How is angle closure glaucoma treated?
- 1. Anti-glaucoma eye drops Anti-glaucoma eye drops are often the first plan of action, as most cases of glaucoma can be controlled with eye drops. Types of eye drops: ...
- 2. Iridotomy Iridotomy is a laser procedure in which a tiny hole is created in the iris to release fluid build-up, and improve fluid drainage through the anterior angle.
- 3. Trabeculectomy ...
- 4. Suprachoroidal shunts ...
How do doctors treat angle closure glaucoma?
What Is Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma?
- Symptoms. They come on quickly. ...
- Diagnosis. If you think you have acute angle closure glaucoma, you’ll need to see an ophthalmologist right away -- it’s an emergency.
- Treatment. The first thing your doctor will do to treat your acute angle closure attack is try to get rid of some of the pressure in your eye.
- Prevention. ...
What are the symptoms of an angle closure attack?
- Eye redness
- Blurry or hazy vision
- Severe eye or head pain
- Nausea and vomiting
Which laser treatment is used to correct closed angle glaucoma?
“iridotomy” is the name of a laser procedure preformed for eyes with narrow angles, eyes that are at risk for “angle-closure glaucoma” Alternative names for this common procedure include: laser peripheral iridotomy, iridectomy, and in short: LPI or PI.
How is chronic angle-closure glaucoma treated?
The condition can often be treated permanently with lasers. The standard treatment for this type of glaucoma is called an iridectomy, which makes a hole to let fluid drain from the eye. It's important to get your eyes checked regularly, as some people may develop a case of chronic angle-closure glaucoma later in life, even after laser treatment.

What is the first line treatment for angle-closure glaucoma?
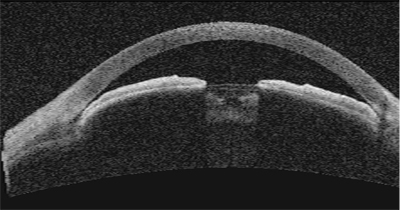
Laser peripheral iridotomy [Fig. 4] is the current standard approach to initial treatment of AC. It alleviates pupillary block, which is a common underlying mechanism of AC [Box 3].
What is the best treatment for closed-angle glaucoma?
In addition to medication and laser, surgery can be successful in treating both open-angle and closed-angle glaucoma. These surgeries include trabeculectomy, glaucoma drainage device (tube shunt), and cyclophotocoagulation, among others.
How serious is angle-closure glaucoma?
Acute angle closure glaucoma is a medical emergency. If the high pressure is not reduced within hours, it can permanently damage your vision. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should immediately contact your eye doctor or go to a hospital emergency room.
How long does it take to go blind from angle-closure glaucoma?
Glaucoma is a slowly progressing problem. On an average, untreated Glaucoma takes around 10-15 years to advance from early damage to total blindness. With an IOP (Intraocular Pressure) of 21-25 mmHg it takes 15 yrs to progress, an IOP of 25-30 mmHg around seven years and pressure more than 30 mmHg takes three years.
What drugs treat closed-angle glaucoma?
Treating closed-angle glaucomaacetazolamide, which reduces the fluid in your eye.beta blockers, which lower the amount of fluid your eye produces.steroids, which reduce inflammation.painkillers (as a comfort measure)drugs to treat nausea and vomiting.pilocarpine, which opens the angle between your iris and cornea.
What medication should be avoided with angle-closure glaucoma?
Medication classes addressed in this review that may increase the risk of angle closure glaucoma include anticholinergics, adrenergic agonists, certain classes of antidepressants, sulfonamides, and topiramate.
What are the classic signs of angle-closure glaucoma?
Patients with angle closure glaucoma may first notice intermittent headaches, eye pain, and halos around lights. Alternatively, they may have an acute angle closure attack, which is accompanied by severe eye pain, headache, blurry vision, and sometimes even nausea and vomiting.
Can you go blind with closed-angle glaucoma?
The damage causes your vision to slowly get worse. There are several types of glaucoma, with open-angle glaucoma and acute angle-closure glaucoma being the most common. Every form of glaucoma causes reduced vision and can cause blindness without treatment.
Which type of glaucoma is the most serious?
Certain drugs and eye diseases can cause yet another form of the disease, called secondary glaucoma. But probably the most serious form of the disease is closed-angle glaucoma. It occurs when the angle becomes suddenly blocked, causing pressure in the eye to rise sharply.
Do all glaucoma patients eventually go blind?
Glaucoma is a serious, lifelong eye disease that can lead to vision loss if not controlled. But for most people, glaucoma does not have to lead to blindness. That is because glaucoma is controllable with modern treatment, and there are many choices to help keep glaucoma from further damaging your eyes.
How should you sleep to lower eye pressure?
Sleeping with your head elevated may reduce your eye pressure at night and decrease your risk of glaucoma-related vision problems. Baseline eye pressure was measured prior to sleep, then at two-hour intervals during a sleep period lasting six hours.
