How to Conduct Convenience Sampling
- Step 1: Determine the population of interest for your research.
- Step 2: Select the participants for your data collection process.
What are the pros and cons of convenience sampling?
Jun 17, 2020 · How do you use convenience sampling? Convenience sampling is a type of sampling where the first available primary data source will be used for the research without additional requirements. In other words, this sampling method involves getting participants wherever you can find them and typically wherever is convenient. Click to see full answer.
What are the problems with convenience sampling?
Sep 27, 2021 · How to Conduct Convenience Sampling Step 1: Determine the population of interest for your research. Step 2: Select the participants for your data collection process.
What are examples of convenience sampling?
Oct 07, 2021 · Follow these three simple steps to conduct convenience sampling. Sample collection: Start by collecting data from respondents and noting them down. Repeat: Repeat the process of the data collection of the next data using different respondents/participants.
What are the benefits of convenience sampling?
Convenience Sampling. Convenience sampling is the most common form of nonprobabilistic sampling, mostly because it is misused. Convenience sampling is a method of collecting samples by taking samples that are conveniently located around a location or Internet service. We have all seen studies that leverage students in the computer science classes.

How do you use convenience sampling examples?
A basic example of a convenience sampling method is when companies distribute their promotional pamphlets and ask questions at a mall or on a crowded street with randomly selected participants. Businesses use this sampling method to gather information to address critical issues arising from the market.
When can convenience sampling be used?
Applications of Convenience Sampling One of the most obvious answers is you should opt for convenience sampling when dealing with a large sample size within a limited timeframe. Organizations might opt for convenience sampling to measure brand perception and awareness within their target market.Sep 27, 2021
Why do we use convenience sampling in research?
In business and Market research, convenience sampling provides data from the perspective of the audience about the brand image and reputation. It is also used to obtain opinions about newly launched products or on a small-scale project.
Can convenience sampling be used in quantitative research?
Yes, convenience sampling is allowed in quantitative research. What is crucial is, since convenience sampling is prone to the challenge of representativeness, the researcher must ensure the sample is relatively a reflection of the population of the study.
Can you use purposive and convenience sampling together?
If a study conducted on a convenience and purposive sample was methodologically sound, the internal validity would be good; but because the sample was both a convenience and purposive sample, the external validity would be limited by the restrictions defined by the convenience and purposive nature of the sample ( ...Dec 17, 2020
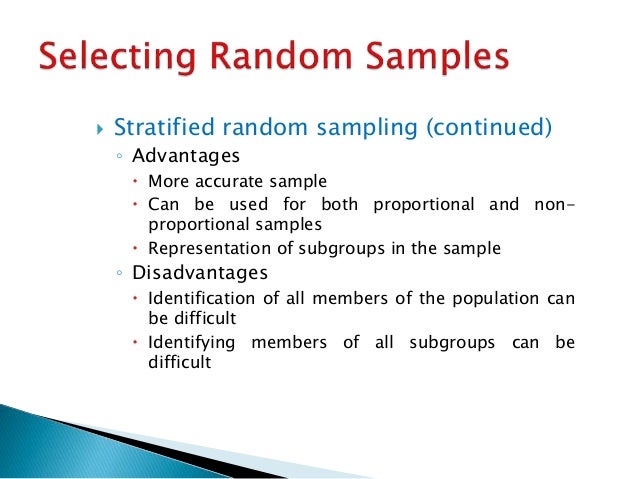
What are the pros and cons of convenience sampling?
The key advantages of convenience sampling are that it is cheap, efficient, and simple to implement. The key disadvantage of convenience sampling is that the sample lacks clear generalizability.Sep 20, 2017
How does convenience sampling affect results?
Convenience samples do not produce representative results. If you need to extrapolate to the target population, convenience samples aren't going to get you there. For example, there was the 2008 AOL poll with 272,939 votes in which 61% of respondents voted for John McCain for U.S. President and 39% for Obama.Sep 16, 2013
Can convenience sampling be used in qualitative research?
Convenience sampling is non-probability sampling that is often used for clinical and qualitative research. This sampling technique often selects clinical cases or participants that are available around a location (such as hospital), medical records database, Internet site, or customer-membership list.Jul 21, 2021
What is convenience sampling?
The method of collecting data from random participants for research is known as convenience sampling.
