
Follow these two steps to calculate your retained earnings:
- Subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets to get your stockholder equity.
- Find the common stock line item in your balance sheet. If the only two items in your stockholder equity are common stock and retained earnings, take the total stockholder equity and subtract the common stock line item figure. The difference is retained earnings.
What is the formula to calculate ending retained earnings?
To Calculate Ending Retained Earnings we can use the below formula: Ending RE = Beginning RE + Net Income (Profit or Loss) – Dividends i.e Ending RE = Beginning RE – Net Loss – Dividends
Why does the balance sheet show negative retained earnings?
The retained earnings account is adjusted every time a new entry is added to the income or expense account. If the net loss for the current period is higher than the retained earnings at the beginning of the period, those retained earnings on the balance sheet may become negative. This creates a deficit.
How to calculate retained earnings?
How to calculate retained earnings. The formula for calculating retained earnings is as follows: Retained earnings = Beginning retained earnings + Net income or loss - Dividends. For example, a company may begin an accounting period with $7,000 of retained earnings. These are the retained earnings that have carried over from the previous accounting period.
Is retained earnings a current liability?
Is Retained Earnings Current Non Current Liabilities? For accounting purposes, retained earnings are not regarded as a current asset. Assets are those that offer an economic benefit over a particular time period or over a certain distance. By retaining profits, companies are left with income after paying dividends.
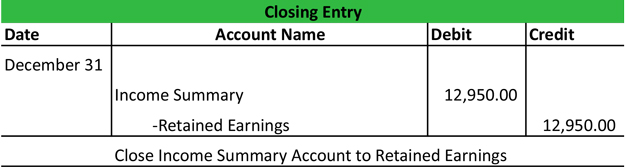
How do you calculate the retained earnings?
The retained earnings are calculated by adding net income to (or subtracting net losses from) the previous term's retained earnings and then subtracting any net dividend(s) paid to the shareholders. The figure is calculated at the end of each accounting period (monthly/quarterly/annually).
Is retained earnings a debit or credit on the trial balance?
credit balanceRetained earnings are an equity account and appear as a credit balance. Negative retained earnings, on the other hand, appear as a debit balance.
How do you find beginning retained earnings on an adjusted trial balance?
1:222:25How To Calculate Retained Earnings - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBeginning retained earnings plus net income minus dividends equals ending retained earnings.MoreBeginning retained earnings plus net income minus dividends equals ending retained earnings.
When a retained earnings has a debit balance it is called as?
If the balance in the Retained Earnings account has a debit balance, this negative amount of retained earnings may be described as deficit or accumulated deficit.
Are retained earnings Current liabilities?
Due to its definition, some people may confuse retained earnings for current liabilities or assets. However, retained earnings are an equity balance on the balance sheet.
What is the beginning balance of retained earnings?
Step 2: Calculate beginning retained earnings Your beginning retained earnings are simply the previous period's ending retained earnings. Retained earnings appear on the equity portion of the balance sheet (Assets = Liabilities + Equity).
What is an example of retained earnings?
Retained earnings are the cumulative profits that remain after a company pays dividends to its shareholders. These funds may be reinvested back into the business by, for example, purchasing new equipment or paying down debt.
Is retained earnings on the income statement?
How to find retained earnings. Retained earnings are shown in two places in your business' financial statements: On the bottom line of your Income Statement (also called the Profit and Loss Statement) In the shareholder's equity section of your Balance Sheet.
Does retained earnings go on the trial balance sheet?
Retained Earnings are listed on a balance sheet under the shareholder's equity section at the end of each accounting period. To calculate Retained Earnings, the beginning Retained Earnings balance is added to the net income or loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted.
What happens when you debit retained earnings?
The normal balance in the retained earnings account is a credit. This means that if you want to increase the retained earnings account, you will make a credit journal entry. A debit journal entry will decrease this account.
Is profit a debit or credit in retained earnings?
ExampleNet profitDebitTransferring net profit earned to retained earningsTo Retained EarningsCreditCredit the increase in the balance of retained earnings
Can retained earnings be negative?
