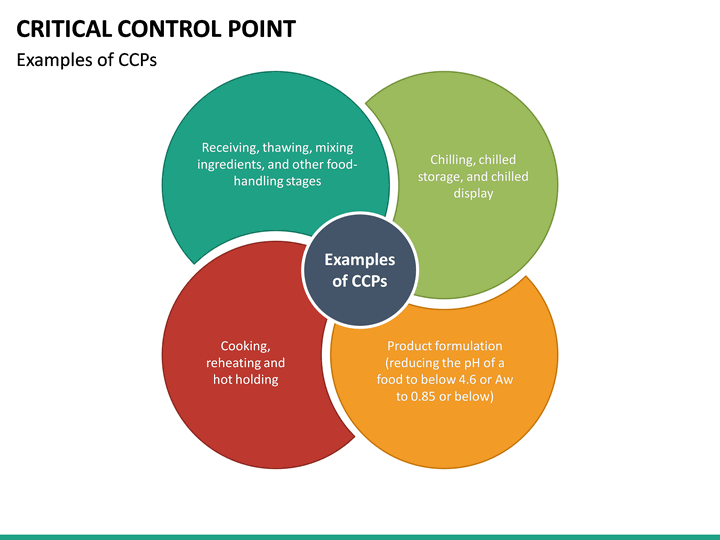
What are the most common CCPs?
It is a point, step or procedure at which controls can be applied and a food safety hazard can be prevented, eliminated or reduced to acceptable (critical) levels. The most common CCP is cooking, where food safety managers designate critical limits.
What are the 9 critical control points?
Critical control point decision treesfood ingredients and packaging.food and beverage suppliers.policies and procedures.equipment and preparation surfaces.food safety training programs.number of Food Safety Supervisors in the business.physical layout of the premises.
What are the 7 critical control points in HACCP?
Seven basic principles are employed in the development of HACCP plans that meet the stated goal. These principles include hazard analysis, CCP identification, establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification procedures, and record-keeping and documentation.
What is an example of a CCP?
Critical control points are located at any step where hazards can be either prevented, eliminated, or reduced to acceptable levels. Examples of CCPs may include: thermal processing, chilling, testing ingredients for chemical residues, product formulation control, and testing product for metal contaminants.
Why is CCP important?
Critical Control Point (CCP): A step at which control can be applied and is essential to prevent or eliminate a food safety hazard or reduce it to an acceptable level.
What is the difference between CP and CCP?
A CCP is different from a CP (Figure 3). A CCP indicates a high food safety risk (likely to occur) and a CP indicates a low food safety risk (not likely to occur). Food safety relies on identification and control of CCP's, while, CP's may be used for quality specifications.
Is cold storage a CCP?
#1 Cold storage. For example, if you offer raw meat to your customers, cold storage immediately becomes a CCP. The principle behind using cold storage for storing and transporting fresh or raw products is that at low food temperatures, all biological processes are slowed down or even stopped.
What is the first HACCP step?
1. Conduct a hazard analysis. The first step in any Food Safety Plan (or HACCP Plan) is to identify all possible food safety hazards that could occur in your business.
How would you determine a critical limit in the HACCP process?
Principle 3: Establish Critical Limits The critical limit is usually a measure such as time, temperature, water activity (aw), pH, weight, or some other measure that is based on scientific literature and/or regulatory standards.
How do you write a Haccp plan?
The 7 steps of writing the HACCP Plan are: Build a monitoring procedure system for CCPs. Identify corrective action procedures. Establish verification procedures. Record-keeping and documentation.
What are the 7 steps of HACCP in order?
These 7 HACCP principles include 1) hazard analysis, 2) critical control points, establishing 3) critical limits, 4) monitoring procedures, 5) corrective actions, 6) verification procedures, and 7) documentation and record-keeping procedures.
How many types of CCP are there?
8 critical control point examples to include in your HACCP system. In brief, here are the 8 recommended critical control points you need to manage in your HACCP system.
How many critical control points Dnata have?
It is vital that dnata Catering adhere to food safety standards and take all the necessary steps to ensure the food produced is safe to eat. In this course we will be looking at 8 CCPs and 3 CPs that we follow at dnata. This course is mandatory and designed for all employees in the dnata catering business.
