How do you harvest a sheet of fascia?
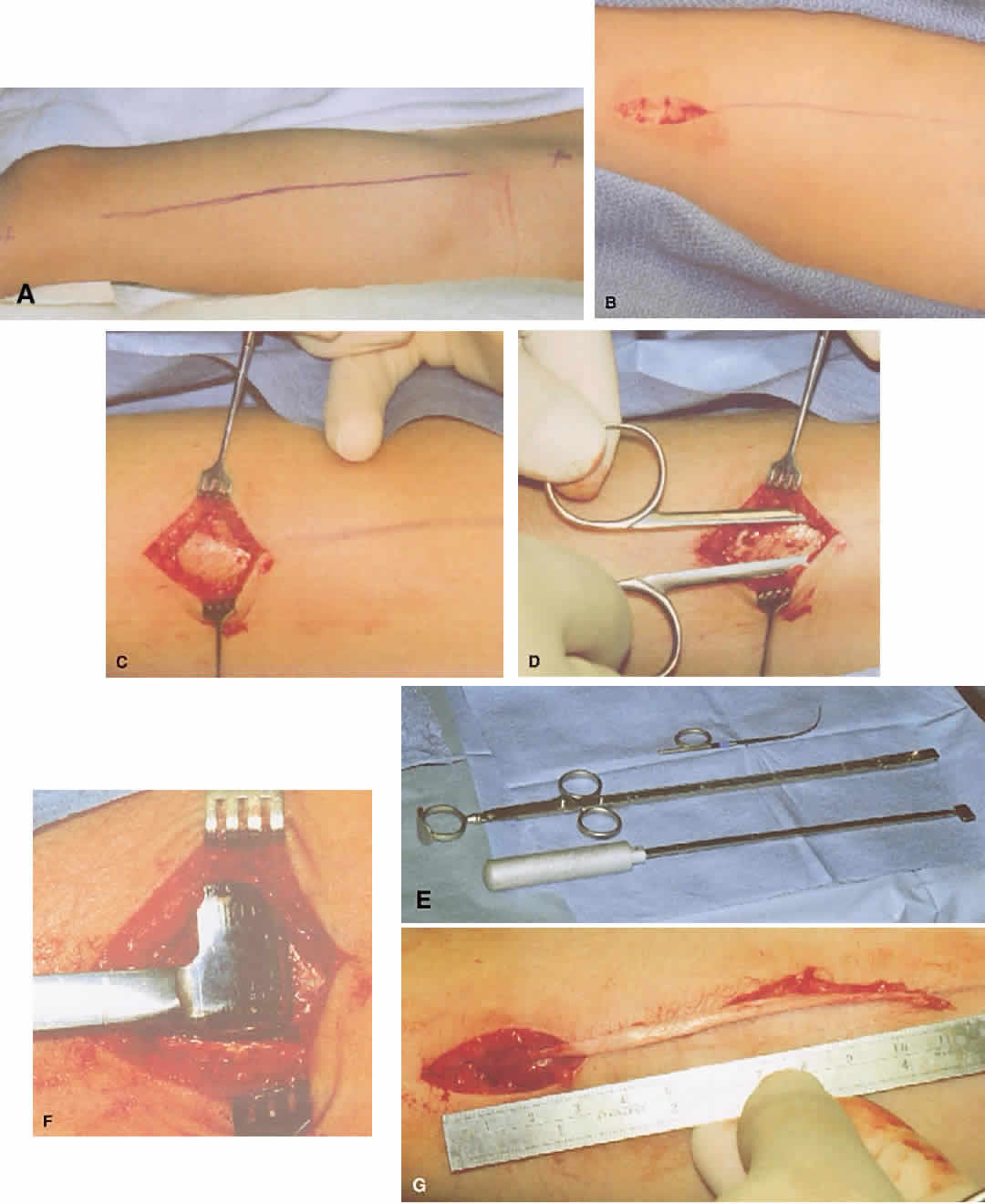
Harvest of a Sheet of Fascia Through a Longitudinal Incision A longitudinal incision, approximately 3-5 cm long, is made along the lateral thigh, the center of which lies over the junction of the upper and middle one-third of the upper leg. The incision is carried down to the ileotibial band of the fascia lata.
How is the fascia lata harvested after hydrodissection?
