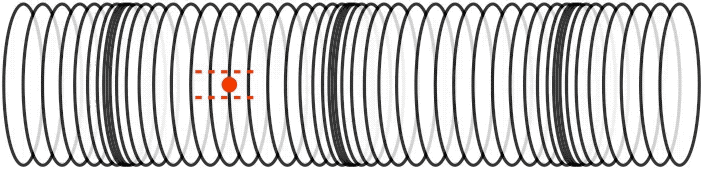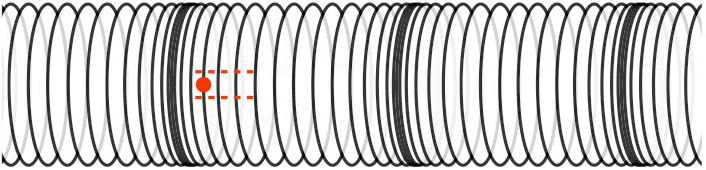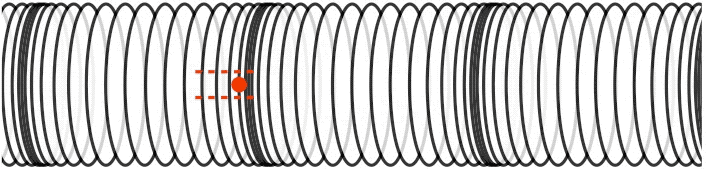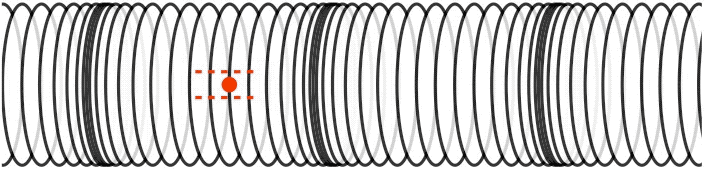
How do you create a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave?
We can make a horizontal transverse wave by moving the slinky vertically up and down. In a longitudinal wave the particles are displaced parallel to the direction the wave travels. An example of longitudinal waves is compressions moving along a slinky.
What is an example of something that makes a longitudinal wave?
A sound wave traveling through air is a classic example of a longitudinal wave. As a sound wave moves from the lips of a speaker to the ear of a listener, particles of air vibrate back and forth in the same direction and the opposite direction of energy transport.
How can you produce longitudinal waves on the spring?
Solution : A longitudinal wave can be set up in a streched spring by compressing the coils in a small region, and releasing the compressed region. The disturbance will proceed to propagated as a longitudinal pulse.
What are 3 examples of longitudinal waves?
Examples of longitudinal waves include: sound waves. ultrasound waves. seismic P-waves....Transverse wavesripples on the surface of water.vibrations in a guitar string.a Mexican wave in a sports stadium.electromagnetic waves – eg light waves, microwaves, radio waves.seismic S-waves.
How is clapping a longitudinal wave?
Clapping hands together to give applaud produces a sound wave. This is similar to the longitudinal wave where the region of compression and rarefaction of a wave in a fixed time period is formed between each clap.
What are the 3 parts of a longitudinal wave?
A compression is where the particles of the medium are closest together, and a rarefaction is where the particles are farthest apart. Amplitude is the distance from the relaxed point in the medium to the middle of a rarefaction or compression. A wavelength is the distance between two equivalent points.
Is light a longitudinal wave?
Light is an example of a transverse wave. With regard to transverse waves in matter, the displacement of the medium is perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
How do longitudinal waves work?
0:482:56Transverse & Longitudinal Waves | Waves | Physics | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAn example of longitudinal waves is sound when a drum is struck the drum skin vibrates which causesMoreAn example of longitudinal waves is sound when a drum is struck the drum skin vibrates which causes the air particles next to it to vibrate this causes the next air particle to vibrate.
Which waves are longitudinal waves?
Longitudinal And Transverse Waves : Example Question #1 Explanation: Sound waves are longitudinal waves, meaning that the waves propagate by compression and rarefaction of their medium.
Where are longitudinal waves found?
Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. When a tuning fork or stereo speaker vibrates it moves back and forth creating regions of compressed air (where the pressure is slightly higher) and regions in between where the air has a lower pressure (called a rarefaction).
What is the best example of a longitudinal wave?
Sound Waves in the Air: The sound waves are the best example of a longitudinal wave and are produced by vibrating or disturbing the motion of the particles that travel through a conductive medium. An example of sound waves in a longitudinal direction of propagation is the tuning fork.
Are water waves longitudinal or transverse?
Water waves are an example of waves that involve a combination of both longitudinal and transverse motions. As a wave travels through the waver, the particles travel in clockwise circles. The radius of the circles decreases as the depth into the water increases.
What travels as a longitudinal wave?
Sound waves in air (and any fluid medium) are longitudinal waves because particles of the medium through which the sound is transported vibrate parallel to the direction that the sound wave moves. A vibrating string can create longitudinal waves as depicted in the animation below.
What is a real life example of a longitudinal and transverse wave?
Water waves: Water waves are an example of both longitudinal and transverse waves. The movement of particles in water waves is in a clockwise direction.
Where are longitudinal waves found?
