In the brain, acetylcholine functions as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. The brain contains a number of cholinergic areas, each with distinct functions; such as playing an important role in arousal, attention, memory and motivation. Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is an organic chemical that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals, and humans, as a neurotransmitter—a chemical message released by nerve cells to send signals to other cells. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid an…
How does acetylcholine effect behavior?
It plays a role in arousal, memory, learning, and neuroplasticity. It also helps to engage sensory functions upon waking, helps people sustain focus, and acts as part of the brain's reward system. Acetylcholine helps maintain rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, the part of sleep during which people dream.
What part of the brain does acetylcholine affect?
Acetylcholine functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). In the CNS, cholinergic projections from the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex and hippocampus support the cognitive functions of those target areas.
What happens when acetylcholine increases?
Excessive accumulation of acetylcholine (ACh) at the neuromuscular junctions and synapses causes symptoms of both muscarinic and nicotinic toxicity. These include cramps, increased salivation, lacrimation, muscular weakness, paralysis, muscular fasciculation, diarrhea, and blurry vision.
How does acetylcholine help the brain?
Brain and CNS Acetylcholine also acts at various sites within the CNS, where it can function as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. 1 It plays a role in motivation, arousal, attention, learning, and memory, and is also involved in promoting REM sleep.
What happens if you lack acetylcholine?
Specifically, without acetylcholine, muscles cannot contract. Symptoms of myasthenia gravis can range from mild to severe. They may include: weakness in the arms, legs, hands, fingers, or neck.
What is the main role of acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine is the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the autonomic nervous system (a branch of the peripheral nervous system) that contracts smooth muscles, dilates blood vessels, increases bodily secretions, and slows heart rate.
What causes too much acetylcholine?
Exposure to organophosphate (OP) pesticides or certain nerve agents used in warfare can cause levels of acetylcholine in the body to rise very high. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) say that these chemicals lead to a buildup of acetylcholine in the nervous system, causing symptoms of: wheezing.
Can too much acetylcholine cause depression?
Acetylcholine normally enhances cortical sensitivity to external stimuli and decreases corticocortical communication, increasing focused attention. However, increases in ACh signaling can lead to symptoms related to anxiety and depression.
What feelings does acetylcholine produce?
Neuromodulators and Emotional FeelingsDopamine: Pleasure. ... Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine): Displeasure. ... Norepinephrine: Fear/anger. ... Acetylcholine: Calmness/willingness.
Why is acetylcholine important for memory?
Acetylcholine also promotes memory formation and consolidation by supporting hippocampal and cortical synaptic plasticity—the ability for strengthening or weakening of signaling between neurons over time to shape learning and memory.
Does acetylcholine affect memory?
Acetylcholine (ACh) plays an important role in memory function and has been implicated in aging-related dementia, in which the impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning strongly manifests. Cholinergic neurons densely innervate the hippocampus, mediating the formation of episodic as well as semantic memory.
What memory related problem is caused by a lack of acetylcholine?
2) Alzheimer's Disease In Alzheimer's disease, the so-called “cholinergic” neurons — the brain cells that primarily use acetylcholine — gradually become damaged and destroyed. Additionally, important molecules called acetylcholine transporters may also become impaired as the disease progresses.
What receptors does acetylcholine act?
[1] The molecule acetylcholine activates muscarinic receptors, allowing for a parasympathetic reaction in any organs and tissues where the receptor is expressed. Nicotinic receptors are ionotropic ligand-gated receptors that are also responsive to Ach, but they are mostly in the central nervous system.
What memory related problem is caused by a lack of acetylcholine?
2) Alzheimer's Disease In Alzheimer's disease, the so-called “cholinergic” neurons — the brain cells that primarily use acetylcholine — gradually become damaged and destroyed. Additionally, important molecules called acetylcholine transporters may also become impaired as the disease progresses.
Where acetylcholine is released?
Acetylcholine is synthesized in cholinergic neurons and is the principal regulator of GI motility and pancreatic secretion. Acetylcholine is stored in nerve terminals and released by nerve depolarization. Released acetylcholine binds to postsynaptic muscarinic and/or nicotinic receptors.
Where are receptors for acetylcholine located?
Acetylcholine receptors are found on the surface of muscle cells, concentrated in the synapse between nerve cells and muscle cells.
What is the role of acetylcholine in the brain?
Acetylcholine is a critical neurotransmitter that plays an important role in the normal function of the brain and body. Disruptions in the release and function of this neurotransmitter can result in significant problems in areas such as memory and movement.
