
How do you qualify for nocturnal oxygen? Sleeping w/ out OSA (E1390) SpO2 = 89% and qualifying secondary diagnosis, or SpO2 ≤88% for at least 5 cumulative minutes during a minimum 2 hour recording time, taken during sleep (nocturnal, stationary oxygen qualification only).
What are the eligibility requirements for home oxygen therapy?
How do you qualify for nocturnal oxygen? Sleeping w/ out OSA (E1390) SpO2 = 89% and qualifying secondary diagnosis, or SpO2 ≤88% for at least 5 cumulative minutes during a minimum 2 hour recording time, taken during sleep (nocturnal, stationary oxygen qualification only). Click to see full answer.
When is nocturnal oximetry performed for oxygen reimbursement qualification?
Mar 02, 2022 · How do you qualify for nocturnal oxygen? March 2, 2022 by wanda Sleeping w/ out OSA (E1390) Typically, to qualify for home oxygen therapy, you must have either: An arterial blood gas (PaO2) at or below 55 mm Hg or an oxygen saturation at or below 88%, taken at rest (awake) Likewise, why is oxygen needed at night?
When should nocturnal supplemental oxygen be used for hypoxemia?
chronic stable state conditions (nocturnal, stationary oxygen qualification only): • Nocturnal oximetry, for the purpose of oxygen reimbursement qualification, may only be performed after optimal positive airway pressure settings have been determined and the beneficiary is using the positive airway pressure device at those settings.
What are the signs and symptoms of nocturnal hypoxemia?
Mar 21, 2022 · For these patients, continuing oxygen therapy is not helpful. How do you qualify for nocturnal oxygen? Sleeping w/ out OSA (E1390) SpO2 = 89% and qualifying secondary diagnosis, or SpO2 ≤88% for at least 5 cumulative minutes during a minimum 2 hour recording time, taken during sleep (nocturnal, stationary oxygen qualification only).
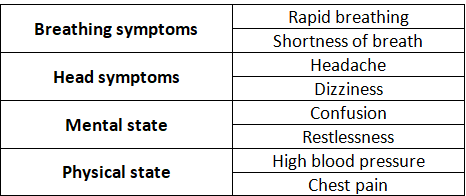
How do you qualify for oxygen at night?
Sleeping w/ out OSA (E1390) SpO2 = 89% and qualifying secondary diagnosis, or SpO2 ≤88% for at least five cumulative minutes during a minimum two-hour recording time, taken during sleep (nocturnal, stationary oxygen qualification only).
What is a qualifying diagnosis for oxygen?
SpO2 = 89% and qualifying secondary diagnosis, or SpO2 ≤88% for at least 5 cumulative minutes during a minimum 2 hour recording time, taken during sleep (nocturnal, stationary oxygen qualification only).
What criteria must be met for Medicare to pay for home o2 therapy?
For Medicare to cover oxygen equipment and supplies, beneficiaries must have the following: Have a prescription from your doctor. Have documentation from your doctor showing you have a lung disorder preventing you from receiving enough oxygen and that other measures have not been successful in improving your condition.
What level of oxygen can you have at home?
How do you know if you need home oxygen? Normal blood oxygen levels are 95 percent and above. Home oxygen therapy is helpful when your level is 88 percent or less.
Does Medicare cover oximeter?
Medicare does not cover pulse oximeters. Some private insurance plans do cover pulse oximetry services.May 26, 2020
Does Medicare cover oxygen for sleep apnea?
If you have chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), Medicare will usually cover several different therapies, ranging from home-use oxygen, pulmonary rehabilitation, and continuous positive airway pressure devices (CPAP). 1 To qualify, you must have a breathing condition that these therapies will improve.Sep 18, 2020
Does Medicare pay for portable oxygen?
While Original Medicare does cover oxygen and oxygen tanks, often in the form of rentals of the required equipment, it doesn't cover POCs because they are quite expensive. Medicare can typically save money by paying for oxygen tank rentals instead.Jun 16, 2021
Does Medicare pay for home oxygen?
Medicare considers home oxygen equipment and accessories to be durable medical equipment (DME), which it covers. Medicare Part B medical insurance will cover oxygen equipment and accessories used in your home if your doctor determines that the supplies are medically necessary and you meet certain other criteria.
Description Information
Please Note: This may not be an exhaustive list of all applicable Medicare benefit categories for this item or service.
Transmittal Information
03/1987 - Clarified coverage criteria for home oxygen use including portable and stationary oxygen systems. Effective date 04/13/1987. (TN 13)
How to get oxygen for Medicare?
For Medicare to cover oxygen equipment and supplies, beneficiaries must have the following: 1 Have a prescription from your doctor 2 Have documentation from your doctor showing you have a lung disorder preventing you from receiving enough oxygen and that other measures have not been successful in improving your condition 3 Proof of gas levels in your blood from your doctor
What is hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy is a form of therapy where your whole body gets exposed to oxygen through increased atmospheric pressure. The oxygen distributes through a chamber. Medicare usually includes coverage for this therapy.
Who is Lindsay Malzone?
Lindsay Malzone is the Medicare expert for MedicareFAQ. She has been working in the Medicare industry since 2017. She is featured in many publications as well as writes regularly for other expert columns regarding Medicare.
Does Medicare Supplement cover coinsurance?
Yes, supplement plans help cover the 20% coinsurance that Medicare doesn’t cover. It also covers other cost-sharing in the form of deductibles Choosing Medigap means you choose peace of mind. For those wanting to protect retirement savings, a Medicare Supplement plan will do just that.
