How to Calculate the True Population Proportion
- 1 Divide the number Divide the number of people in the sample population who have the characteristic being tested by the total number of people in the sample to get the sample proportion.
- 2 Subtract the sample proportion from one ...
- 3 Take the square root ...
- 4 Multiply the result by 1.96 ...
- 5 Subtract the result ...
What are four ways to determining population size?
- Uniform dispersion. In uniform dispersion, individuals of a population are spaced more or less evenly. ...
- Random dispersion. In random dispersion, individuals are distributed randomly, without a predictable pattern. ...
- Clumped dispersion. In a clumped dispersion, individuals are clustered in groups. ...
How do you estimate population proportion?
How do you calculate proportion in research? Formula Review p′ = x / n where x represents the number of successes and n represents the sample size. The variable p′ is the sample proportion and serves as the point estimate for the true population proportion.
What are some ways to estimate population?
- More accurate estimates can generally be made for an entire country than for geographic sub-divisions of a country. ...
- More accurate estimates and projections can generally be made for the total population of an area than for the demographic characteristics of the population. ...
- Direct data are preferred to indirect data. ...
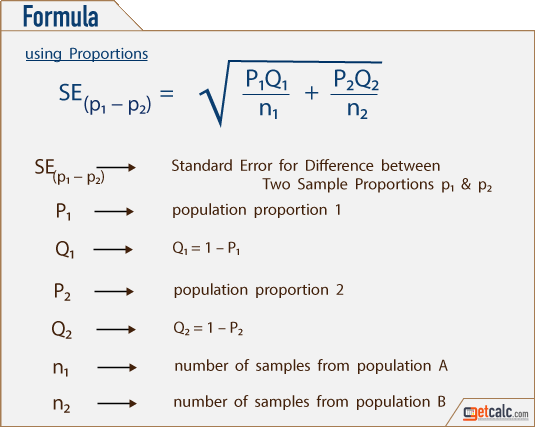
What is the formula for population proportion?
z= (p−P)σ where P is the hypothesized value of population proportion in the null hypothesis, p is the sample proportion, and σ is the standard deviation of the sampling distribution. Click to see full answer. Likewise, people ask, what is the formula for a one sample z interval for a population proportion?
How do you determine sample proportion?
Formally, the sample proportion formula is given by: ^p=xn, p ^ = x n , where ^p —pronounced p -hat—is the sample proportion, x is the number of successes in the sample, and n is the size of the sample.
What is the population proportion in statistics?
A part of a population with a particular attribute, expressed as a fraction, decimal or percentage of the whole population. For a finite population, the population proportion is the number of members in the population with a particular attribute divided by the number of members in the population.
How do you find the population proportion on a calculator?
How to calculate a population proportion?First, determine the characteristic or parameter to be analyzed. ... Next, measure the total number of people that have that characteristic. ... Next, determine the total population. ... Finally, calculate the population proportion using the formula: P = 500/1000 = .
Is the population proportion equal to the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion?
Group of answer choices The population proportion is equal to the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion. If you increase your sample size, the mean of the sampling distribution of the proportion will get closer to the population proportion.
What do you do if the population proportion is unknown?
If the proportion of the population (p) is unknown use p = 0.5 which assumes maximum heterogeneity (i.e. a 50/50 split). The degree of precision (d) is the margin of error that is acceptable.
How do you find the proportion of a population with mean and standard deviation?
This is given by the formula Z=(X-m)/s where Z is the z-score, X is the value you are using, m is the population mean and s is the standard deviation of the population. Consult a unit normal table to find the proportion of the area under the normal curve falling to the side of your value.
How do you calculate a population proportion with a 95 confidence interval?
To calculate the confidence interval, we must find p′, q′. p′ = 0.842 is the sample proportion; this is the point estimate of the population proportion. Since the requested confidence level is CL = 0.95, then α = 1 – CL = 1 – 0.95 = 0.05 ( α 2 ) ( α 2 ) = 0.025.
