
Literal Comprehension Strategies. The first key to comprehending a written passage is to understand it from a literal point of view. A literal comprehension involves understanding the written meaning of a passage; the definition of words, the context of the writing, the main idea of the passage and the sequence of thought chosen by the author.
Full Answer
What are the strategies of literal comprehension?
Literal Comprehension Strategies. The first key to comprehending a written passage is to understand it from a literal point of view. Literal comprehension is the understanding of the written meaning of a passage: the definition of words, the context of the writing, the main idea of the passage, and the sequence of thought chosen by the author.
What is reading comprehension?
Reading comprehension is the ability to process information that we have read and understand its meaning. This is a complex process with three levels of understanding: literal meaning, inferential meaning, and evaluative meaning. Literal meaning is what the text describes as happening in the story.
How do you find the answer to a literal meaning?
The answers to questions based on literal meaning will always be found in the text. For example: Who was building the tower? The answer is Billy. Here are examples of the type of information that could be identified as literal meaning: Inferential meaning involves determining what the text means. You start with the stated information.
What is a written literal response?
Written responses can vary in difficulty. The lowest level of written literal response requires the students to complete a partially constructed sentence. Teachers can include a selection of responses (taken directly from the text) from which to choose.
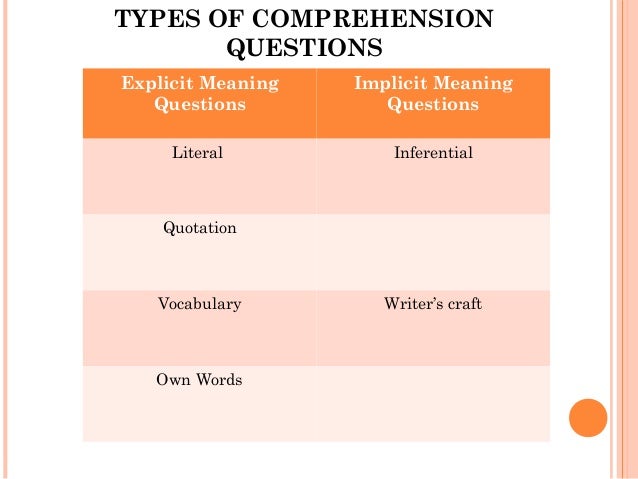
What is literal comprehension example?
The literal meaning of the story was that Billy built a tower out of blocks. The answers to questions based on literal meaning will always be found in the text. For example: Who was building the tower? The answer is Billy.
How do you create a literal comprehension?
Students can underline or highlight the key words. quickly reading through a text to get the main idea. Students can skim read by looking at headings and sub–headings, pictures, diagrams, captions, any italicised or bold words, and the first and last paragraphs of the text.
What is literal comprehension of a text?
Literal comprehension occurs at the surface level when a reader/viewer acknowledges what they can see and hear. The details are stated and clear for anyone to identify. Literal comprehension is often referred to as 'on the page' or 'right there' comprehension. This is the simplest form of comprehension.
How do you assess literal comprehension?
To assess her students' literal comprehension, Rebecca uses informal strategies such as asking them frequent, concrete questions about what is happening in the books they are reading. She reads their written responses to text with an eye toward evaluating the evidence they use to back up different points they make.
What are 4 types of comprehension?
The 4 Types of Comprehensions in Pythonlist comprehension.generator comprehension.set comprehension.dictionary comprehension.
What are the 5 reading comprehension strategies?
There are 5 separate strategies that together form the High 5 Reading Strategy.Activating background knowledge. Research has shown that better comprehension occurs when students are engaged in activities that bridge their old knowledge with the new. ... Questioning. ... Analyzing text structure. ... Visualization. ... Summarizing.
How do you measure comprehension skills?
There are many ways to assess comprehension. One simple way to assess comprehension is by asking students to retell what they read and/or asking a couple of questions and scoring their responses using our Retell Rubric. Maximize time by using the same passage you used for the fluency assessment.
What are literal comprehension questions?
Literal comprehension questions are the “how, what, who, when, where” types of questions. Readers will use decoding skills, as well as syntax and semantic skills to recognise and remember directly stated information.
What are the 3 levels of reading comprehension?