Is angle-closure glaucoma sudden?
Angle-closure glaucoma This form of glaucoma occurs when the iris bulges. The bulging iris partially or completely blocks the drainage angle. As a result, fluid can't circulate through the eye and pressure increases. Angle-closure glaucoma may occur suddenly or gradually.
What is the number one treatment for glaucoma?
The most common treatment for glaucoma is prescription eye drops. They work by lowering the pressure in your eye and preventing damage to your optic nerve. These eye drops won't cure glaucoma or reverse vision loss, but they can keep glaucoma from getting worse.
What foods to avoid if you have narrow-angle glaucoma?
Time to cut out fried foods, baked goods and any product with an ingredient list that includes hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils. Saturated foods that include red meat, beef, lard, shortening and oils can also worsen glaucoma.
What is the gold standard treatment for glaucoma?
Prostaglandin analogs: the “gold standard” for glaucoma.
Does cataract surgery cure closed angle glaucoma?
Dr. Eisengart notes that cataract surgery can be useful in both open- and closed-angle glaucoma, but especially narrow- or closed-angle glaucoma.
How to treat acute angle closure?
Treatment. The first thing your doctor will do to treat your acute angle closure attack is try to get rid of some of the pressure in your eye. They might use: Drops that narrow your pupil. Medication to lowers the amount of fluid your eye makes. Once your IOP has dropped a little, your doctor may use a laser to:
What is the cause of angle closure glaucoma?
It isn’t as common as other types of glaucoma, which cause pressure buildup much more slowly over time.Acute angle-closure glaucoma is caused by a rapid or sudden increase in pressure inside the eye, called intraocular pressure (IOP).
What is the name of the procedure that checks for damage to the optic nerve?
Ophthalmoscopy: Your doctor checks for damage to your optic nerve with a small lighted device.
Can angle closure glaucoma cause eye dilation?
If you don’t treat the problem quickly enough, you could lose your sight completely. You might have an attack of angle closure glaucoma if you have narrow drainage systems and your eyes dilate (your pupil gets bigger) too much or too quickly.
How is acute angle-closure glaucoma diagnosed?
The diagnosis is made from the symptoms and the appearance of your eye. A likely diagnosis may be made by your GP, by an emergency doctor or by an optician. The diagnosis is confirmed by an examination done by an eye specialist (an ophthalmologist). This usually involves examining your eye using a special light and magnifier called a slit lamp and measuring the pressure in your eye. A specialist can also use a gonioscope to directly examine the outflow channels around the trabecular meshwork area of your eye.
What is acute angle-closure glaucoma?
Acute angle-closure glaucoma occurs when the flow of aqueous humour out of the eye is blocked and pressure inside the eye becomes too high very quickly. It is an emergency because if it is not treated quickly, it can lead to permanent loss of vision. Acute angle-closure glaucoma is also sometimes referred to as acute closed-angle glaucoma or just acute glaucoma. For ease, this leaflet will use the term 'acute glaucoma'.
Is angle closure glaucoma an emergency?
It is an emergency because if it is not treated quickly, it can lead to permanent loss of vision. Acute angle-closure glaucoma is also sometimes referred to as acute closed-angle glaucoma or just acute glaucoma. For ease, this leaflet will use the term 'acute glaucoma'.
What to put in glaucoma emergency kit?
Put together an acute angle-closure glaucoma emergency kit containing all the medication ( see panel),2needles and syringes that may be needed. Include a copy of the treatment protocol and the contact details of the nearest ophthalmologist. This will ensure that you and your team are prepared. Check expiry dates regularly as this sight-threatening emergency is uncommon. The storage container should be clearly labelled and kept in the emergency room for easy access. Every team member must know where the kit is stored and be familiar with its contents.
What is the treatment goal for IOP?
Treatment goal:immediate lowering of IOP and alle viation of inflammation, pain, nausea.
How long does it take for IOP to decrease?
After approximately 1 hour, the decrease in IOP should improve blood supply to the iris and make it more responsive to pilocarpine.
Why is cataract extraction considered a definitive treatment?
Because the lens plays a major role in the mechanism of acute angle-closure glaucoma, cataract extraction can be considered as a definitive treatment for patients with co-existing cataract and presenting IOP >55 mmHg.1After the acute attack is successfully treated with medication, the cataract is replaced by a thinner artificial lens implant, thereby relieving the pupil block.
Is angle closure glaucoma an emergency?
Acute angle-closure glaucoma is an ophthalmic emergency as it can lead to irreversible blindness if not identified and treated immediately.
What are the risk factors for angle closure?
Common risk factors include hyperopia, female gender, use of antihistamines and cold medications and advanced age.
Why is my primary angle closed?
Primary angle closure is usually caused by an anatomic problem: e.g., an occludable angle due to high iris insertion, a shallow anterior chamber in a hyperopic eye, a plateau iris that is being pushed forward by an anteriorly rotated ciliary body or lens rise from a growing cataract.