What is the formula for population size?
The population size estimate is obtained by dividing the number of individuals receiving a service or the number of unique objects distributed (M) by the proportion of individuals in a representative survey who report receipt of the service or object (P).
How do you calculate sample size without population?
For sample size calculation of unknown population size, you can use the following formula: n= z2. [p*q]/d2), which is used to calculate the sample size of a qualitative variable in prevalence or cross-sectional studies.
How do you find the mean of the sampling distribution of the sample proportion?
The mean of our sampling distribution of our sample proportion is just going to be equal to the mean of our random variable X divided by n.
Which is the correct formula for the mean of the sampling distribution of a sample proportion?
The Sampling Distribution of the Sample Proportion. For large samples, the sample proportion is approximately normally distributed, with mean μˆP=p. and standard deviation σˆP=√pqn.
How do you find the mean and standard deviation of a sampling distribution?
For samples of any size drawn from a normally distributed population, the sample mean is normally distributed, with mean μX=μ and standard deviation σX=σ/√n, where n is the sample size.
Is population proportion The mean?
Each of these formulas is designed to answer a specific question: the mean proportion addresses the question about the average per person and the population proportion addresses the question of population intakes.
What is proportion formula?
The product of means in the ratio is equal to the product of extremes. Two ratios are said to be equal if their cross products are equal. The Proportion Formula is given as, a : b :: c : d ⇒ a b = c d.
How do you find the proportion in a frequency table?
To do this, divide the frequency by the total number of results and multiply by 100. In this case, the frequency of the first row is 1 and the total number of results is 10. The percentage would then be 10.0. The final column is Cumulative percentage.
Formula for a Population Proportion
A population proportion always ranges between 0 and 1 (or 0% to 100% in percentage terms) and it is calculated as follows:
How to Estimate a Population Proportion
Since it is usually too time-consuming and costly to collect data for every individual in a population, we often collect data for a sample instead.
Confidence Interval for a Population Proportion
Although the sample proportion provides us with an estimate of the true population proportion, there’s no guarantee that the sample proportion will exactly match the population proportion.
Example: Confidence Interval for a Population Proportion
Suppose we want to estimate the proportion of residents in a city that are in favor of a certain law. We select a random sample of 100 residents and ask them about their stance on the law. Here are the results:
How many statistical inference methods are there?
There are two major statistical inference methods:
How to calculate interval estimates?
Most interval estimates can be calculated as the sample statistic plus or minus the margin of error.
What percentage of smokers fall inside the interval?
It doesn’t say that the percentage of smokers in the state have a 90% chance of falling inside the interval. Rather, 90% of all interval estimates will capture or contain the true percentage of smokers.
What is statistical inference?
There are two major statistical inference methods: Confidence Intervals .
Why do we assume 95% confidence interval?
Note, if you aren’t given a confidence interval, then we always assume 95% confidence because it is considered a conservative estimation. Please note that a confidence interval is not a probability interval. It doesn’t say that the percentage of smokers in the state have a 90% chance of falling inside the interval.
How to find the Z score of a normal distribution?
If P ′ ∼N P ′ ∼ N (p, √pq n p q n ) then the z -score formula is z = p′ −p √pqn p ′ − p p q n
What percentage of confidence intervals contain the true value for the population percent of students that are registered voters?
Ninety percent of all confidence intervals constructed in this way contain the true value for the population percent of students that are registered voters.
What is the confidence interval for a larger sample?
The confidence interval for the larger sample is narrower than the interval from Example 6. Larger samples will always yield more precise confidence intervals than smaller samples. The “plus four” method has a greater impact on the smaller sample. It shifts the point estimate from 0.26 (13/50) to 0.278 (15/54). It has a smaller impact on the EPB, changing it from 0.102 to 0.100. In the larger sample, the point estimate undergoes a smaller shift: from 0.270 (159/588) to 0.272 (161/592). It is easy to see that the plus-four method has the greatest impact on smaller samples.