Reading comprehension is the ability to process information that we have read and to understand its meaning. The three levels of comprehension are the literal level, inferential level and the critical/evaluative level. The Literal Level: It is simply what the text says and what actually happens in the story.
What are the three types of comprehension questions?
Literal, inferential, and evaluative questions help learners read and think in different ways. To help students monitor their comprehension, it helps to ask questions while you read.
What is literal comprehension?
Literal comprehension refers to basic information in a text that can be directly found. It is surface level and the first type of reading comprehen...
What is an example of inferential comprehension?
Inferential comprehension refers to information that lies below the surface. It is not clearly stated and must be inferred by the reader based on t...
What are the three levels of comprehension?
There are three main levels of comprehension. These include literal comprehension which is the lowest in the hierarchy, followed by inferential com...
On this page
Explicitly teaching students to work through a process and procedure to provide written responses to literal questions on a text requires numerous opportunities using a variety of texts. When teaching the process and procedure, select short texts on a familiar topic at the student's independent reading level.
Activity 2
Select a text that students are able to read. The activity aims to develop the students questioning and information location skills.
What does "literal" mean in a text?
Literal meaning: In the simplest terms, it is exactly what the text says. Inferential meaning: It is what is determined that the text means, but isn't directly stated in that text . Evaluative meaning: It is what the text says about the world outside of the story. Learning Outcomes.
What are the levels of comprehension?
Reading comprehension involves three levels of understanding: literal meaning, inferential meaning, and evaluative meaning. This lesson will differentiate and define these three levels. Updated: 05/11/2020
What should you be able to do as you complete the lesson?
Learning Outcomes. As you complete the lesson, you should be able to: Explain what reading comprehension is. Understand the importance of reading comprehension. Describe the kinds of information you get from literal, inferential and evaluative meaning.
What is the literal meaning of Billy's story?
Let's use our story about Billy to provide an example. The literal meaning of the story was that Billy built a tower out of blocks. The answers to questions based on literal meaning will always be found in the text. For example: Who was building the tower? The answer is Billy.
How many levels of reading comprehension are there?
Now that you've learned about three levels of reading comprehension, you're ready to put those into practice! Read the following continuation of Billy's story from the lesson, and then answer the questions that follow.
What is the meaning of "literal"?
Literal meaning is simply what the text says . It is what actually happens in the story. This is a very important level of understanding because it provides the foundation for more advanced comprehension. Without understanding the material on this level, you could not go any farther.
What are the three levels of understanding?
This is a complex process with three levels of understanding: literal meaning, inferential meaning, and evaluative meaning. Literal meaning is what the text describes as happening in the story. This level of understanding provides the foundation for more advanced comprehension. Inferential meaning involves taking the information provided in ...
How to write a short story?
Here the reader finds the answer in the text. The reader might be asked to do any of the following: 1 Identify the main ideas of the paragraph or short story. 2 Recall details that support the main ideas. 3 Organize the sequence in which the main events occurred.
What does level reading do?
What it does: Leveled reading helps readers to go beyond the surface of a text in a step-by-step way.

Research Facts
- A dictionary is an important tool for literal comprehension, but alone, it may not be enough. Researching the definition of words, to form a literal comprehension, begins with studying the definitions of words, but also requires a little experience with the way the author used the word during the time of the writing. Beyond the dictionary definitio...
Understanding in Context
- While each word in a passage has a specific definition, each word is also defined by the words surrounding it in a sentence. A contextual analysis of a word involves looking at these surrounding words for clues about the meaning, or alternate meaning, of unfamiliar words. To form a contextual understanding a word, identify the definition of surrounding words and review how th…
Read For Main Idea
- The main idea of a passage is the primary idea presented by the work. Passages can be a part of a larger work, or written in the context of another work, such as a small passage from a story. Studying a passage from this perspective requires that the passage be read from the point of view of the main idea. As an example, William Blake wrote two major poetry collections, “Songs of Inn…
Sequential Study
- A sequential study is reading a passage in a specific order. The order of the passage becomes an important element for understanding how you should interpret it. For instance, if you are reading an action sequence, each statement builds the scene, adding more information to the image as the passage describes the action. Reading the last line first would leave you confused, with no in…