
Test your blink reflex by looking into a mirror. Bring your right palm toward your right eye quickly, stopping just short of making contact with your face. Repeat with the left palm and the left eye. Note if you did not blink. Testing your reflexes at home does not substitute for a medical evaluation.
How do you test for Oppenheim reflex?
For the Oppenheim reflex, the anterior tibia, from just below the patella to the foot, is firmly stroked with a knuckle. The Oppenheim test may be used with the Babinski test or the Chaddock test to make withdrawal less likely. The snout reflex is present if tapping a tongue blade across the lips causes pursing of the lips.
How do you elicit the blink reflex?
It can be elicited by shining a strong light (e.g. flashlight, otoscope light, etc.) on the eyes. Blink reflex can also be elicited by a sudden movement of an object towards the eye.
What is a corneal reflex test?
The corneal reflex is also sometimes referred to as the eye-blink reflex. This reflex causes you to blink if something touches your eye, and it serves to protect your eye from surface damage. 1 Corneal reflex testing is often part of a neurological examination.
What is the pathway of the blink reflex?
The diagram below depicts the pathway of the blink reflex. The subject is supine and asked to stay relaxed with their eyes open or gently closed. The active electrode (A) is placed over the inferior aspect of the orbicularis oculus while the reference electrode (R) is placed either over the bony prominence of the zygomatic arch or the nose.
What is the normal blink reflex?
The reflex occurs at a rapid rate of 0.1 seconds. The purpose of this reflex is to protect the eyes from foreign bodies and bright lights (the latter known as the optical reflex). The blink reflex also occurs when sounds greater than 40–60 dB are made.
Why is blink reflex test done?
It is an electrodiagnostic test that evokes the corneal reflex. It evaluates the integrity of the trigeminal and facial nerve.
How is the corneal reflex tested?
The corneal reflex is tested by closure of the eyelids in response to irritation of the cornea by touching with a sterile cotton applicator. It involves afferent impulses transmitted by the trigeminal nerve and efferent motor impulses via the facial nerve.
What is a blink test neurology?
Abstract. The blink reflex - a simple, non-invasive and inexpensive test - may be indicative of lesions or dysfunctions of the brainstem, and particularly assesses the trigeminal-facial arch. Results from alterations of the blink reflex in patients with headaches have provided controversial data.
Is blinking of eyes a reflex action?
Blinking of eyes is not a reflex action, but it is an involuntary action. A reflex action is one which occurs spontaneously whereas involuntary action happens without the conscious control or will of an organism.
What muscle do we use to blink?
Orbicularis Action The orbicularis oculi muscle is innervated by cranial nerve VII (the facial nerve). Contraction of the palpebral portion closes the eyelid gently, and the palpebral orbicularis is the muscle of action in an involuntary blink and a voluntary wink; relaxation of the levator muscle follows.
Where do you touch your corneal reflex?
Test corneal reflex The patient is asked to look to the left side as the cotton tip is brought in from the right side to touch the right cornea gently. This is demonstrated inFig. 21.11. A prompt bilateral reflex closure of the eyelids is the normal response.
How do you check for corneal reflex in unconscious patient?
Corneal Reflex (Cranial Nerves V, VII) (20) Stimulus is applied from the side while the patient is looking in the opposite direction. Gently touching or stroking the cornea with a wisp of moistened cotton. Positive results will elicit bilateral blinking of eyes.
What is the doll's eye reflex?
The oculocephalic reflex (doll's eyes reflex) is an application of the vestibular-ocular reflex (VOR) used for neurologic examination of cranial nerves 3, 6, and 8, the reflex arc including brainstem nuclei, and overall gross brainstem function.
What triggers the blink reflex?
The corneal blink reflex is caused by a loop between the trigeminal sensory nerves and the facial motor (VII) nerve innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscles. The reflex activates when a sensory stimulus contacts either free nerve endings or mechanoreceptors within the epithelium of the cornea.