What is the confidence interval for a poll?
Often, election polls are calculated with 95% confidence, so, the pollsters would be 95% confident that the true proportion of voters who favored the candidate would be between 0.37 and 0.43: (0.40 – 0.03,0.40 + 0.03).
Why do we use point estimates for confidence intervals?
Because we do not know the true proportion for the population, we are forced to use point estimates to calculate the appropriate standard deviation of the sampling distribution. Studies have shown that the resulting estimation of the standard deviation can be flawed.
Is a proportion a statistical measure?
Some statistical measures, like many survey questions, measure qualitative rather than quantitative data. In this case, the population parameter being estimated is a proportion. It is possible to create a confidence interval for the true population proportion following procedures similar to those used in creating confidence intervals for population means. The formulas are slightly different, but they follow the same reasoning.
What is significance testing for population proportions?
Significance testing for population proportions means we will test a claim about a population by looking at a sample and using a sample statistic.
What happens when the p-value is small?
If our p-value is small, we reject our null hypothesis and have significant evidence to conclude the alternative.
What is pooled variance?
Pooling variances, or pooled variances, means we will combine both variances to find an overall variance. In essence, we are going to assume that the variance of each population is the same.
Do schools have different proportions of students who receive free or reduced lunch?
Thus showing that there is no significant evidence to conclude that the proportions of students at the two schools who receive free or reduced lunch are different.
How to find sample proportion?
The formula for calculating the sample proportion is the number of occurences ( x) divided by the sample size ( n ):
What is population proportion?
A population proportion is the share of a population that belongs to a particular category.
How to find lower and upper bounds of confidence interval?
The lower and upper bounds of the confidence interval are found by subtracting and adding the margin of error ( E) from the point estimate ( p ^ ).
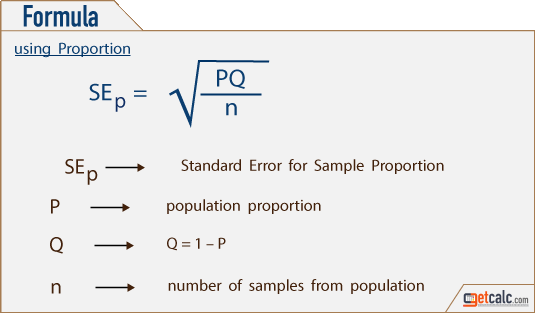
How to find standard error?
The standard error p ^ ( 1 − p ^) n is calculated from the point estimate ( p ^) and sample size ( n ).
What is the standard normal distribution used for?
We use the standard normal distribution to find the margin of error for the confidence interval.
What is the confidence level of 95%?
If we choose 95% as the confidence level, the α is 0.05.
What is the remaining probability of a 5% probability?
The remaining probability ( α) is then: 5%, or 1 - 0.95 = 0.05.
What is sample proportion?
The sample proportion is what you expect the results to be. This can often be determined by using the results from a previous survey, or by running a small pilot study. If you are unsure, use 50%, which is conservative and gives the largest sample size. Note that this sample size calculation uses the Normal approximation to the Binomial distribution. If, the sample proportion is close to 0 or 1 then this approximation is not valid and you need to consider an alternative sample size calculation method.
Can you be included in a sample if you don't respond?
Note that if some people choose not to respond they cannot be included in your sample and so if non-response is a possibility your sample size will have to be increased accordingly. In general, the higher the response rate the better the estimate, as non-response will often lead to biases in your estimate.
What is the probability of 0.0281?
Using a table of standard normal values with a z -value of z0 = -1.91 we find that the probability value is 0.0281. Using technology (which doesn’t do as much rounding as we do with our calculations), we find that the probability value is 0.0282691712.
When did Gallup polls show confidence in schools?
On June 1, 2005, the Gallup Organization ( www.gallup.com) released results of a poll in which 372 of 1004 adults aged 18 years or older stated that they had “a great deal” of confidence in public schools.
