What are the 4 stages of bone healing?
- Hematoma formation.
- Fibrocartilaginous callus formation.
- Bony callus formation.
- Bone remodeling.
Does bone grow back after fracture?
How do you know a fracture is healing?
- What You Experience During Healing. The following steps are what you will go through as your broken bone is healing:
- Pain Decreases. ...
- Range of Motion Increases. ...
- Swelling Goes Down. ...
- Bruising Subsides. ...
- Orthopedic Clinic in Clinton Township, MI.
How long does bone take to heal after fracture?
What slows down bone healing?
Do broken bones hurt as they heal?
What helps broken bones heal faster?
Why do fractures hurt more at night?
Do broken bones make you more tired?
Which bone takes the longest to heal?
How does the body heal from a fracture?
How Your Body Heals. When you sustain an injury that leads to a fracture then, your body will immediately begin to rush nutrients to the site of the damage. First, your body will enter a fight or flight state. This means that your heart rate will increase, you’ll feel woozy, and you’ll need to sit down.
What happens if you break a bone?
If you have broken a bone, then you are probably willing time to fly by quickly so that you can get back to normal life. Broken bones are painful, but they’re also extremely inconvenient! This latter fact is something that many people don’t fully appreciate until they find themselves on the receiving end, but having a broken bone will leave you unable to exercise, unable to carry out manual work, and unable to sleep!
What is the counter process to bone resorption?
Thus, the counter process to this “bone resorption” is handled by osteo blasts. These cells will lay down new bone matrix at the site of the “bone turnover,” during a process known as a reversal.
What is the role of fibroblasts in bone formation?
Next, the fibroblasts will start to provide a “basement membrane” or “collagenous network.” This is essentially what will provide the scaffolding that supports the formation of new bone. This is used when healing any new cells, however, and is not unique to the bone. This matrix starts to form around the edge of the fracture and then moves inward toward the center, where it will begin to build large amounts of type 3 collagen and bone. To do this, it needs to be supplied with the required amount of proteins, oxygen, and other nutrients.
What is the process of laying down new bone matrix?
These cells will lay down new bone matrix at the site of the “bone turnover,” during a process known as a reversal. When you fracture a bone then, all your body has to do is to ramp up that bone turnover process in order to lay down more new matrix and help you restore the damaged tissue. This is called formation.
What happens to the blood vessels that form when the tissue is no longer needed?
Eventually, the new blood vessels that formed that are no longer needed will die off via apoptosis (cell death) and the area will return to normal.
Is bone dead matter?
Many people think of bones as inert or dead matter – and indeed this was the scientific view at one point. Today though, we know that bones are every bit as “alive” and as “plastic” as any other tissue in the body. Just like our brains and muscles, our bones are changing all the time depending on how we use them.
How long does it take for a broken bone to heal?