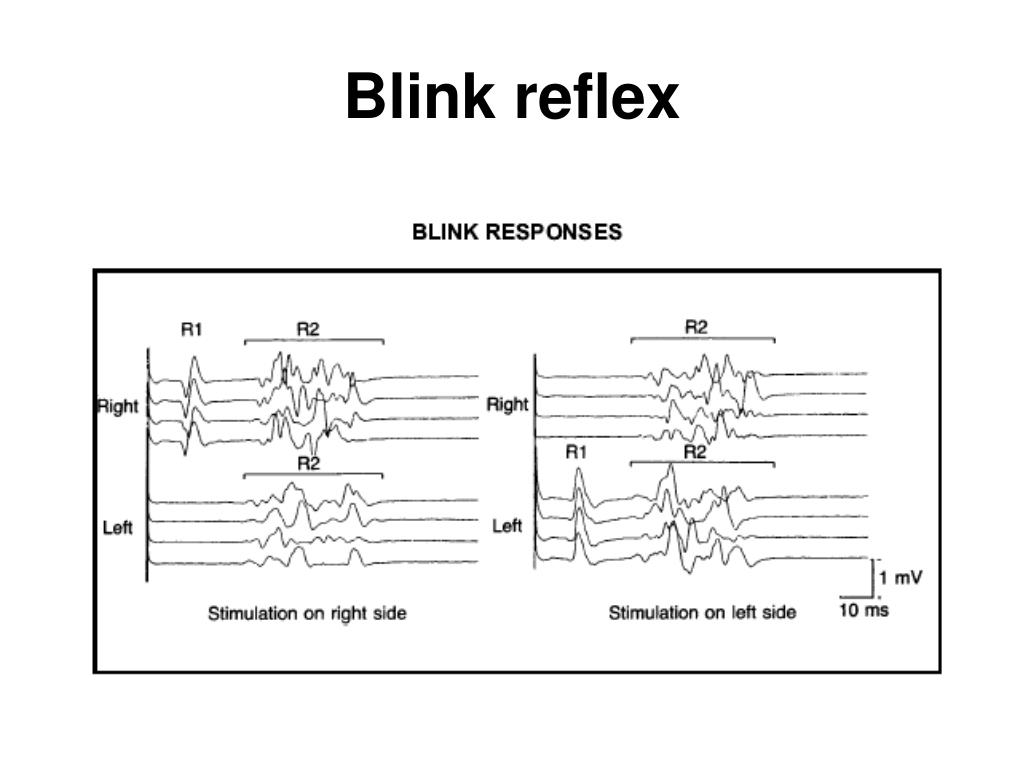
What is R1 and R2 in blink reflex?
Blink reflex has two components: R1 and R2. Direct stimulation of the facial nerve produces a compounded muscle action potential (CMAP) of the facial nerve. R1 is the short loop reflex, that occurs only on the side of stimulation. R2 is a longer loop reflex that occurs bilaterally.
Why does my jaw jerk?
The jaw jerk is a brisk, partial, upward jerk of the jaw caused by contraction of the temporalis, masseter and medial pterygoid muscles in response to striking the chin when the mouth is open.
Why is pupil reflex important?
The pupillary light reflex allows the eye to adjust the amount of light reaching the retina and protects the photoreceptors from bright lights. The iris contains two sets of smooth muscles that control the size of the pupil (Figure 7.2).
What triggers the blink reflex?
The corneal blink reflex is caused by a loop between the trigeminal sensory nerves and the facial motor (VII) nerve innervation of the orbicularis oculi muscles. The reflex activates when a sensory stimulus contacts either free nerve endings or mechanoreceptors within the epithelium of the cornea.
Why are reflexes important?
Reflexes protect your body from things that can harm it. For example, if you put your hand on a hot stove, a reflex causes you to immediately remove your hand before a "Hey, this is hot!" message even gets to your brain.
Why do we blink when something is thrown at us?
