:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/spa-bath-at-home-5659f2ee3df78c6ddf5096ea.jpg)
What is the treatment for a Salter-Harris fracture?
Once it identified as a definite Salter-Harris fracture how it is treated depends on the age of the child and on which classification it is. Type one– to treat this classification they will cast it to prevent any movement of the bone. Once it has healed there is no residual bone growth problems
What are the types of Salter Harris fractures?
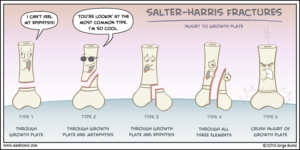
Salter-Harris fractures are classified into 5 types: Type I is a fracture through the growth plate. The fracture line extends through the physis or within the growth plate. Type I fractures are due to the longitudinal force applied through the physis which splits the epiphysis from the metaphysis.
How long does it take for a Salter Harris fracture to heal?
Type one, type four, and type five– approximately four to six weeks healing time Type two– approximately six weeks healing time Type three– up to six weeks healing time Complications When a child or adolescent has a Salter-Harris fracture there is a chance that the bone may not heal at all or heal poorly.
What kind of Doctor do you see for a Salter Harris fracture?
In all but the simplest non-displaced fractures, one should consult with an orthopedic surgeon prior to discharge. A missed or inappropriately treated Salter-Harris fracture has lifelong implications. Once the patient has been treated, follow up is required to ensure that healing is taking place.
Does a Salter-Harris fracture need a cast?
Your child's injury may need to be put in a cast or splint if a Salter-Harris fracture is known or suspected. This will help prevent more injury to the growth plate and surrounding bone. If the bone is not displaced (moved out of place), your child may get a cast to secure the bone as it heals.
How long does it take for a Salter fracture to heal?
Healing usually takes about 4-6 weeks, at which time it will be safe for your child to return to sports and activities. It is very rare for a Salter-Harris I fracture to cause problems with the growth of the distal fibula (less than 1% of fractures).
Do you need a cast for a fractured growth plate?
Treatment for growth plate fractures depends on the severity of the fracture. The least serious fractures usually require only a cast or a splint. If the fracture crosses the growth plate or goes into the joint and is not well-aligned, surgery may be necessary.
Is Salter-Harris fracture painful?
The most common presentation of a Salter-Harris fracture is localized joint pain following a traumatic event (e.g., collision, crush injury, or fall). The patient may present with swelling around the joint in addition to focal tenderness over the physis.
What parts of the bone does a Salter-Harris fracture affect?
A Salter-Harris fracture is an injury to the growth plate area of a child's bone. The growth plate is a soft area of cartilage at the ends of long bones. These are bones that are longer than they are wide. Salter-Harris fractures can occur in any long bone, from fingers and toes, to arm and leg bones.
What is a Salter-Harris type 1 fracture?
A Salter-Harris type 1 fracture is the mildest type of fracture that can occur to a growth plate. The distal fibula is the bone on the outside of the ankle. This injury typically occurs after inverting, or rolling the ankle.
How serious is a growth plate fracture?
Growth plate fractures often need immediate treatment because they can affect how the bone will grow. An improperly treated growth plate fracture could result in a fractured bone ending up more crooked or shorter than its opposite limb. With proper treatment, most growth plate fractures heal without complications.
Can you walk on a fractured growth plate?
Fractures of the growth plate in the tibia are more serious. These fractures require children to keep weight off the ankle for six weeks. If the bones are out of alignment, surgery may be needed to correctly realign the joint surface or straighten the limb for proper healing.
How long does it take to recover from a fractured growth plate?
How long does it take to recover from a growth plate injury? With proper care, the vast majority of growth plate injuries heal without complication. This will typically involve a few weeks or months in a cast, depending on the location and severity of the injury.
Which examination may be used to demonstrate a Salter-Harris fracture?
Taggart et al reported that the use of point-of-care ultrasonography in the emergency department setting could correctly diagnose Salter-Harris fractures. Findings of periosteal fluid at the level of the metaphysis and widening of the physis allowed for the diagnosis of a fracture.
What is the Salter-Harris classification?
Type I fractures disrupt the physis. Type II fractures involve a break from the growth plate up into the metaphysis, with the periosteum usually remaining intact. Type III fractures are intra-articular fractures through the epiphysis that extend across the physis.
Is a fracture a break?
A fracture is a broken bone, the same as a crack or a break. A bone may be completely fractured or partially fractured in any number of ways (crosswise, lengthwise, in multiple pieces).
Can a fracture heal in 2 weeks?
How Long Does a Fracture Take to Heal? Most fractures heal in 6-8 weeks, but this varies tremendously from bone to bone and in each person based on many of the factors discussed above. Hand and wrist fractures often heal in 4-6 weeks whereas a tibia fracture may take 20 weeks or more.