What is the function of acetylcholine?
Function in the Body. Acetylcholine (ACh) is an abundant neurotransmitter in the human body. It is found in both the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). 1. The name acetylcholine is derived from its structure. It is a chemical compound made up of acetic acid and choline.
Why is acetylcholine important?
Because acetylcholine plays an important role in muscle actions, drugs that influence this neurotransmitter can cause various degrees of movement disruption and even paralysis. For example, the brain might send out a signal to move the right arm. The signal is carried by nerve fibers to the neuromuscular junctions.
What is acetylcholine?
Brain and CNS. Acetylcholine also acts at various sites within the CNS, where it can function as a neurotransmitter and as a neuromodulator. 1 It plays a role in motivation, arousal, attention, learning, and memory, and is also involved in promoting REM sleep .
Which system is acetylcholine in?
Muscles. In the PNS, acetylcholine is a major part of the somatic nervous system. Within this system, it plays an excitatory role leading to the voluntary activation of muscles. Within the autonomic system, acetylcholine controls a number of functions by acting on neurons in the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems.
Who discovered acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine was the first neurotransmitter to be identified. It was discovered by Henry Hallett Dale in 1914, and its existence was later confirmed by Otto Loewi. Both individuals were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1936 for their discovery. 4
What is the function of acetylcholine?
The name "acetylcholine" is derived from its chemical structure, as it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Tissues of the body that use this chemical messenger or are responsive to it are referred to as cholinergic. There is a class of chemicals called anticholinergics that interfere with acetylcholine's action on tissues as well. While ACh operates as a neurotransmitter in many parts of the body, it is most commonly associated with the neuromuscular junction. The neuromuscular junction is where motor neurons located in the ventral spinal cord synapse with muscles in the body to activate them. Acetylcholine also functions as a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, acting both as the neurotransmitter between preganglionic and postganglionic neurons as well as being the final release product from parasympathetic postganglionic neurons.[1]
What receptors does acetylcholine interact with?
Acetylcholine performs its actions by binding the cholinergic receptors (muscarinic and nicotinic). Acetylcholine performs various functions through cholinergic muscarinic receptors.
How do cholinesterase inhibitors affect the acetylcholine receptors?
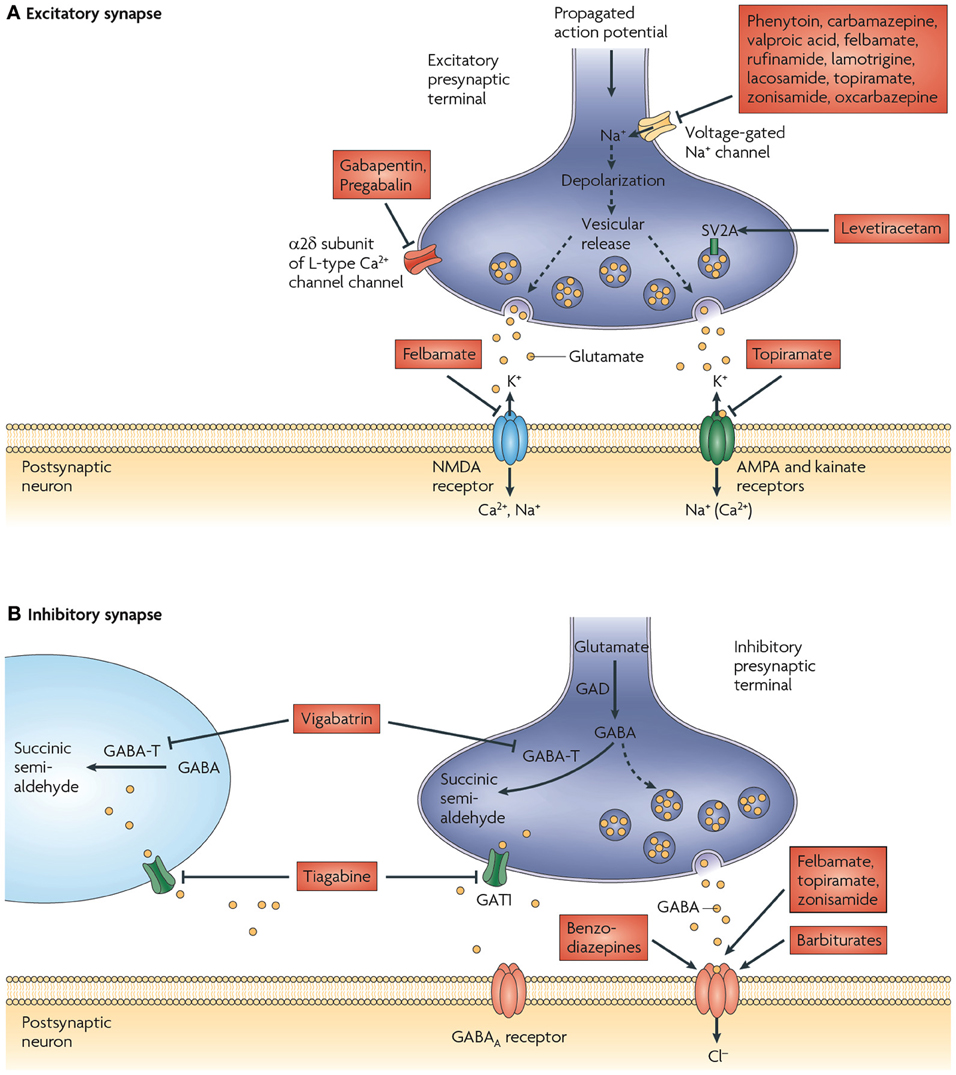
Cholinesterase inhibitors cause an increase in activity at acetylcholine receptors by blocking the breakdown of acetylcholine. Because the blocking of acetylcholinesterase causes a build-up of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, there is continuous activation of the cholinergic receptors. Pharmacologically, cholinesterase inhibitors can help to treat Alzheimer disease and myasthenia gravis since, in both conditions, there is a severe reduction in the amount of native acetylcholine receptor stimulation. Specifically, in Alzheimer disease, there is a decrease in acetylcholine in the neocortex. In myasthenia gravis, there is a severe reduction in the amount of N1 receptors at the neuromuscular junction due to the aberrant production of autoantibodies. Many toxins are cholinesterase inhibitors as well, and these toxins can cause death if given in high enough dosages.
How does botulinum toxin work?
Botulinum toxin works by preventing acetylcholine release from the presynaptic terminals. Hence, local injections can be useful in treating muscle spasticity, cosmetic wrinkles, and migraines. Black widow spider venom has the opposite effect of botulinum toxin. It causes the cells to release all of their acetylcholine, causing excessive muscle contraction. If all acetylcholine supplies are exhausted due to the venom, then paralysis occurs.
Where does acetylcholine synthesis occur?
The synthesis of acetylcholine occurs in the terminal ends of axons. Choline acetyltransferase (CAT) is the enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of choline with acetyl-CoA to create a new molecule of acetylcholine. CAT is produced in the neuronal soma (body) and subsequently transported to the axon terminus via axoplasmic transport in which vesicles full of various proteins are “hitched” to actin filaments that span the length of the neuron for transport. Although localized mainly to the axon terminus, CAT is present throughout the neuron itself. [5][6]
Where are the nicotinic receptors located?
The muscular type is found specifically on the surface of muscle cells at the neuromuscular junction. The neuronal subtype is in the peripheral and central nervous systems. Specifically, N2 receptors are present in the adrenal medulla, on the postsynaptic cell bodies of neurons within the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems, as well as in various locations in the brain such as the ventral tegmental area, hippocampus, prefrontal cortex, amygdala, and the nucleus accumbens. [12]
Where is acetylcholine placed in the axon?
In the axon terminal, newly formed acetylcholine will be placed in vesicles with a minuscule number of free molecules still free in the cytosol. The vesicles are acidified via an energy-dependent pump (H-ATPase), which is utilized to create a gradient for acetylcholine to enter via vesicular acetylcholine transporter (VAChT), which exchanges one vesicular proton for one molecule of acetylcholine. [7]
What are the symptoms of acetylcholine?
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) say that these chemicals lead to a buildup of acetylcholine in the nervous system, causing symptoms of: 1 wheezing 2 sweating 3 weakness 4 headaches 5 fainting 6 diarrhea and vomiting 7 mental changes 8 muscle twitching 9 convulsions 10 paralysis 11 respiratory arrest
What is the role of acetylcholine in Parkinson's disease?
Increasing levels. Botox. Summary. Acetylcholine is a chemical messenger, or neurotransmitter, that plays an important role in brain and muscle function. Imbalances in acetylcholine are linked with chronic conditions, such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease.
What diseases are associated with acetylcholine?
In this article, we look at how acetylcholine is linked with various health conditions, including Alzheimer’s disease, myasthenia gravis, and Parkinson’s disease. We also discuss treatments for acetylcholine-related conditions.
Why is choline important for the nervous system?
The body requires choline for proper brain and nervous system function. It is also necessary for muscle control and to create healthy membranes around the body’s cells.
How to get acetylcholine?
Eating a healthful diet can help a person get adequate choline, which the body uses to create acetylcholine. Ask a doctor before taking choline supplements, due to their potentially serious side effects.
How do medications increase acetylcholine?
Certain medications can increase levels of acetylcholine. They do this by blocking the action of enzymes that break down the neurotransmitter.
Does acetylcholine help with Parkinson's?
People who have Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease tend to have low levels of acetylcholine. There is no proven way to maintain ideal levels of acetylcholine and prevent neurological disease s. However, researchers are developing advanced treatments to help people with these health conditions live longer, healthier lives.
What is the role of acetylcholine in memory?
Acetylcholine is a brain chemical that plays a major role in your ability to learn and remember. Having an adequate acetylcholine level is critical for a normal memory now and for mental sharpness as you age.
How to increase acetylcholine levels?
Here are the best ways to increase acetylcholine levels with food. 1. Eat Foods That Contain Choline. The precursor to acetylcholine is choline, a vitamin B complex-related nutrient found mainly in fatty animal foods. Choline crosses the blood-brain barrier into the brain where it gets converted into acetylcholine.
How to balance acetylcholine?
Manage Your Blood Sugar to Balance Acetylcholine. One last dietary tip for keeping up your acetylcholine level is to balance your blood sugar levels. Hypoglycemia, insulin resistance, and diabetes can all interfere with acetylcholine synthesis. ( 10)
What is the best supplement for acetylcholine?
Of all the choline-based supplements available, alpha-GPC (L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine) is considered one of the best forms for raising acetylcholine levels. It’s well absorbed and can readily enter the brain. It shows promise as a potential Alzheimer’s treatment and is used to enhance memory and cognition.
What are the signs of low acetylcholine?
One of the signs of low acetylcholine is a craving for fatty foods.
Which choline supplement is best for acetylcholine?
Of all the choline-based supplements available, alpha-GPC (L-alpha-glycerylphosphorylcholine) is considered one of the best forms for raising acetylcholine levels.
Where does choline go in the body?
Choline crosses the blood-brain barrier into the brain where it gets converted into acetylcholine.
What is the role of acetylcholine in the brain?
There are a variety of cholinergic areas in the brain, each with different roles, such as playing an important role in excitement, concentration, memory, and motivation. It is believed to play a major role in memory and learning, and in the brain ...
What system does acetylcholine affect?
Acetylcholine tends to have several functions in the central nervous system.
What is the chemical structure of acetylcholine?
Its name derives from its chemical structure: it is an acetic acid and choline ester. Sections of the body that use or are influenced by acetylcholine are considered cholinergic elements. Cholinergic and anticholinergics, respectively, are called substances that increase or decrease the overall cholinergic system function.
Which neurotransmitter decreases parasympathetic activity?
In the parasympathetic nervous system, Atropine, an antagonist of muscarinic ACh receptors, decreases the parasympathetic activity of muscles and glands. Neostigmine is an indirect agonist of the ACh receptor that inhibits acetylcholinesterase, preventing acetylcholine breakdown.
What is acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain and body of several animal types (including humans), a chemical message produced by nerve cells to send signals to other cells, such as neurons, muscle cells, and cells of the gland. Its name derives from its chemical structure: it is an ...
Where does acetylcholine enter the neuromuscular junction?
In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction when a nerve impulse arrives at the terminal of a motor neuron. There, it interacts with a receptor molecule in a muscle fiber’s postsynaptic membrane (or end-plate membrane).
Where is acetylcholine released?
In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction when a nerve impulse arrives at the terminal of a motor neuron. There, it interacts with a receptor molecule in a muscle fiber’s postsynaptic membrane (or end-plate membrane). This binding alters the membrane permeability, opening up channels that allow positively charged sodium ions to flow into the muscle cell (see the end-plate potential).
What is the role of acetylcholine in the brain?
Summary. Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter that plays a role in muscle movement, thinking, working memory, and other aspects of the brain. Low levels have been associated with memory impairment and brain disorders.
Why do people take acetylcholine supplements?
Because acetylcholine plays a role in brain functions, supplements that increase acetylcholine levels have gained interest as nootropics, natural or synthetic substances that may improve your mental performance.
How much acetylcholine is in a large hard boiled egg?
However, you can eat foods or take dietary supplements that indirectly increase the release of acetylcholine or inhibit its breakdown. ). Beef liver: 3 ounces (85 grams) contain 65% of the Daily Value (DV). Egg: 1 large hard-boiled egg contains 27% of the DV. Beef top round: 3 ounces (85 grams) contain 21% of the DV.
What is the name of the enzyme that relays messages from the brain to the body?
). It’s produced from acetyl coenzyme A, which comes from the sugar molecule glucose, and choline, with the help of an enzyme called choline acetyltransferase ( 1. Trusted Source.
What foods contain cholin?
Choline is present in many foods, including ( 6 ): 1 Beef liver: 3 ounces (85 grams) contain 65% of the Daily Value (DV). 2 Egg: 1 large hard-boiled egg contains 27% of the DV. 3 Beef top round: 3 ounces (85 grams) contain 21% of the DV. 4 Soybeans, roasted: 1/2 cup (86 grams) contains 19% of the DV. 5 Chicken breast, roasted: 3 ounces (85 grams) contain 13% of the DV. 6 Fish, cod: 3 ounces (85 grams) contain 13% of the DV. 7 Shiitake mushrooms, cooked: 1/2 cup (73 grams) contains 11% of the DV. 8 Kidney beans, canned: 1/2 cup (128 grams) contains 8% of the DV. 9 Quinoa, cooked: 1 cup (185 grams) contains 8% of the DV. 10 Milk, 1%: 1 cup (240 mL) contains 8% of the DV. 11 Vanilla yogurt, nonfat: 1 cup (245 grams) contains 7% of the DV. 12 Broccoli, boiled: 1/2 cup (78 grams) contains 6% of the DV. 13 Brussels sprouts, boiled: 1/2 cup (78 grams) contains 6% of the DV.
Which is better for acetylcholine?
If you’re simply looking to raise acetylcholine levels, choline supplements are a better option.
Which choline supplements are best for acetylcholine?
The best choline supplements for raising acetylcholine levels are alpha-GPC and citicoline, as they tend to be absorbed better and contain more choline per unit weight ( 7, 8 ).
What is the role of anticholinergic drugs in the brain?
In the brain, acetylcholine is involved in learning and memory. In the rest of the body, it stimulates the autonomic nerves—those that regulate contractions of blood vessels, airways, and our cardiovascular and digestive systems.
Why do older people take stronger drugs?
As we age, our ability to process medication changes. The kidneys and liver clear drugs more slowly, so drug levels in the blood remain higher for a longer time. People also gain fat and lose muscle mass over time.
Why are benzodiazepines considered dangerous for older people?
The Beer's List published by the American Geriatrics Society has long recognized benzodiazepines, antihistamines, and tricyclic antidepressants as potentially inappropriate for older adults, given their side effects . Such drugs are on the list because they share troubling side effects—confusion, clouded thinking, and memory lapses—that can lead to falls, fractures, and auto accidents.
How does age affect medication?
People also gain fat and lose muscle mass over time. Both these changes affect the way drugs are distributed to and broken down in body tissues. And because these drugs are stored in body fat, they can continue to produce effects days after people stop taking them, especially in people with a higher proportion of body fat. In addition, older people tend to take more prescription and over-the-counter medications, each of which has the potential to suppress or enhance the effects of the others.
Which benzodiazepine is at greater risk than a short acting one?
The type of drug taken also mattered. People who were on a long-acting benzodiazepine like diazepam (Valium) or flurazepam (Dalmane) were at greater risk than those on a short-acting one like triazolam (Halcion), lorazepam (Ativan), alprazolam (Xanax), or temazepam (Restoril).
Do drugs cause body fat?
People also gain fat and lose muscle mass over time. Both these changes affect the way drugs are distributed to and broken down in body tissues. And because these drugs are stored in body fat, they can continue to produce effects days after people stop taking them, especially in people with a higher proportion of body fat.
Is benzodiazepine linked to Alzheimer's?
The benzodiazepine study. A team of researchers from France and Canada linked benzodiazepine use to an increased risk of being diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. In the study, the greater people's cumulative dose of benzodiazepines, the higher their risk. The researchers relied on a database maintained by the Quebec health insurance program.