The yellow shaded area delineates the fascia lata for harvesting. After hydrodissection with saline, a 2 cm superior incision is made and deepened to the plane of the FL. A Boies elevator is used to tunnel under the skin flap. The FL is incised with a blade, and the elevator is used to mobilize the fascia off the underlying muscles.
What are the landmarks and boundaries for fascia lata harvest?
The landmarks and boundaries for fascia lata harvest are shown. The yellow shaded area delineates the fascia lata for harvesting. After hydrodissection with saline, a 2 cm superior incision is made and deepened to the plane of the FL. A Boies elevator is used to tunnel under the skin flap.
What is the “S”-shaped incision for fascia lata?
This article describes an “S”-shaped incision for the open approach of harvesting wide sheets of fascia lata with reference to the important anatomical landmarks. Forty-three patients required dural replacement in cases of tumors, trauma, or cerebrospinal fluid leak involving the anterior skull base.

How is fascia lata formed?
At the knee, the fascia lata receives a fibrous continuation from the biceps femoris tendon, from the sartorius and the quadriceps femoris. The FL is attached to the sacrum and coccyx posteriorly. Its lateral origins are from the iliac crest, the inguinal ligament, and the superior pubic ramus anteriorly.
Why is the fascia lata important?
The fascia lata wraps the large muscles of the thigh and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments. In doing so, it limits the outward expansion of contracting muscles, making muscular contraction more efficient in compressing veins to push blood towards the heart.
What is fascia lata allograft?
Fascia lata allograft is a fibrous connective tissue recovered from the lateral aspect of the thigh. It is most commonly used for clinical applications such as labrum repairs, dural replacement, fascial reanimation and reconstructions of the rotator cuff and cruciate ligaments.
What is fascia lata syndrome?
Tensor fascia lata fasciitis, also known as iliotibial band friction syndrome (ITBFS), is an overuse injury with a population specific incidence. This syndrome is caused by repetitive rubbing of the iliotibial band over the lateral femoral condyle during knee flexion and extension.
How do you release a tight TFL?
0:431:43Effective TFL (Tensor Fascia Latae) Muscle Release Technique for ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou can bend the straight leg a bit to give it a break so the muscle isn't pulled tight and we canMoreYou can bend the straight leg a bit to give it a break so the muscle isn't pulled tight and we can actually apply more pressure into. It you.
Where does the fascia lata end?
The fascia lata is the deep fascia of the thigh. It encloses the thigh muscles and forms the outer limit of the fascial compartments of thigh, which are internally separated by the medial intermuscular septum and the lateral intermuscular septum....Fascia lataTA98A04.7.03.002TA22689FMA13902Anatomical terminology6 more rows
Where does the fascia lata insert?
It inserts distally to the IT track/band, which is comprised of the fascial aponeurosis of the gluteus maximus and the tensor fascia latae. The IT band then runs along the lateral aspect of the thigh, where it attaches to the lateral condyle of the tibia, specifically the Gerdy tubercle.
What is fascia lata sling?
A fascia lata sling operation is a static procedure as it aims to improve the symmetry of the mouth when your face is at rest. The aim of the operation is to provide you with enough mouth symmetry at rest that other people will not be able to tell you have facial palsy affecting your mouth when you are not smiling.
Is fascia lata a muscle?
The tensor fasciae latae (TFL) is a muscle of the proximal anterolateral thigh that lies between the superficial and deep fibres of the iliotibial (IT) band. There is high variability in muscle belly length, although, in most patients, the TFL muscle belly ends before the greater trochanter of the femur.
Can you grow the tensor fasciae latae?
The tensor fasciae latae is a fast-twitch muscle. This means that the best way to build dynamic strength is to use plyometric training. Once the muscle is warm then we can work on increasing its length through stretching and muscle flexibility.
How long does TFL take to heal?
Once you get to the root cause of the TFL overload, and start turning on the right muscles, then the TFL can breath again and the pain dissipates quickly. It will take 4-6 weeks to complete the 4 R's so that the pain does not recur.
Can tight fascia cause hip pain?
Tensor fasciae latae trigger points and tightness can cause pain in the hip joint area and anterolateral portion of the thigh which can extend as far as the knee. This pain can feel like deep hip pain which can be further aggravated by walking or laying down on the affected side.
What action does the tensor fasciae latae perform?
The main function of this muscle is to produce the extension and lateral rotation of the leg on the knee joint. Additionally, it contributes to the movements of the thigh, acting as a relatively weak abductor and medial rotator on the hip joint.