How do you know if a fracture isnt healing?
Symptoms of a fracture that is not healing normally include tenderness, swelling, and an aching pain that may be felt deep within the affected bone. Often, the bone isn't strong enough to bear weight, and you may not be able to use the affected body part until the bone heals.
How long does a hairline fracture take to heal in a child?
Because it usually takes up to six to eight weeks to completely heal from a hairline fracture, it's important to modify your activities during that time.
Can a minor fracture heal on its own?
Although minor fractures can heal on their own, more serious fractures will require surgery. If you've experienced a fracture in your foot and/or ankle, you'll need to be treated by an orthopaedic surgeon who has knowledge of the intricate workings of the bones, tendons, ligaments and muscles of the foot and ankle.
What is a Salter-Harris fracture?
A Salter-Harris fracture refers to a injury, or fracture, through the growth plate of a long bone. Examples of a long bone are the tibia in the arm...
What is the most common type of Salter-Harris fracture?
A type II Salter-Harris fracture is the most common pediatric physeal fracture, occurring frequently in children over 10 years of age. This fractur...
What causes a Salter-Harris fracture?
Salter-Harris fractures usually result from a traumatic event, such as a fall or motor vehicle collision. The bone injury may also develop over tim...
What are the signs and symptoms of a Salter-Harris fracture?
Signs and symptoms of a Salter-Harris fracture will often begin with pain, followed by swelling around the end of the injured long bone. The area a...
How do you diagnose a Salter-Harris fracture?
For diagnosis, a clinician will typically conduct a medical evaluation that includes a review of the history of the event, symptoms, and a physical...
How do you treat a Salter-Harris fracture?
Initial treatment will often focus on controlling swelling and pain. Elevation of the affected limb and icing the area may manage swelling. Pain ma...
What are the most important facts to know about a Salter-Harris fracture?
A Salter-Harris fracture is a growth plate fracture in one of a child’s long bones. It is one of the most common bone injuries in children. There a...
What is a Salter-Harris fracture?
A Salter-Harris fracture refers to a injury, or fracture, through the growth plate of a long bone. Examples of a long bone are the tibia in the arm and the humerus in the leg. Present in children, the growth plate, also called the physeal or epiphyseal plate, is an area of cartilage that actively develops into new bone, increasing the bone’s length until the child stops growing around the ages of 14 to 18. If a Salter-Harris fracture is not diagnosed and treated quickly, it can lead to permanent growth arrest, during which the bone stops growing entirely. Salter-Harris fractures are the most common types of fractures in children, especially in those assigned male at birth, and are more likely to cause bone deformity or growth arrest at younger ages.
What are the signs and symptoms of a Salter-Harris fracture?
Signs and symptoms of a Salter-Harris fracture will often begin with pain, followed by swelling around the end of the injured long bone. The area around the fracture may also feel painful to touch. A person with a fracture may not be able to put weight on the affected limb or may have a limited range of motion. In addition, a bone deformity may be visible as a result of the fracture.
What are the most important facts to know about a Salter-Harris fracture?
A Salter-Harris fracture is a growth plate fracture in one of a child’s long bones. It is one of the most common bone injuries in children. There are five common types of Salter-Harris fractures, which range in severity according to their potential for growth disturbance. Type I fractures are least likely to impair bone growth, while type V is the most likely to disturb a child’s bone growth. Type II is the most common type of Salter-Harris fracture and refers to a bone fracture through the growth plate and part of the metaphysis. In addition to the 5 common types, there are 4 additional, rare types of Salter-Harris fractures. Salter-Harris fractures are usually caused by traumatic injuries and result in symptoms of pain and swelling near the end of a long bone. Diagnosis is often made through a clinical examination and X-ray. Treatment for all types of these fractures typically involves rest, application of ice, and elevation of the limb. Regarding further treatment, type I and II may require only setting the fracture and stabilizing it with a cast or splint, while type III and IV may require surgery to set the bones.
How to treat a fractured bone?
Type I and II fractures are often treated with a closed reduction, which involves setting a bone back in place without surgery. After realignment of the bone, a cast or splint is typically applied to keep the bone stable so it may heal properly. Children with these fractures usually recover with minimal effect on bone growth. On the other hand, type III and IV fractures usually require a surgical procedure, known as an open reduction, in order to set the bone back into its place, and internal fixation, in which metal is used to stabilize the bone, is often necessary. Since type V is frequently diagnosed weeks after the original injury, treatment options can vary significantly and depend on the severity of bone deformity or arrest.
Why are type I fractures missed?
Type V fractures are frequently missed because they involve only injury to the growth plate instead of physical breakage.
What is a Thurston-Holland fragment?