What are the benefits of convivence sampling?
Convenience sampling is a great method of data sampling thanks to it being budget-friendly, quick to conduct and does not require specialised equip...
How to eliminate the inaccuracy in convenience sampling?
Conducting the process multiple times can help to reduce the resulting bias and make the results more accurate when conducting convenience sampling.
When can we use convenience sampling?
Convenience sampling can be conducted when the study results do not require pinpoint accuracy for the right outcome. For example, it can include cu...
What is convenience sampling?
Definition: Convenience sampling is defined as a method adopted by researchers where they collect market research data from a conveniently available pool of respondents. It is the most commonly used sampling technique as it’s incredibly prompt, uncomplicated, and economical. In many cases, members are readily approachable to be a part of the sample.
Why do researchers use convenience sampling?
In most cases, testing the entire community is practically impossible because they are not easy to reach . Researchers use convenience sampling in situations where additional inputs are not necessary for the principal research.
What is convenience sampling?
Convenience sampling is a method of collecting samples by taking samples that are conveniently located around a location or Internet service. We have all seen studies that leverage students in the computer science classes.
What are the two types of sampling?
The two major types of sampling are probability and nonprobability (Bailey, 1994; Levy & Lemeshow, 1999; Robson, 2002). In probability sampling, the probability of selection of each participant is known. In nonprobability sampling, the interviewer does not know the probability that a person will be chosen from the population. Probability sampling is expensive and time-consuming and may not even be possible because there is no complete list of everyone in a population. For many interview studies, you are likely to be dealing with nonprobability samples where you can use one or a combination of the following approaches (Bailey, 1994; Robson, 2002 ):
What is nonprobability sampling?
Nonprobability sampling means that respondents are recruited from an opt-in panel that may or may not represent your desired population.
What is user research?
In an ideal world, a user research activity should strive to represent the thoughts and ideas of the entire user population. Ideally, an activity is conducted with a representative random sample of the population so that the results are highly predictive of the entire population. This type of sampling is done through precise and time-intensive sampling methods. In reality, this is rarely done in industry settings and only sometimes done in academic, medical, pharmaceutical, and government research.
What is satisficing in survey?
Satisficing is a decision-making strategy where individuals aim to reach satisfactory (not ideal) results by putting in just enough effort to meet some minimal threshold. This is situational, not intrinsic to the individual ( Holbrook, Green, & Krosnick, 2003; Vannette & Krosnick, 2014 ). By that, we mean that people do not open your survey with a plan to satisfice; it happens when they encounter surveys that require too much cognitive effort (e.g., lengthy, difficult-to-answer questions, confusing questions). When respondents see a large block of rating scale questions with the same headers, they are likely to straight-line (i.e., select the same choice for all questions) rather than read and consider each option individually. Obviously, you want to make your survey as brief as possible, write clear questions, and make sure you are not asking things a participant cannot answer.
What is acquiescence bias?
Some people are more likely to agree with any statement, regardless what it says. This is referred to as acquiescence bias. Certain question formats are more prone to bring out this behavior than others and should be avoided ( Saris, Revilla, Krosnick, & Shaeffer, 2010 ). These include asking respondents if or how much they agree with a statement, any binary question (e.g., true/false, yes/no), and, of course, leading questions (e.g., “How annoyed are you with online advertising?”). We will cover how to avoid these pitfalls later in the chapter.
What are the three types of cross-cultural studies?
Cross-cultural studies can apply three types of schemes to sample cultures. Three types of sampling can be envisaged. The first is probability (or random) sampling. Because of the large cost of a probability sample from all existing cultures, it often amounts to stratified (random) sampling of specific cultures (e.g., Western cultures). The second and most frequently observed type of culture sampling is convenience sampling. The choice of cultures is governed here by availability and cost efficiency: researchers decide to form a research network and all participants collect data in their own country. In the third type, called systematic sampling, the choice of cultures is more based on substantive considerations. A culture is deliberately chosen because of some characteristic, such as in Segall et al.'s (1966) study in which cultures were chosen on the basis of features of the ecological environment such as openness of the vista.
Popular Answers (1)
" I looked through some books, and they basically said no because its not a representative sample."
All Answers (14)
" I looked through some books, and they basically said no because its not a representative sample."