What is an example of a critical limit in a HACCP plan?
Procedural critical limits For example: The critical limits for controlling Salmonella in chicken pieces at the cooking step (CCP) could be 70°C for 2 minutes. Both the time and temperature are critical limits and must both be achieved.
Is sieving a CCP?
Sieving is a CCP, I would argue for the #C15 dry powder FBOs. Specially if it is the most robust way of foreign body elimination. It could also be a CCP in other categories like #C12 and #C13, where it is filtration.
What is a critical control point?
By definition of the FDA, a critical control point is any manufacturing step where control can be applied for the prevention or elimination of any potential food safety hazard. Significant focus is placed on a critical control point along your food production process. A breach or loss of control of the established parameters for this critical control point can cause adverse public health issues.
What is the first step to understanding a critical control point in food preparation?
The first step to understanding a critical control point in food preparation is knowing that control measures are categorized according to their nature, relationship to the process, and the level of risk to the consumer should the measure fail.
What are control measures?
A control measure is an action or an activity that can minimize or eliminate an identified hazard or reduce its likelihood of occurrence to an acceptable level. In other words, a control measure is any action, step, task, process, or procedure intended to address a food safety hazard. The term control measure is used because not all hazards can be prevented, but all of them can be effectively controlled.
What is the difference between CP, CCP, PRP, and oPRP?
In a HACCP food safety plan, other terminologies such as control point, prerequisite programs, and operational prerequisite programs may come up. To sort out any possible confusion surrounding these terms, let’s look into four main terms that you will come across when determining control measures and any critical control point for food safety.
Why is it important to document all critical control points?
You need to carefully develop and document all your critical control points because accurately identified CCPs are fundamental to controlling food safety hazards. An accurate record of established CCPs is also one of the 7 HACCP principles, and is essential for establishing a food safety management system when compiling your HACCP food safety programs.
Why is a critical control point considered a CCP?
A method is considered as a CCP if there is no other subsequent step that will minimize or eliminate the hazard present in the product. This means that the process must be successfully executed. A series of factors are considered before a process step is considered as a critical control point. This is why it is helpful to use a risk matrix or a decision tree to identify the risk level of each step of the process.
What is a control point?
Control Point (CP): Any step where any biological, chemical, and physical factors can be controlled. This term is generally used for processes that may or may not be critical in eliminating hazards, but contribute to their prevention and reduction. An example of a control point may be prewashing potatoes to eliminate physical hazards prior to blanching which serves a different purpose.
What is a control measure?
Control Measure: Any action or activity that can be used to prevent, eliminate or reduce a significant hazard.
Why is the term "control measure" used in hazard analysis?
The term control measure is used because not all hazards can be prevented, but virtually all can be controlled.
How to implement HACCP?
Initially, the HACCP coordinator and team are selected and trained as necessary. The team is then responsible for developing the initial plan and coordinating its implementation. Product teams can be appointed to develop HACCP plans for specific products. An important aspect in developing these teams is to assure that they have appropriate training. The workers who will be responsible for monitoring need to be adequately trained. Upon completion of the HACCP plan, operator procedures, forms and procedures for monitoring and corrective action are developed. Often it is a good idea to develop a timeline for the activities involved in the initial implementation of the HACCP plan. Implementation of the HACCP system involves the continual application of the monitoring, record-keeping, corrective action procedures and other activities as described in the HACCP plan.
What is a CCP decision tree?
CCP Decision Tree: A sequence of questions to assist in determining whether a control point is a CCP.
How many principles are there in HACCP?
Food safety systems based on the HACCP principles have been successfully applied in food processing plants, retail food stores, and food service operations. The seven principles of HACCP have been universally accepted by government agencies, trade associations and the food industry around the world.
What is the National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Criteria for Foods?
The National Advisory Committee on Microbiological Criteria for Foods (NACMCF) is an advisory committee chartered under the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) and comprised of participants from the USDA (Food Safety and Inspection Service), Department of Health and Human Services (U.S. Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention) the Department of Commerce (National Marine Fisheries Service), the Department of Defense (Office of the Army Surgeon General), academia, industry and state employees. NACMCF provides guidance and recommendations to the Secretary of Agriculture and the Secretary of Health and Human Services regarding the microbiological safety of foods.