The blink reflex also happens when a strange or unfamiliar object touches the outer part of our eye, called the cornea. That one is called the corneal blink reflex. Our eyes and ears pass messages to special nerves, called the sensory nerves, to cells in the bottom part of our brain, in the brain stem.
How to do reflex test?
Use 1 swift stroke. Reflex testing only requires a single impact with the hammer. Move the hammer and your wrist in a 45 to 60 degree arc towards the tendon. This stroke should be done quickly and firmly, tap the center of the tendon.
What muscle is most commonly tested for reflexes?
Pick a muscle to test. There are a wide variety of muscle reflexes that can be tested. The most common is the knee but any joint or large muscle can be assessed. Some reflexes that are usually tested during neurological exams include:
Why do doctors use reflexes?
Use reflex results for diagnosis. Doctors use your grade of reflexes to verify whether your nerves are working effectively. If the muscle reacts correctly, the nerves in the muscle are communicating with the brain as they should. If the muscle doesn't react well, then there is an issue in the nerves between the muscle and the brain. This problem could be caused by a variety of issues, so your doctor will continue with addition medical tests to find the source of the problem. [9]
How to tap a tendon?
The tendon should be tap firmly but not with enough force to cause pain. The goal should be to tap the tendon with the least amount of force possible while still eliciting a reflex. This can take some practice to get right.
What is the head of a reflex hammer made of?
The head of a reflex hammer is made of rubber. This helps to ensure that it does not hurt when the hammer taps a tendon.
Why do you hold a hammer lightly?
Holding the hammer lightly ensures that you do not apply too much force when you tap the tendon.
What is a reflex hammer?
There are a variety of styles of reflex hammers to choose from. Some are light and small, and are designed to be swung with a small amount of force. Others are slightly weighted and use gravity to exert force onto the tendon. These hammers are available from medical supply businesses and online retailers.
How to stroke Babinski reflex?
For Babinski reflex, the lateral sole of the foot is firmly stroked from the heel to the ball of the foot with a tongue blade or end of a reflex hammer. The stimulus must be noxious but not injurious; stroking should not veer too medially, or it may inadvertently induce a primitive grasp reflex. In sensitive patients, the reflex response may be masked by quick voluntary withdrawal of the foot, which is not a problem in Chaddock or Oppenheim reflex testing.
What is the normal response of the plantar reflex?
Babinski, Chaddock, and Oppenheim reflexes all evaluate the plantar response. The normal reflex response is flexion of the great toe. An abnormal response is slower and consists of extension of the great toe with fanning of the other toes and often knee and hip flexion. This reaction is of spinal reflex origin and indicates spinal disinhibition due to an upper motor neuron lesion.
What muscle is a palmomental reflex?
The palmomental reflex is present if stroking the palm of the hand causes contraction of the ipsilateral mentalis muscle of the lower lip.
What is the lateral foot of Chaddock reflex?
For Chaddock reflex, the lateral foot, from lateral malleolus to small toe, is stroked with a blunt instrument.
What is the snout reflex?
The snout reflex is present if tapping a tongue blade across the lips causes pursing of the lips.
What nerve is used in the Jendrassik maneuver?
Ankle jerk (by S1) Jaw jerk (by the 5th cranial nerve) Any asymmetric increase or depression is noted. Jendrassik maneuver can be used to augment hypoactive reflexes: The patient locks the hands together and pulls vigorously apart as a tendon in the lower extremity is tapped.
What is the introduction to neurologic examination?
Introduction to the Neurologic Examination The neurologic examination begins with careful observation of the patient entering the examination area and continues during history taking. The patient should be assisted as little as possible... read more
How to stroke Babinski reflex?
For Babinski reflex, the lateral sole of the foot is firmly stroked from the heel to the ball of the foot with a tongue blade or end of a reflex hammer. The stimulus must be noxious but not injurious; stroking should not veer too medially, or it may inadvertently induce a primitive grasp reflex. In sensitive patients, the reflex response may be masked by quick voluntary withdrawal of the foot, which is not a problem in Chaddock or Oppenheim reflex testing.