The separated piece of the metaphysis is called a Thurston-Holland fragment. In addition to a type II fracture, there are four other common Salter-Harris fractures types according to the Salter-Harris classification system, which is often used to classify physeal fractures. These fractures, distinguished by the specific part ...
How to diagnose a fracture?
For diagnosis, a clinician will typically conduct a medical evaluation that includes a review of the history of the event, symptoms, and a physical examination of the area. Most commonly, the medical evaluation is followed by an X-ray. Type I fractures can occasionally be seen on an X-ray as a slight separation of the epiphysis from the bone, but usually these fractures are not visible since they affect the cartilage and not the bone. Accordingly, a type I fracture diagnosis is most often based upon the symptoms and medical evaluation alone. Type V fractures are frequently missed because they involve only injury to the growth plate instead of physical breakage. These fractures are usually diagnosed during follow-up visits when there is evidence of growth arrest. However, clinical suspicion of type V fractures are important when there is a history of compression and tenderness near the growth plate.
What is Salter Harris fracture?
Physical Therapy. A Salter-Harris fracture is a break near, through, or along the growth plate in a bone. 1 This usually occurs in children or adolescents and can cause functional limitations in walking and running (if the fracture is in the knee or ankle) or reaching and lifting (if the fracture is in an upper extremity).
What happens if you don't treat Salter Harris?
If not treated properly, a Salter-Harris fracture can lead to limb deformity and a loss of functional mobility. Buckle and Greenstick Fractures in Kids.
What is the purpose of a sling for a fractured hand?
If the fracture is in the hand, wrist, elbow, or shoulder, a sling may be used to immobilize the limb and prevent reinjury. A physical therapist can teach you how to properly adjust the sling to ensure it is fitted properly.
What to do after a fractured ankle?
If the fracture is in the ankle or knee, crutches or a walker may be needed to get around and avoid placing weight on the healing bone.
How to restore range of motion?
Flexibility exercises can help stretch tightened muscles and joints, while joint mobilization (a hands-on technique used to passively move joints) can help restore the range of motion. 10 . Strength: Strengthening exercises, like plyometric strength ening exercises, can be effective in restoring sports fitness.
What can a physical therapist do after surgery?
A physical therapist can perform scar tissue massage and mobilization to improve the mobility of a scar. 13
Can Salter Harris fractures be reduced?
Frequently, Salter-Har ris fractures can be reduced manually. For severe fractures, a procedure called an open reduction internal fixation (ORIF) may be required in which open surgery is performed to correct the bone position. Pinning and screws can help secure the bone fragments in place.
What is Salter Harris fracture?
Salter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are therefore specifically applied to bone fractures in children. The classification system used to grade fractures according to the involvement of the physis, metaphysis, and epiphysis is important as it has implications for both prognosis and treatment.[1][2][3][4]This classification also facilitates communication between providers.
What is the importance of a physical exam after a Salter Harris fracture?
When patients return for evaluation weeks and even years after the initial injury and/or treatment, it is important to conduct a proper physical exam including strength testing, limb length discrepancies, and range of motion.
What is an intra-articular fracture?
This is an intra-articular fracture extending from the physis into the epiphysis. If the fracture extends the complete length of the physis, this type of fracture may form two epiphyseal segments. Since the epiphysis is involved, damage to the articular cartilage may occur. One example of this is a Tillaux fracture of the ankle, which is a fracture of the anterolateral aspect of the growth plate andepiphysis.
What is a type 1 fracture?
This is when the fracture line extends through the physis or within the growth plate. Type I fractures are due to the longitudinal force applied through the physis which splits the epiphysis from the metaphysis. Beware that a normal radiograph cannot exclude a physis injury in a symptomatic pediatric patient.
What is the Salter Harris classification system?
The Salter-Harris classification system is a method used to grade fractures that occur in children and involve the growth plate, which is also known as the physis or physial plate. The classification system grades fractures according to the involvement of the physis, metaphysis, and epiphysis. The fracture grade has important implications for both prognosis and treatment. This activity reviews the evaluation, and management of Saltar-Harris fractures and stresses the role of the interprofessional team in the care of affected patients.
Which zone of calcification is most commonly affected when a physeal fracture occurs?
compression vs. tension forces). The zone of hypertrophic/maturing cells is commonly affected when fractures occur.
What are the complications of a periosteal fracture?
The complications include growth arrest with potential for deformity and limb length discrepancy. An entrapment of periosteum within the fracture is a rare complication which requires an MRI scan. Beware that entrapped periosteum can prevent a complete reduction of the fracture.
Who is at risk for a Salter Harris fracture?
Any child who is still growing can be at risk for having a Salter-Harris fracture. The highest risk groups are teenage males. Other risks can include:
How many classifications are there for Salter Harris fractures?