When a company records a loss, this too is recorded in retained earnings. If the amount of the loss exceeds the amount of profit previously recorded in the retained earnings account as beginning retained earnings, then a company is said to have negative retained earnings.
What are retained earnings?
First things first: What are retained earnings? And maybe more importantly, why should I care?
How to calculate retained earnings
Now that we’re clear on what retained earnings are and why they’re important, let’s get into the math. To calculate your retained earnings, you’ll need three key pieces of information handy.
The retained earnings formula
Got all the numbers you need? It’s time to get out the calculator. Here’s the basic formula for calculating retained earnings:
Example of retained earnings calculation
Let’s take a look at an example of our formula in the real world. Malia owns a small bookstore and wants to bring on an investor to help expand the shop to multiple locations. The investor wants to know what retained earnings look like to date.
How much should my retained earnings be?
Good question! If you calculated along with us during the example above, you now know what your retained earnings are. But what does that number mean? Knowing financial amounts only means something when you know what they should be.
Are there any disadvantages of retained earnings calculations?
While understanding your retained earnings is important for business owners, and a requirement in many situations, it does have its drawbacks.
What is the purpose of Trial Balance?
A trial balance is a bookkeeping worksheet that compiles the totals of all ledgers into equal debit and credit account column totals. A company maintains a trial balance on a regular basis, usually at the end of each reporting period.
What are the rules for journaling and trial balance?
A trial balance is a collection of debit and credit balances obtained from various accounts in the ledger, including cash and bank balances from the cash book. The total of the debit and credit balances extracted from the ledger must be tallied in order to prepare a trial balance.
What are the three facets of retained earnings?
You can, however, keep track of retained earnings on a separate financial statement called the statement of retained earnings. Assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity are the three parts of the balance sheet.
What is the best way to tell if my trial balance is correct?
How to Locate and Correct Errors Retracing the trial balance steps is the simplest way to start.
Is the trial balance based on cash or credit?
Exhibit 2: A ledger T-account with cash on hand for several day transactions. Because cash on hand is an asset account, debits increase the balance while credits decrease it. As a result, this asset account is said to have a debit (DR) balance.
What happens to a complete trial balance?
The trial balance is a list of all accounts used by a company, including debit and credit balances. After the adjusting entries have been completed, the adjusted trial balance is complete. This trial balance contains all of the final accounts’ balances and is used to prepare financial statements.
Is it possible to use your retained earnings?
Retained earnings should increase the company’s value, as well as the value of the money you invest in it. If a company can use retained earnings to generate above-average returns, it should keep those earnings rather than paying them out to shareholders.
How to calculate retained earnings?
At the end of the period, you can calculate your final Retained Earnings balance for the balance sheet by taking the beginning period, adding any net income or net loss, and subtracting any dividends.
What is retained earnings?
Retained Earnings (RE) are the accumulated portion of a business’s profits that are not distributed as dividends to shareholders but instead are reserved for reinvestment back into the business. Normally, these funds are used for working capital and fixed asset purchases (capital expenditures) or allotted for paying off debt obligations.
How do dividends impact retained earnings?
How Dividends Impact Retained Earnings. Distribution of dividends to shareholders can be in the form of cash or stock. Both forms can reduce the value of RE for the business. Cash dividends represent a cash outflow and are recorded as reductions in the cash account. These reduce the size of a company’s balance sheet.
What happens if a company does not believe it can earn a sufficient return on investment from retained earnings?
If a company does not believe it can earn a sufficient return on investment from those retained earnings (i.e., earn more than their cost of capital), then they will often distribute those earnings to shareholders as dividends or conduct a share buybacks.
What is balance sheet?
Balance Sheet The balance sheet is one of the three fundamental financial statements. These statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. and asset value as the company no longer owns part of its liquid assets. Stock dividends, however, do not require a cash outflow.
Why is retained earnings negative?
The Retained Earnings account can be negative due to large, cumulative net losses. Naturally, the same items that affect net income affect RE. Examples of these items include sales revenue, cost of goods sold, depreciation, and other operating expenses. Non-cash items such as write-downs or impairments and stock-based compensation also affect ...
Do dividends require cash outflow?