The anatomy and physiology behind how fractures heal is fascinating. Once the physician treats and realigns a broken bone, it generally takes about six to eight weeks for the process of bone growth and repair to complete. Well look at this repair and remodeling process, along with common types of broken bones in this article.
What is the process of healing a broken bone?
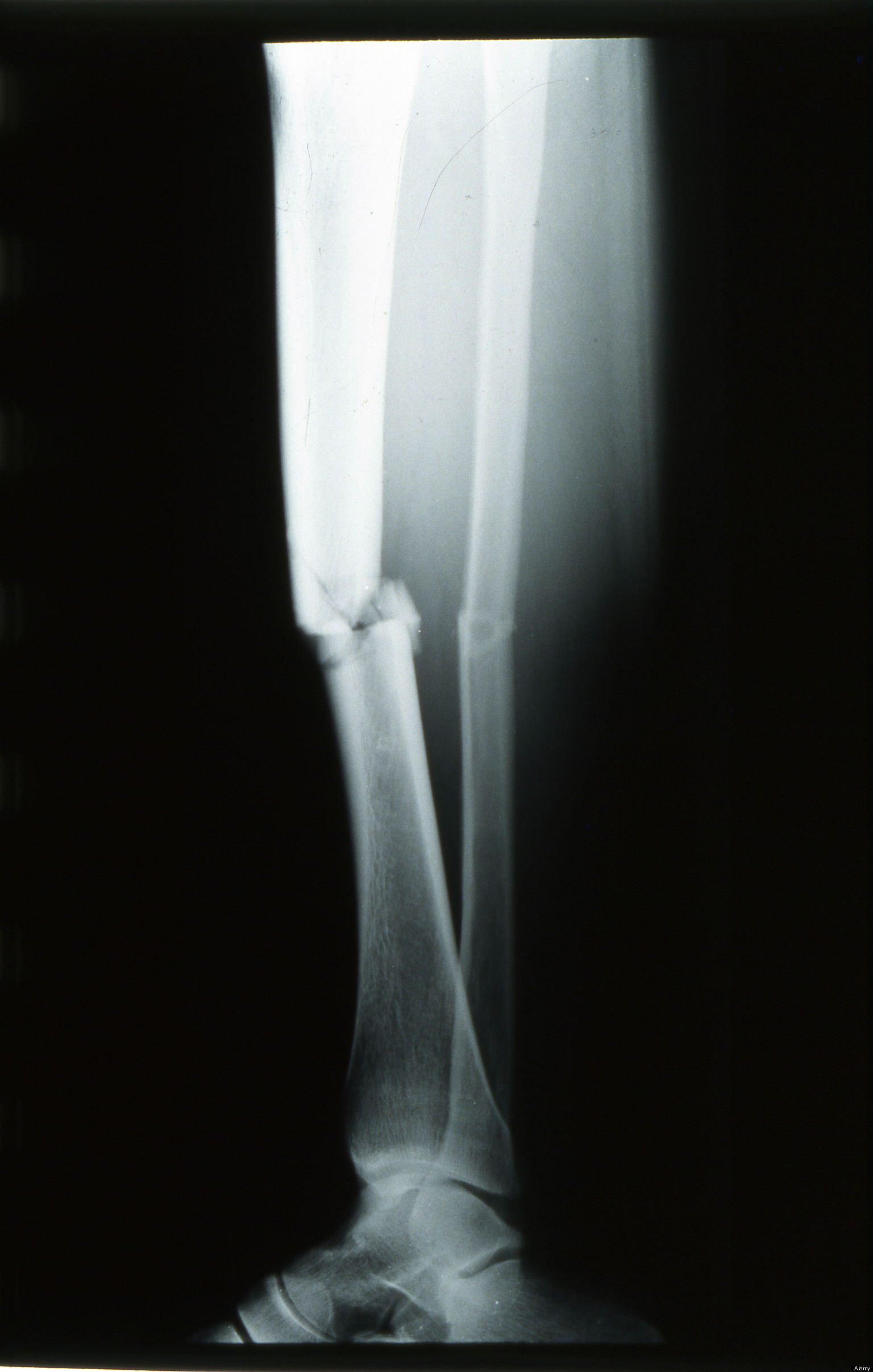
Bone fracture healing process. After you get a broken bone, your body reacts by forming a mass of clotted blood at the fracture site. The clot is called a hematoma. (Hemat/o means blood, and oma means mass.) The hematoma forms because blood vessels in the bone and surrounding tissue are torn and bleed profusely.
How long does it take for fibrocartilaginous callus to regenerate?
The fibrocartilaginous callus will slowly begin starting to change into bony callus in about a week. During this bone regeneration phase, it takes about two months until the bony callus forms a strong connection between the two pieces.
What is a depressed fracture?
Depressed fracture: The bone is pressed inward and is typical in a skull fracture. Epiphyseal fracture: This fracture is when the epiphysis and diaphysis separate at the epiphyseal plate. Greenstick fracture: The bone does not break completely. One side of the shaft breaks, and the other side just bends.
What is a compound fracture?
Penetration: A compound fracture also known as an open fracture is one in which the bone penetrates the skin. A simple fracture also known as a closed fracture is one in which the bone does not penetrate the skin. In addition to the classifications listed above, fractures can be explained by the appearance and type of break.
What is a nondisplaced fracture?
Position: A nondisplaced fracture means the bone ends stay in their regular position after the break. A displaced fracture means the bone ends are no longer aligned in their regular position. Completeness: A broken bone can also be classified by the completeness of the break. A complete fracture is one in which the bone is broken all ...
What is a fracture that is fragmented into three or more pieces?
Comminuted fractures: Bone is fragmented into three or more pieces. These fracture types are common in elderly people, whose bones are brittle.
How long does it take for a bone to heal after a fracture?
Around 3 to 4 weeks after the injury, the formation of new mature bone starts. This can take a long time – several years, in fact, depending on the size and site of the fracture. However, there are cases wherein bone healing is not successful, and these cause significant health problems.
How do broken bones heal?
The secret lies in stem cells and bone’s natural ability to renew itself. Bone heals by making cartilage to temporarily plug the hole created by the break. This is then replaced by new bone. Many people think of bones as being solid, rigid, and structural.
Why are non-healing fractures higher in smokers?
Scientists believe that this may be due to the fact that blood vessel growth in the healing bone is delayed in smokers.
Why is bone important?
Bone is, of course, key to keeping our bodies upright, but it is also a highly dynamic and active organ. present. This mechanism of daily maintenance comes in handy when we are faced with a broken bone. It allows stem cells to first produce cartilage and then create new bone to heal the break, all of which is facilitated by a finely tuned sequence ...