Sound waves (in air and in solids) are examples of longitudinal waves. When a tuning fork or stereo speaker vibrates it moves back and forth creating regions of compressed air (where the pressure is slightly higher) and regions in between where the air has a lower pressure (called a rarefaction).
What are some examples of waves in everyday life?
9 Real Life Examples Of Transverse WaveRipples in Water Pond.Plucking a Guitar String.Earthquake (Seismic S wave)Tsunami Waves.X-Rays.Electromagnetic Waves.Oscillating String or Rope.
The longitudinal wave formula is given by the equation _____.
y(x,t)=y o cos[w(t-x/c)]
List the characteristics of sound?
The characteristics of the sound are as follows: Loudness Pitch Quality
What happens when a pebble is dropped into a pond with still water?
When a pebble is dropped into a pond with still water, there is the formation of ripples on the surface of the water. These ripples are in the circ...
State true or false: Mechanical waves are also known as elastic waves.
The given statement is true. Mechanical waves are also known as elastic waves because they depend on the elastic property of the waves.
Name the condition in which sound waves can travel through the gas.
For a sound wave to travel through the gas, the required condition is an adiabatic condition. This is because when the sound waves travel they prod...
What is a mechanical wave?
A mechanical wave is a type of wave that is generated by the oscillation matter, which transmits energy through the propagating medium.
What are the two types of mechanical waves?
Longitudinal waves and transverse waves are the two types of mechanical waves.
What is meant by a longitudinal wave?
A longitudinal wave is a type of wave in which the medium’s vibration is parallel to the direction of the wave, and the medium’s displacement is in...
What are the main characteristics of a longitudinal wave?
Compression, rarefaction, wavelength, amplitude, period and frequency are the main characteristics of a longitudinal wave.
1. What are Three Examples of Longitudinal Waves?
Examples of longitudinal waves: Sound waves, Vibration in spring, Tsunami waves, etc.
2. What are the Characteristics of Longitudinal Waves?
Characteristics of longitudinal waves, just like in the transverse waves the following properties can be defined for longitudinal waves: wavelength...
3. What do you understand about wave velocity ?
When the distance is travelled in a motion per unit time in a cyclic or periodic manner in any direction, it is known as Wave velocity. The common...
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
The longitudinal waves are mechanical waves and these are readily used in nature for transmitting energy from one point to another within the medium. There are several examples of longitudinal waves.
Transverse and Longitudinal Waves
Let us understand what are transverse and longitudinal waves with the following list of differences. Both the longitudinal and transverse play an important role in elaborating the concept of sound. Thus the major difference between the transverse wave and longitudinal wave are as follows:
Did You Know
Dogs are sensitive to sound at a higher frequency than humans, allowing them to hear noises that humans can not.
Longitudinal Wave
Humans can easily hear the sound of an engine from the highway or music from a booming speaker.
Examples of Longitudinal Waves
Some examples of longitudinal waves are sound waves and P-waves. Sound waves are produced from the vibration of the particles in a medium. Consider a tuning fork struck by rubber which then begins to vibrate. The air molecules around the prongs of the tuning fork also start to vibrate, compressing and expanding the surrounding air in the process.
Parts of a Longitudinal Wave
Similar to other types of waves, there are also several parts of a longitudinal wave. Consider the longitudinal wave diagram below and its similarity to compression and rarefaction in a slinky toy.
1. Speaking on the mic
A sound wave is a significant example of a longitudinal wave. When a speaker speaks some words in front of the microphone, he/she hit the air thousands of time per second at different frequencies. The sound particles travel along with the air particles and enter the mic to produce sound.
2. Clapping
When we clap while singing a birthday song or on any other occasion, do you know, what makes our hand produce that familiar sound of a clap. When we applaud, we compress and displace the air particles between our hands for a part of a second, which produces the sound of a clap we are familiar with.
3. Vibrating Drumheads
All of us are familiar with the sound of a drum, and most of us have also tried hitting the drum in different beats. When we hit the drum with the mallet, drum head vibrates and produce soundwaves. The soundwaves are generated because the drum head moves outward and inward, making air particles to move (vibrate) in the same direction.
4. Tsunami Waves
Tsunamis cause damage to coastal regions and that’s why people residing in coastal areas are afraid of them. Most people think that sea waves are a transverse wave as they go up and down. However, sea waves, including Tsunami, are the example of both transverse as well as a longitudinal wave.
5. Earthquake (Seismic-P wave)
It is said that animals can sense the earthquake waves much before humans. They have the ability to sense the seismic P waves, which travel only in the interior of the earth. Even humans can feel a little bump and rattle of these waves, but they are mostly unnoticeable to us.
6. Vibration in Window Panels after a Thunder
Whenever it is raining heavily, and thunders are there, you might have noticed the vibration in window panels of your home; it happens because of sound waves. Lightning causes an increase in the air pressure and temperature, which creates a shock wave of sound that we hear like a loud boom and cause our window panels to vibrate.
7. Music Woofers
Have you ever noticed the movement of the woofer cone; moving in and out or ever felt air pressure on your hand when you try to cover the mouth of a woofer? It’s because woofers work on the phenomenon of a longitudinal wave. They move the air particles in or out, producing sound.