Stock dividends, however, do not require a cash outflow. Instead, they reallocate a portion of the RE to common stock and additional paid-in capital accounts. This allocation does not impact the overall size of the company’s balance sheet, but it does decrease the value of stocks per share.
How to find retained earnings on balance sheet?
Follow these two steps to calculate your retained earnings: Subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets to get your stockholder equity. ...
How to calculate retained earnings?
To calculate retained earnings subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets to get your stockholder equity, then find the common stock line item in your balance sheet and take the total stockholder equity and subtract the common stock line item figure (if the only two items in your stockholder equity are common stock and retained earnings).
How to find stockholder equity?
Subtract a company’s liabilities from its assets to get your stockholder equity. Find the common stock line item in your balance sheet. If the only two items in your stockholder equity are common stock and retained earnings, take the total stockholder equity and subtract the common stock line item figure. The difference is retained earnings.
What happens if a company has a net loss on their income statement?
If the company is experiencing a net loss on their Income Statement, then the net loss is subtracted from the existing retained earnings.
What is retained earnings?
Retained Earnings are the portion of a business’s profits that are not given out as dividends to shareholders but instead reserved for reinvestment back into the business. These funds are normally used for working capital and fixed asset purchases or allotted for paying of debt obligations.
Where are retained earnings listed?
Retained Earnings are listed on a balance sheet under the shareholder’s equity section at the end of each accounting period. To calculate Retained Earnings, the beginning Retained Earnings balance is added to the net income or loss and then dividend payouts are subtracted. The formula for Retained Earnings posted on a balance sheet is:
How many lines should be in a retained earnings statement?
There should be a three-line header on a Statement of Retained Earnings. The first line is the name of the company, the second line labels the document “Statement of Retained Earnings” and the third line stats the year “For the Year Ended XXXX”.
How to calculate retained earnings on balance sheet?
Thus, to calculate retained earnings on the balance sheet, you need three items as per the retained earnings formula: beginning period retained earnings, current year net profit/loss, and dividends paid (cash and stock dividends .
How to calculate retained earnings?
Retained earnings are calculated by adding the current year’s net profit (if it’s a net loss, then subtracting the current period net loss) to (or from) the previous year’s retained earnings (which is the current year’s retained earnings at the beginning) and then subtracting dividends paid in the current year from the same.
What Is Retained Earnings?
Retained earnings refer to the residual net income or profit after tax which is not distributed as dividends to the shareholders but is reinvested in the business. Typically, the net profit earned by your business entity is either distributed as dividends to shareholders or is retained in the business for its growth and expansion.
How Do You Prepare a Retained Earnings Statement?
The heading includes three things. In the first line, provide the name of the company (Company A in this case). Then, mark the next line, with the words ‘Retained Earnings Statement’. Finally, provide the year for which such a statement is being prepared in the third line (For the Year Ended 2019 in this case).
How to Calculate the Effect of a Cash Dividend on Retained Earnings?
Cash dividends are dividends paid in cash on a per-share basis. Let’s look at the journal entries when cash dividends are issued to understand the effect of cash dividends on retained earnings. For $1 cash dividends declared on all 100,000 outstanding shares by the company, the journal entries would be as follows:
What to do when your business has surplus income?
When your business earns a surplus income, you have two alternatives. You can either distribute surplus income as dividends or reinvest the same as retained earnings.
What is the beginning period of retained earnings?
Beginning Period Retained Earnings is the balance in the retained earnings account as at the beginning of an accounting period. That is the closing balance of the retained earnings account as in the previous accounting period.
How to use retained earnings?
An organization's ownership can use its retained earnings in a number of ways. Some may choose to invest in business operations, such as by hiring more staff or increasing the production capacity of high-performing products. If an organization is working to launch a new or updated product, some of the surplus funds may be used in this effort. Mergers, partnerships and acquisitions can be beneficial to organizations, helping to increase their success and reach a wider audience, so surplus profits may be used in these efforts. Other examples of uses include paying outstanding debt and purchasing back shares of stock.
What are retained earnings on a balance sheet?