What is the immediate response to a fracture?
The immediate response to a fracture is bleeding from the blood vessels dotted throughout our bones. The clotted blood collects around the bone fracture. This is called a hematoma, and it contains a meshwork of proteins that provide a temporary plug to fill the gap created by the break.
What is the immune system responsible for healing?
The immune system now springs into action to orchestrate inflammation, which is an essential part of healing. Stem cells from the surrounding tissues, bone marrow, and blood respond to the immune system’s call, and they migrate to the fracture.
Where does new bone form?
New bone starts to form mostly at the edges of the fracture. This happens in much the same way that bone is made during normal, everyday maintenance. To fill the void space between the broken ends, cells produce soft cartilage.
What happens when you break a bone?
Within a couple hours, a blood clot forms around the break. Inside the blood clot, special cells called phagocytes begin cleaning bone fragments and killing any germs which might have gotten in around the break. Phagocytes are part of the immune system. The word phagocyte means 'cells that eat' in Greek, so these cells are named after the way they surround and destroy unwanted bacteria and material.
What cells help bone heal?
show/hide words to know. Chondroblasts: cell that make cartilage and help in bone healing after a break. Hard callus: a hard bump that forms around a fracture when a bone is broken and healing. Osteoclast: cells in your body that break down bone material in order to reshape it.
What is a soft bump that forms around a fracture when a bone is broken and healing?
Soft callus: a soft bump that forms around a fracture when a bone is broken and healing.
How long does a callus last?
This stage can last anywhere from 4 days to 3 weeks. A hard callus forms next as osteoblast cells create new bone, adding minerals to make it hard. This stage typically begins 2 weeks after the break, and ends somewhere between the 6th and 12th week. Lastly, the bone is remodeled.
How does bone heal?
How Does a Bone Heal? 1 Inflammation starts immediately after the bone is fractured and lasts for several days. When the bone is fractured, there is bleeding into the area, leading to inflammation and clotting of blood at the fracture site. This provides the initial structural stability and framework for producing new bone. 2 Bone production begins when the clotted blood formed by inflammation is replaced with fibrous tissue and cartilage (known as soft callus). As healing progresses, the soft callus is replaced with hard bone (known as hard callus), which is visible on x-rays several weeks after the fracture. 3 Bone remodeling, the final phase of bone healing, goes on for several months. In remodeling, bone continues to form and becomes compact, returning to its original shape. In addition, blood circulation in the area improves. Once adequate bone healing has occurred, weightbearing (such as standing or walking) encourages bone remodeling.
How long does it take for a bone to heal?
Bone generally takes six to 12 weeks to heal to a significant degree. In general, children's bones heal faster than those of adults. The foot and ankle surgeon will determine when the patient is ready to bear weight on the area.
What causes bone fragments to slow down?
A wide variety of factors can slow down the healing process. These include: Movement of the bone fragments; weightbearing too soon. Smoking, which constricts the blood vessels and decreases circulation. Medical conditions, such as diabetes, hormone-related problems or vascular disease.
Why is immobilization important for fractured bones?
For all patients with fractured bones, immobilization is a critical part of treatment because any movement of bone fragments slows down the initial healing process. Depending on the type of fracture or surgical procedure, the surgeon may use some form of fixation (such as screws, plates or wires) on the fractured bone and/or a cast to keep ...
What to do if ankle bone is not healing?
If the bone is not healing as well as expected or fails to heal, the foot and ankle surgeon can choose from a variety of treatment options to enhance bone growth, such as continued immobilization for a longer period, bone stimulation or surgery with bone grafting or use of bone growth proteins.
What is the process of producing bone?
This provides the initial structural stability and framework for producing new bone. Bone production begins when the clotted blood formed by inflammation is replaced with fibrous tissue and cartilage (known as soft callus).
What is the role of physical therapy in bone recovery?
Once the bone is adequately healed, physical therapy often plays a key role in rehabilitation. An exercise program designed for the patient can help in regaining strength and balance and can assist in returning to normal activities.
How long does it take for a fracture to heal?
From start to finish, the whole process of the 3 stages of fracture healing can take anywhere from a few months to years depending on many different factors. However, the length of healing depends upon things like. the site of the injury, your general health, and. nutritional status.
What is bone healing?
Bone healing is something that will affect almost all of us at some point in our lives. The process of bone healing isn’t simple. Instead, it’s a delicate dance that involves a complex network of proteins, tissues, specialized cells, and a whole host of vitamins and minerals.
Why is forté fracture important?
Forté Fracture brings together the intense combination of nutritional elements important in facilitating fracture healing.
What are the best vitamins for bone fractures?