How much does canned oxygen cost?
Typically, canned oxygen with a concentration of around 95%, runs at about $50 per unit. Canned oxygen could be costly if you were to rely on the constant use of an oxygen machine. Costs could quickly escalate to more than $1,160 per day and more than $426,000 per year!
Does Medicare cover oxygen therapy?
Oxygen therapy can serve as a source of relief for those with severe asthma, COPD, emphysema, or other respiratory diseases. Medicare covers oxygen therapy in a hospital or at home when you meet specific criteria.
What is NOD in COPD?
However, with lung disease, the changes in ventilation mentioned above lead to nocturnal oxygen desaturation (NOD). 22, 23 The definition of NOD is somewhat arbitrary, but is usually described in terms of oxygen nadir or time below some oxygen saturation limit, such as 88% or 90%. NOD is most well studied within the context of COPD, and appears to be common. Various studies have reported that 27–70% of patients with COPD with awake oxygen saturation of 90–95% experience substantial desaturation at night, particularly during REM sleep ( Fig. 2 ). 24 – 27 In the most recent study (in which patients were treated according to current guidelines), 38% of COPD subjects with a daytime P aO2 of 56–69 mm Hg (mean 65 mm Hg) spent ≥ 30% of the night with an oxygen saturation < 90%. 28 In those with severe COPD, the desaturation nadir during sleep is more profound even than during exercise, with oxygen saturation falling an average of 6 ± 3.6% during peak exercise and 13.1 ± 8.9% during sleep. 29 Both awake oxygen saturation and daytime arterial carbon dioxide level predict NOD, although imperfectly. 30, 31
What is the prescription for O2?
A practice I see commonly used is to do a 6-minute walk test or other simple exercise test, and if the patient desaturates , the prescription is written, “Use O 2 during exercise and sleep,” the assumption being there's some kind of link between the stress test of sleep and the stress test of walking down the hall. What's the literature supporting that link?
Which system is responsible for breathing?
In addition to chemoreceptor inputs, breathing is also affected by input from both the limbic system and cortex, by efferent input from muscles of locomotion, and by receptors within the lungs themselves. Cortical inputs allow emotion (eg, anxiety) to affect respiration.
Who coined the term "overlap syndrome"?
David Flenley coined the term “overlap syndrome” for the co-existence of OSA and COPD in the same individual.60However, he allowed for the possibility that any respiratory disease (eg, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis) could “overlap” with OSA in the same individual (Fig. 3).
What is the overlap syndrome?
David Flenley coined the term “overlap syndrome” for the co-existence of OSA and COPD in the same individual. 60 However, he allowed for the possibility that any respiratory disease (eg, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis) could “overlap” with OSA in the same individual ( Fig. 3 ). The most well studied of the overlap syndromes, and the one that Flenley focused on, is that of COPD and OSA. However, there has been an increasing focus looking at OSA in a variety of pulmonary diseases, including idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension, asthma, and sickle cell disease. In part this reflects the increasing prevalence of OSA in the general population, but may also reflect the use of corticosteroids to manage many pulmonary diseases. Corticosteroids might contribute to OSA through weight gain, or perhaps more directly by theoretically causing an upper airway muscle myopathy, or some other mechanism.
Can oxygen be used for sleep apnea?
If used, oxygen should be dosed as needed, and patients should be monitored for hypercapnia. Because of its prevalence, obstructive sleep apnea may commonly overlap with lung disease in many patients and have important consequences.
Is overlap syndrome common?
The overlap syndrome is probably a common and under-recognized clinic al entity, in part due to lack of physician awareness and because it has never been more rigorously defined. (The definitions and criteria for both COPD and OSA have also changed over time.) For example, because both COPD and OSA occur on a spectrum of severity, it is unclear at what level of severity the combined diseases begin to have additive or synergistic clinical relevance. It is also unknown if patients with severe COPD and mild OSA should be evaluated and treated similarly to those with mild COPD and severe OSA. Regardless, given the high prevalence of both COPD and OSA, we would expect a large cohort of patients affected with both of these common diseases. Most early studies examined patients with one of these disorders to see how many were also affected with the other illness. These initial studies were not true cross-sectional studies and tended to suggest that the prevalence of the overlap syndrome was very high, suggesting a link between COPD and OSA. 61 – 63 More recent data from the Sleep Heart Health Study and the European MONICA II study did not find an association between the 2 diseases. 64, 65 The major limitation of these studies is that most subjects had very mild airway obstruction on spirometry. Whether any pathophysiological link exists between OSA and severe COPD is still unknown. It is also still worth emphasizing that, although there may be no increased association between relatively mild COPD and OSA, because of the rising prevalence of these diseases, a patient with either disorder alone will still often have the other disease by chance alone. For example, in the Sleep Heart Health Study and the MONICA II study, GOLD stage II COPD was found in 19% and 11% of subjects, respectively. Sleep-disordered breathing was seen in 14% of subjects in Sleep Heart Health Study (respiratory disturbance index > 15 events/h) and 11% of subjects (apnea-hypopnea index > 5 events/h and excessive daytime sleepiness) in the MONICA II cohort. Thus, even by chance alone, a patient with one disorder has a greater than 10% chance of also having the other disease. When evaluating a patient with one disorder, it is reasonable to screen for the other, at least based on history and review of systems.