The retained earnings on a balance sheet refers to the amount of net income remaining after paying out dividends to its shareholders. Businesses generate earnings that can be reflected on the balance sheet as negative earnings, also known as losses, and positive earnings, also known as profits.
How to get an accurate picture of an organization's financial position?
In order to get an accurate picture of an organization's financial position, it is important to look at the entire balance sheet, including the gross and net income figures and the retained earnings. Investing in a company is a major decision that should involve careful financial analysis and an overall assessment of how the organization is performing from a financial standpoint.
How does retained earnings differ from revenue?
Revenue is the most commonly utilized figure when looking at the financial performance of a business, and it includes any income generated before the deduction of any operating expenses and overhead costs. Revenue is also referred to as gross sales. Retained earnings reflects the profits that are held or saved for future use. All overhead costs and operating expenses have already been deducted, as this number only shows what is left over.
Why are balance sheets important?
Balance sheets are critical in the accounting industry, as they represent a summary of the financial balances of an organization or individual. Certain information is presented on a balance sheet and used to make assessments about the financial viability of an organization. One key component of a business balance sheet is the retained earnings. In this article, we will discuss retained earnings on a balance sheet and how to calculate this key piece of information.
When a business reports positive earnings, can the owner or leaders utilize the surplus?
When a business reports positive earnings, the owner or leaders can utilize the surplus by re-investing in the company and/or paying shareholders in the form of dividends. Any profits earned by an organization that are not paid to shareholders count as retained earnings and are included on the retained earnings section of the balance sheet.
What are the factors that affect retained earnings?
Some of the key factors that can impact net income include the cost of goods sold, sales revenue, operating expenses and depreciation or a drop in the value of what is being offered to customers . Stock-based compensation, impairments and write-downs are all examples of non-cash items that can have an effect on the net income, which will then cause a change to the retained earnings.
What is trial balance?
A trial balance is a report that lists the balances of all general ledger accounts of a company at a certain point in time. The accounts reflected on a trial balance are related to all major accounting. Accounting Accounting is a term that describes the process of consolidating financial information to make it clear and understandable for all.
Why is trial balance prepared?
In addition to error detection, the trial balance is prepared to make the necessary adjusting entries to the general ledger. It is prepared again after the adjusting entries are posted to ensure that the total debits and credits are still balanced. It is not an official financial statement.
What is the difference between trial balance and general ledger?
The main difference from the general ledger is that the general ledger shows all of the transactions by account, whereas the trial balance only shows the account totals, not each separate transaction. Finally, if some adjusting entries were entered, it must be reflected on a trial balance. In this case, it should show the figures before ...
What are the undetectable errors in a trial balance?
Undetectable errors in a trial balance. A trial balance can trace the mathematical inaccuracy of the general ledger. However, there are a number of errors that cannot be detected by this report: Error of omission: The transaction was not entered into the system.
What is error of original entry?
Error of original entry: The double-entry transaction includes the wrong amounts on both sides.
sma09gc Active Member
Can someone please explain how the retained earnings are calculated in the trial balance?
Colin McKee ActEd Tutor Staff Member
Hi, This sounds quite a general question, and doesn't seem to relate to any specific past paper question or course question. In general, the trial balance will give the accumulation of all the previous retained earnings that the company has made in the past, up to the start of the financial year.
Simon James ActEd Tutor Staff Member
Retained earnings aren't "calculated" in the trial balance (the trial balance is simply a snapshot of accounting info). The accumulated past profits which have been retained (rather than paid out as dividend) are "shown" in the trial balance.
What is post closing trial balance?
The post-closing trial balance (also known as after-closing trial balance) is the last step of accounting cycle and is prepared after making and posting all necessary closing entries to relevant ledger accounts. Since closing entries close all temporary ledger accounts, the post-closing trial balance consists of only permanent ledger accounts (i.e, balance sheet accounts). The purpose of preparing a post-closing trial balance is to assure that accounts are in balance and ready for recording transactions in the next accounting period.
What is the purpose of preparing a post-closing trial balance?
The purpose of preparing a post-closing trial balance is to assure that accounts are in balance and ready for recording transactions in the next accounting period.