In particular, the B vitamins and vitamin C, D, and K play vital roles in fracture healing.
Why is nutrition important for bone healing?
Good nutrition can influence the speed, comfort, and completeness of the bone-building process, and ultimately the quickness of your bone fracture healing time. Good nutrition means eating a regular diet ...
What is the first stage of a fracture?
Inflammatory stage: The first phase of the fracture healing process starts the moment after bone breaks. At this point, the body goes into action right away. A small blood clot, known as a hematoma, forms around the fracture site which then attracts molecules called white cells.
What nutrients are needed to prevent fractures?
nutrients, amino acids, protein, and a good blood supply (in order for nutrients to be delivered to the places they are needed). Antioxidants – The fracture event creates extensive “free radicals” that rapidly consume available antioxidants such as Vitamin C, E, Lycopene and Alpha Lipoic Acid.
How to heal a broken bone?
Evidence indicates that the same holds true for bone under repair. Further, fracture healing requires good circulation and an adequate flow of nutrient-replenishing blood to the fracture site — both of which are enhanced by exercise. To avoid stress on the broken bone, joint loading, range of motion, and specific tendon-gliding exercises are employed to accelerate healing and assure return of function post fracture. For example, in the case of a broken forearm, exercises would involve movements of the fingers and hand, as well as the elbow and shoulder joints.
What is the first step in healing a fracture?
Fracture healing can be divided into three phases. The inflammation phase is the first stage of healing. Immediately upon fracture, a blood clot forms, allowing the influx of inflammatory, clean-up cells to the wound area. This is followed by a cytokine cascade that brings the repair cells into the fracture gap.
How do antioxidants help with bone fractures?
Antioxidants repair oxidative damage. When a bone fracture occurs, a remarkable yield of free radicals is generated by the damaged tissues. In particular, this damage occurs as the tightly bound collagen strands running through the mineral phase of bone are forcefully broken. These ruptured collagen strands interact with oxygen-yielding oxygen radical metabolites. These free radicals are associated with inflammation, further breakdown of bone collagen, and excessive bone turnover. In fracture healing, increased free-radical production can overwhelm the natural anti-oxidant defense mechanisms. In such cases, antioxidants — including vitamins E and C, lycopene, and alpha-lipoic acid — have been suggested to be beneficial in suppressing the destructive effect of oxidant free radicals on whole body systems and improving fracture healing in animal models and cultured human cell lines.
What is the nutritional demand of fracture healing?
The nutritional demands of healing. Each stage of the fracture healing process brings with it increased nutritional demands . For starters, the whole process requires a great deal of energy—which is generally supplied through the intake of calories in food.
What is the final step of fracture repair?
The final step of fracture repair is known as the remodeling phase. At this stage the callus begins to mature and remodel itself. Woven bone is remodeled into stronger lamellar bone by the orchestrated action of both osteoblast bone formation cells and osteoclast bone resorption cells.
Why is copper important for healing?
COPPER. Copper aids in the formation of bone collagen and is important to the healing process. The body’s demand for both copper and zinc rises according to the severity of the trauma.
When does the second stage of bone repair begin?
The second, reparative stage begins about two weeks after the fracture occurs. In this stage, proteins produced by the osteoblasts and chondroblasts begin to consolidate into what is known as a soft callus. This soft, new bone substance eventually hardens into a hard callus as the bone weaves together over a 6- to 12-week time period.
How does a broken bone heal?
First, blood will rush to the area in order to deliver cells that are necessary for your bone to heal. This also acts as protection for the bone.
How long does it take for a broken bone to heal?
When you break a bone, it can seem like forever before you can do everything normally again. Fortunately, in most cases, a broken bone heals within a few months – during which time you might notice a few signs that your bone is repairing itself.
What is the callus of a bone?
This callus is a type of collagen-rich bone tissue that’s soft at first but hardens over time. New bone will start to form and replace the callus when osteoblasts (new bone-forming cells) move in weeks after the break. The new bone continues to develop until it completely replaces the callus.
What happens when you break a bone?
Pain Decreases. When you first break a bone, you may have extreme pain – especially when you move or try to move the body part. The pain may feel like a sharp, stabbing pain. The pain also worsens if pressure is placed on it. As your bone heals, this decreases.
Can you break a bone in the same spot?
It will then be almost impossible to break the bone in the exact same spot thereafter because the bone will be thicker and stronger in that spot than in the surrounding bone.
Can you move when you break a bone?
You may have a very limited range of motion at first where the break is. Gradually, you will regain your range of motion as a sign that your broken bone is healing.
Does bruising happen with broken bones?
Bruising doesn’t always happen with a broken bone. However, if you do have bruising, it’ll change colors and start to fade over time. Your body slowly absorbs the blood, which is why the bruise changes colors.