What is the reflex response of the great toe?
The normal reflex response is flexion of the great toe. An abnormal response is slower and consists of extension of the great toe with fanning of the other toes and often knee and hip flexion . This reaction is of spinal reflex origin and indicates spinal disinhibition due to an upper motor neuron lesion. For Babinski reflex, the lateral sole of the ...
What is the normal response of the plantar reflex?
Babinski, Chaddock, and Oppenheim reflexes all evaluate the plantar response. The normal reflex response is flexion of the great toe. An abnormal response is slower and consists of extension of the great toe with fanning of the other toes and often knee and hip flexion. This reaction is of spinal reflex origin and indicates spinal disinhibition due to an upper motor neuron lesion.
What muscle is a palmomental reflex?
The palmomental reflex is present if stroking the palm of the hand causes contraction of the ipsilateral mentalis muscle of the lower lip.
What is the lateral foot of Chaddock reflex?
For Chaddock reflex, the lateral foot, from lateral malleolus to small toe, is stroked with a blunt instrument.
What is the snout reflex?
The snout reflex is present if tapping a tongue blade across the lips causes pursing of the lips.
What nerve is used in the Jendrassik maneuver?
Ankle jerk (by S1) Jaw jerk (by the 5th cranial nerve) Any asymmetric increase or depression is noted. Jendrassik maneuver can be used to augment hypoactive reflexes: The patient locks the hands together and pulls vigorously apart as a tendon in the lower extremity is tapped.
How to test for corneal reflex?
Grab a pre-filled sterile saline syringe, typically used to flush IV’s, and squirt a few drops on the eye. Look for the patient to blink. This seems much safer and definitive of a test of the corneal reflex.
What nerves are involved in the corneal reflex test?
The corneal reflex test (blink test) examines the reflex pathway involving cranial nerves V and VII. Classically the provider lightly touches a wisp of cotton on the patient’s cornea. This foreign body sensation should cause the patient to reflexively blink.
What is the second reflex to test spinal cord integrity?
The second reflex to test spinal cord integrity is called crossed extension reflex. This is exhibited by the newborn in supine position by raising his other leg and extending it when the other leg is extended and, the sole of that foot is irritated or rubbed by a sharp object (e.g. thumbnail). This is like the act of the newborn trying to push the hand away that irritates the other leg.
What reflex does a newborn have when it is lying in a prone position?
This reflex is called trunk incurvation reflex.
Why are reflexes important for newborns?
These reflexes aid newborns to survive while they have limited control over their body. These also provide health clues, which is why assessment of the neuromuscular function is part of the general newborn examination. Specific focus should be given to newborns’ alertness, muscle tone and strength, head control, ...
How to test spinal cord integrity in newborns?
First on the list is magnet reflex, which can be elicited by applying pressure on the soles of the foot of newborns lying in supine position. As a response, the newborns would push back against the pressure.
Why does a baby have a sucking reflex?
Touching the newborn’s lips causes the baby to make sucking motions. Like rooting reflex, sucking reflex helps the baby find food. For an instance, when the lips of the baby touch the mother’s breast or a bottle, the baby would begin sucking and so food is taken in. Sucking reflex disappears at six months of age.
What are the 11 reflexes?
Here are simple maneuvers for 11 newborn reflexes: 1. Blink Reflex. Blink reflex is the rapid eye closure exhibi ted by newborns upon coming of objects near it. Similar with adults, this reflex serves a protective function against hurting the eye.
What is it like to watch a newborn kick?
Watching newborns with their odd-timed kicking is a wonderful sight of life inside the hospital. They are like bundles of nerves waiting for nurses and doctors to touch them so they can begin their little spontaneous dance with occasional twitching and flailing. These involuntary movements that newborns exhibit when stimulated are called newborn reflexes.