With Salter Harris fractures they are classified from one to nine according to the growth plate damage and the area of the bone that is fractured. Using this classification system it can help to indicate if surgery will be necessary to realign the fractured bone and stabilize it. Classification one through five are mainly the ones used and the last four classifications are rarely used.
What is type 4 fracture?
Type four – the fracture starts above your growth plate then passes through it, the metaphysic, and the epiphysis, exiting through the joint cartilage. It is often associated with disrupted bone growth patterns. It can result in having a lasting disability. This occurs in approximately ten percent of these fractures.
Why do you need a cast for a Salter Harris fracture?
This will help prevent more injury to the growth plate and surrounding bone.
What to keep out of cast splint?
Keep powder, dirt, and sand out of the cast or splint.
How often should a child have a fracture checked?
Follow up with your child's healthcare provider as directed: Your child may need to have the fracture checked each week as it heals. Ask how often your child needs to see his or her healthcare provider or bone specialist. Write down your questions so you remember to ask them during your visits.
How to care for a child with a fractured leg?
Elevate the area above the level of your child's heart, as often as possible, for 1 to 3 days. Your child may lie back in a bed or chair and put pillows under an injured leg or foot.
How to help a child with a cast?
Ice helps decrease pain and swelling. Put crushed ice in a plastic bag and cover it with a towel. Place the ice over the cast or splint for as long and as often as your child's healthcare provider says you should.
What is Salter Harris fracture?
Salter-Harris fractures (physeal fractures) refer to fractures through a growth plate (physis) and are therefore specifically applied to bone fractures in children. The commonest injuries seen in children with open growth plates are fractures involving epiphyseal plates, or physis .
Where does Salter Harris fracture type 2 extend?
Type II extends through the metaphysis and the growth plate. There is no involvement of the epiphysis. This is the most common of the Salter-Harris fractures.
What type of fracture is less than 2mm?
Type III and IV fractures with displacement of less than 2mm may also be managed non-surgically with a period of non-weight bearing in a cast followed by a period of non-weight bearing in a fracture boot.
What is the treatment for a type 1 fracture?
Type I and most Type II fractures are treated with cast immobilization with closed reduction and casting or splinting. The reduction should be performed carefully to avoid damage to or grating of the physis on any metaphyseal bone fragments.
What is the purpose of physical therapy after a growth plate injury?
Controlled range of motion exercises and light strengthening can be implemented. After the growth plate has undergone sufficient healing, progressive strengthening, range of motion, balance, and proprioception exercises should be implemented. In young athletes, advanced rehabilitation should include sport-specific exercises and drills.
Is Harris-Salter V fracture rare?
Though Harris-Salter V fractures are very rare, they may be seen in cases of electric shock, frostbite, and irradiation. As this fracture pattern tends to result from severe injury, these typically have a poor prognosis leading to bone growth arrest[2]. There are Type VI-Type IX fractures also but these are rare.
How are bone fragments fixed?
The bones are then fixed into place with special implants like screws or wires, or by attaching metal plates to the outer surface of the bone.
What type of fracture breaks through the bone?
Type II Fractures. These fractures break through part of the bone at the growth plate and crack through the bone shaft, as well. This is the most common type of growth plate fracture.
What part of the bone does a fracture break through?
These fractures break through the bone shaft, the growth plate, and the end of the bone.
How to tell if a growth plate fracture is severe?
Other common symptoms include: Visible deformity, such as a crooked appearance of the limb. An inability to move or put pressure on the limb. Swelling, warmth, and tenderness in the area around the end of the bone, near the joint.
Can a bony bridge be removed?
Rarely, a bony bridge will form across the fracture line, stunting the growth of the bone or causing the bone to curve. If this occurs, your doctor may perform a procedure to remove the bony bar and insert fat or other materials to prevent it from reforming. If the problem is diagnosed early, your doctor may be able to take care of it with small surgeries. A long delay in diagnosis—once growth has advanced or is completed or the bone is very curved—will necessitate a more involved procedure to straighten the bone.
Can growth plate fractures heal?
Nonsurgical Treatment. Many growth plate fractures can heal successfully when treated with immobilization: a cast is applied to the injured area and the child limits some types of activity. Doctors most often use cast immobilization when the broken fragments of bone are not significantly out of place.

What Is A Salter-Harris Fracture?
Classification
Symptoms
Risks
- Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the fracture will need to be reduced. This is the process where the bone pieces are put into the correct position to ensure proper healing. Frequently, Salter-Harris fractures can be reduced manually. After the fracture is reduced, the injury will likely be immobilized in a cast. If the fracture is in the ankle or...
Diagnosis
Treatment
Recovery Time
Complications
- Swelling
- Pain
- Tenderness
- Change in the shape of the area that is different than what it normally looks like