Where does the fascia lata insert?
It inserts distally to the IT track/band, which is comprised of the fascial aponeurosis of the gluteus maximus and the tensor fascia latae. The IT band then runs along the lateral aspect of the thigh, where it attaches to the lateral condyle of the tibia, specifically the Gerdy tubercle.
What does fascia mean in anatomy?
Introduction. Fascia is made up of sheets of connective tissue that is found below the skin. These tissues attach, stabilize, impart strength, maintain vessel patency, separate muscles, and enclose different organs.
What does the TFL muscle do?
The TFL works in conjunction with the gluteus maximus, gluteus medius, and gluteus minimus in a wide variety of hip movements, including flexion, abduction, and internal rotation. It acts, via the iliotibial (IT) band's attachment to the tibia, to assist with knee flexion and lateral rotation.
What is Fascia Lata harvesting?
Fascia Lata Harvesting: Minimal Access for Maximum Harvest. A New Technique
What is fascia lata?
Fascia lata is a versatile source of graft material for a variety of surgical specialties. Its use has been described both as an allograft 1 and as an autograft. 2,3 The size of graft required often determines the surgical incision required to obtain it. In the literature, various techniques have been described to make the scar less obvious, including endoscopic harvest, but still either they result in a significant scar and make the harvest more difficult or require access to expensive endoscopic equipment. 4,5
Can fasciotomies be done through small incisions?
We have also successfully used these instruments to carry out fasciotomies through smaller incisions. The major advantage is the blunt dissection of the fascia from the muscle and from the skin, reducing the risk of bleeding.
Is fascia lata an autograft?
Fascia lata is a versatile source of graft material for a variety of surgical specialties. Its use has been described both as an allograft 1 and as an autograft. 2,3 The size of graft required often determines the surgical incision required to obtain it. In the literature, various techniques have been described to make the scar less obvious, including endoscopic harvest, but still either they result in a significant scar and make the harvest more difficult or require access to expensive endoscopic equipment. 4,5
What is needed for FL harvest?
Many techniques have been described for FL harvest, which require endoscopes, strippers, or fasciotomes.4Other small incision techniques have been described, but the graft segment harvested in those series is narrow5and not suitable for our purposes.
How are FL cuts made?
Two parallel cuts are made with long scissors along the length of the FL, its free edge grasped with a Roberts artery forceps, and then pushed inferiorly until no further extension is possible. The artery tip is tented against the skin, and the inferior stab incision is made, delivering the graft via this incision.
What are the harvest limits for a lateral femoral condyle?
The harvest limits are as follows: laterally—4 cm anterior to the lateral intermuscular septum—this is to preserve a 4 cm strip of the iliotibial band; inferiorly—10 cm superior to the lateral femoral condyle joint —this is to preserve the FL condensation around the knee; and superiorly—up to 15 cm from the level of anterior superior iliac spine—this is to avoid harvesting FL on the superior surface of the tensor fascia lata muscle.
When was fascia lata harvested?
We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of all patients at Mayo Clinic Scottsdale who underwent harvesting of fascia lata for use as the graft material during pubovaginal sling procedures (n = 39) or abdominal sacral colpopexies (n = 32) from June 1994 to November 1998.
What are the disadvantages of using a fascia lata?
Disadvantages of the use of fascia lata for reconstructive surgical procedures relate mostly to potential donor site morbidity. Despite the fairly large number of patients who have undergone fascia lata harvesting for reconstructive procedures in various types of surgery, there is little information on either the incidence or the nature of complications.
What is autologous fascia lata used for?
Autologous fascia lata has been used successfully during various urogynecologic and pelvic floor reconstructive surgical procedures as a graft material to replace or to augment absent or weakened native tissues. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 It has been used most commonly as the graft material for the pubovaginal sling procedure. Several large series have shown success rates equivalent to those reported for synthetic material but with fewer complications related to erosion and voiding dysfunction. 10, 11, 12, 13
Is fascial harvest morbid?
The second is in regard to morbidity from the fascial harvest. There are few randomized trials that compare either effectiveness or morbidity of the variety of autologous and allograft materials being propounded to members of the Society. For example, rectus fascia is commonly used for sling procedures, but little has been reported on the morbidity of the harvest (for example, pain or herniation). In addition, although the use of allografts clearly reduces morbidity, the long-term effectiveness of these grafts still remains to be elucidated. Clearly, these are areas that require further study.