What is the best treatment for pupillary block?
Definitive treatment of pupillary block is laser peripheral iridotomy (LPI). If procedural intervention isn’t possible (due to location of patient or poor view of the iris due to corneal edema), medical treatment is a good temporizing measure. Timolol, brimonidine, dorzolamide and their pharmacological similar cousins are common drop treatments. Timolol is fastest with onset of action in about 20 minutes. Prostaglandin analogs act too slowly to be acutely useful.
How to get rid of a swollen eye?
Apply proparacaine and a drop of betadine to the eye. Consider using a lid speculum. Using a 30-gauge needle on a plungerless syringe, enter the anterior chamber parallel to the iris plane. It usually only takes a few seconds to tap sufficiently. Use a drop of antibiotic before and after the procedure.
What happens when fluid stops flowing through the canals in the eye?
Acute angle closure happens when fluid stops flowing through the canals in the eye, creating pressure that can damage the optic nerve.
What laser do you use for LPI?
Laser settings vary greatly amongst physicians. We usually use a YAG laser with 4.0-5.0 mJ energy. Patients are often pre-treated with pilocarpine to constrict the pupil; note pilocarpine can move the lens forward and therefore exacerbate some types of angle closure, but will make the LPI easier. A Blumenthal or Abraham Iridotomy lens is recommended for stabilization and visualization. Target the iris crypts and look for refluxed pigment. Transillumination helps confirm patency. Avoid placing the LPI in clock hours with intermittent lid exposure or those near the tear lake.
What is closed angle glaucoma?
Closed-angle glaucoma is a condition in which the pressure inside of your eye becomes too high. There are a number of diseases that fall under the heading “glaucoma.”. Open-angle glaucoma is the most common form of the condition and it accounts for around 90 percent of all cases of glaucoma. Closed-angle glaucoma is much less common.
Why does pressure build up in closed angle glaucoma?
If you have closed-angle glaucoma, pressure builds because fluid isn’t flowing out of your eye as it should. Fluid is produced in the rear chamber of your eye, behind the iris. This fluid normally flows through your pupil into the front chamber of the eyeball. The fluid then goes through a series of channels called the trabecular meshwork ...
What is the best medication for a swollen eye?
You may need a number of different drugs including: acetazolamide, which reduces the fluid in your eye. beta blockers, which lower the amount of fluid your eye produces. pilocarpine, which opens the angle between your iris and cornea.
Which medication opens the angle between your iris and cornea?
pilocarpine, which opens the angle between your iris and cornea
What is the procedure to remove a hole in the iris?
This is a laser treatment that creates tiny drainage holes in your iris. It is used to treat both acute and chronic closed-angle glaucoma. Surgical Iridectomy. In this less-common treatment, a surgeon makes a small triangular opening in your iris.
Can closed angle glaucoma affect your vision?
Symptoms of chronic closed-angle glaucoma are subtler. You may not notice any changes, or, if the condition progresses, you may realize that your sight is deteriorating and that you’re losing the edges of your field of vision.
Is closed angle glaucoma acute or chronic?
Closed-angle glaucoma can also be described as acute or chronic. Acute cases are more common and occur suddenly. Chronic closed-angle glaucoma develops gradually, making the symptoms harder to spot.
What is the treatment for angle closure glaucoma?
If you're diagnosed with this condition, you'll need urgent treatment to reduce the pressure in your eye. This generally will require both medication and laser or other surgical procedures.
How to reduce intraocular pressure?
Sleep with your head elevated. Using a wedge pillow that keeps your head slightly raised, about 20 degrees, has been shown to reduce intraocular pressure while you sleep. Take prescribed medicine. Using your eyedrops or other medications as prescribed can help you get the best possible result from your treatment.
How to control eye pressure?
These tips may help you control high eye pressure or promote eye health. Eat a healthy diet. Eating a healthy diet can help you maintain your health, but it won't prevent glaucoma from worsening. Several vitamins and nutrients are important to eye health, including zinc, copper, selenium, and antioxidant vitamins C, E, and A.
How to treat glaucoma?
Glaucoma is treated by lowering your eye pressure (intraocular pressure). Depending on your situation, your options may include prescription eyedrops, oral medications, laser treatment, ...
What medications can help with eye pressure?
Medicines in this category include latanoprost (Xalatan), travoprost (Travatan Z), tafluprost (Zioptan), bimatoprost (Lumigan) and latanoprostene bunod (Vyzulta).
How long does it take for a laser to work on trabecular mesh?
It's done in your doctor's office. Your doctor uses a small laser beam to open clogged channels in the trabecular meshwork. It may take a few weeks before the full effect of this procedure becomes apparent.
What is the best treatment for glaucoma?
The following techniques are intended to improve the drainage of fluid within the eye, thereby lowering pressure: Laser therapy. Laser trabe culoplasty (truh-BEK-u-low-plas-tee) is an option if you have open-angle glaucoma.