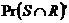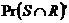
The probability of the union of any number of sets can be found as follows:
- Add the probabilities of the individual events.
- Subtract the probabilities of the intersections of every pair of events.
- Add the probabilities of the intersection of every set of three events.
- Subtract the probabilities of the intersection of every set of four events.
How do you find the probability of intersection of events?
Probability of the intersection of events. To calculate the probability of the intersection of events, we first have to verify whether they are dependent or independent. The probability of the intersection of independent events is: P ( A ∩ B) = P ( A) ⋅ P ( B)
How do you find the probability of a Union of events?
Only then is the probability of the union equal to the sum of probabilities of the event. P (A ∪ B) = P (A) + P (B) Otherwise if the events are not disjoint (ie they have common outcomes) then we would be over measuring and must exclude the measure of the intersection. P (A ∪ B) = P (A) + P (B) − P (A ∩ B)
How to calculate the Union and intersection of events?
Unions and intersections are sets so are not calculated but at most determined. I guess you are talking about the probabilities of sets/events. Without any further info (e.g. independence or mutually disjointness) you cannot calculate the probability of union and intersection of events purely on base of the probabilities of the events.
When to exclude the measure of the intersection of two events?
Only then is the probability of the union equal to the sum of probabilities of the event. Otherwise if the events are not disjoint (ie they have common outcomes) then we would be over measuring and must exclude the measure of the intersection. When dealing with more than two events, the principle of inclusion and exclusion is required

What is the difference between intersection and union?
If it is, it means Union. If it does not, it means intersection. To remember what words go with the symbols, I think of the way the U is facing aswell.
What is mathematics in the real world?
that picture is not truth... it just feels truth-like to you. Mathematics is a set of tools and techniques that helps us model the truth of the real world in different, sometimes more useful ways.
Is everything all together a union?
So basically numbers in both sets would be an intersection and everything all together is a union.
What is the symbol for an element in the intersection of two sets?
An element is in the intersection of two sets if it is in the first set and it is in the second set. The symbol we use for the intersection is ∩. The word that you will often see that indicates an intersection is "and".
What is the symbol for a union?
Unions. An element is in the union of two sets if it is in the first set, the second set, or both. The symbol we use for the union is ∪. The word that you will often see that indicates a union is "or".
What is intersection of events?
Definition: intersections. The intersection of events A and B, denoted A ∩ B, is the collection of all outcomes that are elements of both of the sets A and B. It corresponds to combining descriptions of the two events using the word “and.”.
What is the probability sought?
The probability sought is P(M ∩ T). The table shows that there are 2 such people, out of 28 in all, hence P(M ∩ T) = 2 / 28 ≈ 0.07 or about a 7% chance.
How to identify outcomes in a tree diagram?
Think of using a tree diagram to do so. There are two choices for the first toss. For each of these there are two choices for the second toss, hence 2 × 2 = 4 outcomes for two tosses. For each of these four outcomes, there are two possibilities for the third toss, hence 4 × 2 = 8 outcomes for three tosses. Similarly, there are 8 × 2 = 16 outcomes for four tosses and finally 16 × 2 = 32 outcomes for five tosses.
What is the union of events?
The union of events A and B, denoted A ∪ B, is the collection of all outcomes that are elements of one or the other of the sets A and B, or of both of them. It corresponds to combining descriptions of the two events using the word “or.”.
What does it mean when a volunteer is selected at random?
A volunteer is selected at random, meaning that each one has an equal chance of being chosen. Find the probability that:
How many times can you list an outcome as 4?
Note that an outcome such as 4 that is in both sets is still listed only once (although strictly speaking it is not incorrect to list it twice).
Can events be expressed in terms of other events?
Some events can be naturally expressed in terms of other, sometimes simpler, events.
How to understand probability?
In my experience, the key to understanding ANY kind of probability is understanding the "allowable" sample space. When first defining the idea of probability, the books usually call the sample space Ω. They then draw a Venn Diagram and tell you that the "whole box" represents Ω. Inside the box they draw another set, A (called an event). You observe that part of Ω is in common with A and part of it isn't. In other words, if an element of Ω happens, it's possible that A also happens, but it's also possible that A didn't happen. The larger that A is, the larger the likelihood is that whatever point is chosen in Ω also happens to be in A. That's the "picture" of the probability of A -- how big is A compared to the whole box, Ω.
Is a union a set?
Unions and intersections are sets so are not calculated but at most determined. I guess you are talking about the probabilities of sets/events.
How to find probability of intersection of two independent events?
We can find the probability of the intersection of two independent events as, P (A∩B) = P (A) × P (B), where, P (A) is Probability of an event “A” and P (B) = Probability of an event “B” and P (A∩B) is Probability of both independent events “A” and "B" happening together.
How to find probability of two events?
We apply P (A ∩ B) formula to calculate the probability of two independent events A and B occurring together. It is given as, P (A∩B) = P (A) × P (B), where, P (A) is Probability of an event “A” and P (B) = Probability of an event “B”.
What is the probability of getting a red card from a deck of 52 cards?
The probability of getting a red card from a deck of 52 cards, P (A) = 26/52
What is the intersection of two or more sets?
The intersection of two or more two sets is the set of elements that are common to every set. When events are independent, we can use the multiplication rule, which states that the two events A and B are independent if the occurrence of one event does not change the probability of the other event.
What Is P (A∩B) Formula?
P (A∩B) is the probability of both independent events “A” and "B" happening together. This formula is used to quickly predict the result. P (A∩B) formula can be written as P (A∩B) = P (A) × P (B). P (A∩B) formula is given as: