Antidiuretic
An antidiuretic is a substance that helps to control fluid balance in an animal's body by reducing urination, opposing diuresis. Its effects are opposite that of a diuretic. The major endogenous antidiuretics are antidiuretic hormone and oxytocin. Both of those are also used exogenously as medications in people whose bodies need extra help with fluid balance via suppression of diuresis. In addition, there are v…
How do you increase ADH naturally?
Feb 15, 2021 · How does ADH affect water reabsorption? Antidiuretic hormone stimulates water reabsorbtion by stimulating insertion of “water channels” or aquaporins into the membranes of kidney tubules. These channels transport solute-free water through tubular cells and back into blood, leading to a decrease in plasma osmolarity and an increase osmolarity of urine.
Does ADH increase water retention?
Feb 07, 2020 · How does ADH increase water reabsorption? Antidiuretic hormone stimulates water reabsorbtion by stimulating insertion of " water channels" or aquaporins into the membranes of kidney tubules. These channels transport solute-free water through tubular cells and back into blood, leading to a decrease in plasma osmolarity and an increase osmolarity of …
What triggers the release of ADH?
May 28, 2020 · ADH . Furthermore, how does ADH increase water reabsorption? Antidiuretic hormone binds to receptors on cells in the collecting ducts of the kidney and promotes reabsorption of water back into the circulation. These channels transport solute-free water through tubular cells and back into blood, leading to a decrease in plasma osmolarity and an …
What is the effect of ADH on blood pressure?
Aug 27, 2021 · As ADH signals for increased water reabsorption, the body senses the increase in extracellular volume, and natriuretic mechanisms come into play that cause increased salt excretion via the kidneys. The increased salt in the urine will osmotically attract water to be excreted as well, thus keeping the body in a euvolemic state.
How does ADH increase water permeability?
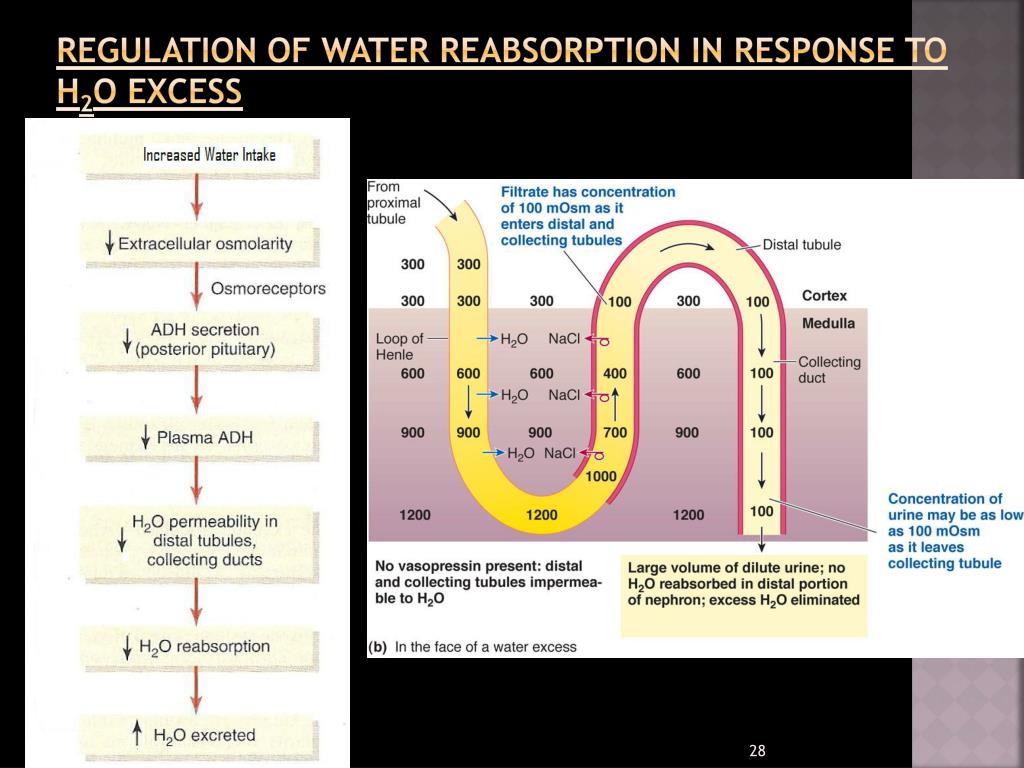
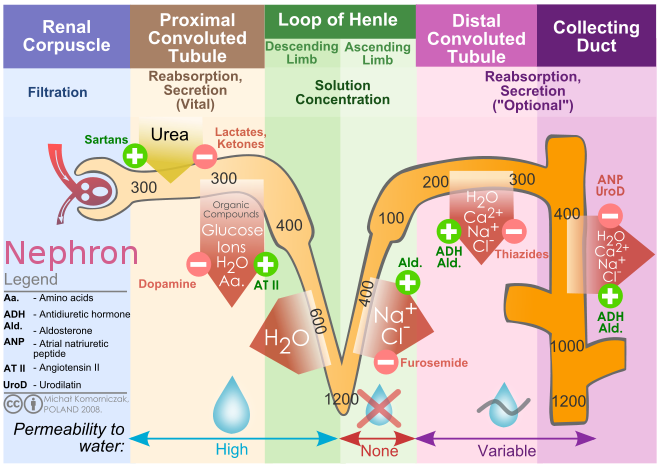
The collecting duct system is under the control of antidiuretic hormone (ADH). When ADH is present, the collecting duct becomes permeable to water. The high osmotic pressure in the medulla (generated by the counter-current multiplier system/loop of Henle) then draws out water from the renal tubule, back to vasa recta.
What does ADH affect water reabsorption and urine volume?
ADH increases the permeability to water of the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct, which are normally impermeable to water. This effect causes increased water reabsorption and retention and decreases the volume of urine produced relative to its ion content.Aug 13, 2020
Does ADH increase or decrease the reabsorption of water?
High ADH increases reabsorption of water and produces a low volume of highly concentrated urine; low ADH is associated with a high volume of highly dilute urine.
Does ADH increase water and sodium reabsorption?
As noted above, ADH plays a role in lowering osmolarity (reducing sodium concentration) by increasing water reabsorption in the kidneys, thus helping to dilute bodily fluids. To prevent osmolarity from decreasing below normal, the kidneys also have a regulated mechanism for reabsorbing sodium in the distal nephron.
How does ADH work GCSE?
ADH is released by the pituitary gland when the blood is too concentrated and it causes the kidney tubules to become more permeable . This allows more water to be reabsorbed back into the blood during selective reabsorption.
How does ADH cause vasoconstriction?
ADH decreases the volume of urine by increasing the reabsorption of water in the kidneys. ADH causes contraction of vascular smooth muscles, constriction of arterioles, and peripheral vasoconstriction. This manifests at the skin as palor and brings about vasodilation of the coronary and cerebral arteries (Fig. 3.5).
What increases ADH secretion?
Other factors that promote the release of ADH include exercise, angiotensin II, and emotional states such as pain. ADH release is inhibited by atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP), which is released by stretched atria in response to increases in blood pressure, as well as alcohol and certain medications.
When the level of ADH increases what happens?
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is a chemical produced in the brain that causes the kidneys to release less water, decreasing the amount of urine produced. A high ADH level causes the body to produce less urine. A low level results in greater urine production.
How does ADH reduce water loss?
When ADH arrives at the kidneys, it causes the kidney nephrons to become more permeable, this allows for water reabsorption and prevents excess water loss.
Does aldosterone increase water reabsorption?
Aldosterone causes an increase in salt and water reabsorption into the bloodstream from the kidney thereby increasing the blood volume, restoring salt levels and blood pressure.
Does ADH influence sodium reabsorption?
antidiuretic hormone enhances the sequestration of sodium in the interstitial fluids of the medulla and papilla'. Importantly, vasopressin increased the absolute amount of sodium per unit of dry solids showing that increases in medullary sodium concentration were independent of effects on water.Nov 1, 2010
What is the main effect of antidiuretic hormone ADH )? Quizlet?
The primary effect of antidiuretic hormone (ADH) in the kidneys is to stimulate: water reabsorption.
How does ADH affect kidney function?
ADH primarily affects the ability of the kidney to reabsorb water; when present, ADH induces expression of water transport proteins in the late distal tubule and collecting duct to increase water reabsorption. Several disease states arise when the body loses control of ADH secretion or responds to its presence. [1]
Where does ADH release?
In states of hypovolemia or hypernatremia, ADH is released from the posterior pituitary gland and binds to the type-2 receptor in principal cells of the collecting duct. Binding to the receptor triggers an intracellular cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) pathway, which causes phosphorylation of the aquaporin-2 (AQP2).
What is the role of vasopressin in the body?
Science has known it to play essential roles in the control of the body’s osmotic balance, blood pressure regulation, sodium homeostasis, and kidney functioning.
Where is arginine vasopressin synthesized?
Last Update: August 29, 2020. Introduction. Vasopressin or antidiuretic hormone (ADH) or arginine vasopressin (AVP) is a nonapeptide synthesized in the hypothalamus. Science has known it to play essential roles in the control of the body’s osmotic balance, blood pressure regulation, sodium homeostasis, and kidney functioning.
What is the ADH?
ADH is a nonapeptide derived from the preprohormone called prepropressophysin, which contains a signal peptide, neurophysin II, and a glycoprotein. In the Golgi apparatus, the signal peptide portion is cleaved from prepropressophysin to produce a prohormone stored in secretory vesicles.
What are the symptoms of low sodium?
Lower levels of sodium are associated with headache, obtundation, seizure, and even coma and respiratory arrest .[4] .
Where is oxytocin produced?
There is also production, albeit in smaller quantities, in neurons with cell bodies located in the paraventricular nuclei, the site primarily responsible for oxytocin, a homologous hormone mostly involved in uterine contraction and milk let down.