What structural differences does an aponeurosis have from a tendon? Tensions are strong and cord-like, and they attach muscle to bone, whereas aponeurosis is sheet-like, and they attach muscle to muscle. Aponeuroses
Aponeurosis
An aponeurosis is a type or a variant of the deep fascia, in the form of a sheet of pearly-white fibrous tissue that attaches sheet-like muscles needing a wide area of attachment. Their primary function is to join muscles and the body parts they act upon, whether it be bone or other muscles. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessel…
How does an aponeurosis differ from a tendon?
tendons are strong and cord-like and attach muscle to bone; aponeurosis are sheet-like and attach muscle to muscle. Aponeuroses are thick membranes that separate muscles from one another. They are tough and resilient.
What is the difference between fascia and aponeurosis?
What is the difference between fascia and aponeurosis? An aponeurosis is made of layers of delicate, thin sheaths. Tendons allow the body to move and be flexible while aponeuroses allow the body to be strong and stable. Aponeuroses can act as fascia. Fascia is a fibrous tissue that envelopes muscles or organs, to bind muscles together or to ...
Does aponeurosis attach muscle to bone?
An aponeurosis is a type of connective tissue that provides a point for a muscle to attach to a bone or cartilage. You may be thinking that a tendon also attaches muscle to bone, and you are correct.
Is tendon same as fascia?
Fasciae are similar to ligaments and tendons as they are all made of collagen except that ligaments join one bone to another bone, tendons join muscle to bone and fasciae surround muscles or other structures. The video below gives a fascinating introduction to fascia. What are tendons ligaments and fascia?

What is the difference between tendon and an aponeurosis?
An aponeurosis looks quite different than a tendon. An aponeurosis is made of layers of delicate, thin sheaths. Tendons, in contrast, are tough and rope-like. An aponeurosis is made primarily of bundles of collagen fibers distributed in regular parallel patterns, which makes an aponeurosis resilient.
How does aponeurosis similar from a tendon structurally?
How does an aponeurosis differ from a tendon structurally? Aponeuroses and tendons are both made of dense, fibrous connective tissue, but they look very different. An aponeurosis is a delicate, thin sheet of tissue that contains collagen-releasing cells called fibroblasts.
How do a tendon and an aponeurosis differ structurally and functionally?
How do tendons and aponeurosis differ structurally? Tendons are cord-like dense regular connective tissue. Aponeurosis are sheetlike sense irregular connective tissue.
What is the difference between a tendon and an aponeurosis quizlet?
Describe the difference between a tendon and an aponeurosis. A tendon is a projection of connective tissue beyond the ends of the muscle that attaches to bone. An aponeurosis is a broad fibrous sheet of connective tissue that connects muscles to adjacent muscles.
What is the similarities between tendon and aponeurosis?
0:064:25Difference between Aponeurosis and Tendon - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipEpineurosis versus tendon on dissecting a human body one comes across various structures in andMoreEpineurosis versus tendon on dissecting a human body one comes across various structures in and around the muscles apart from the blood vessels bones and nerves epineurosis facial ligaments and
What type of structure is aponeurosis?
Aponeuroses are connective tissue sheaths found on the surface of pennate muscles.
What is the structure and function of a tendon?
Tendons are soft, fibrous tissues that connect muscle to bone. Their main function is to transfer muscle generated force to the bony skeleton, facilitating movement around a joint, and as such they are relatively passive, inelastic structures, able to resist high forces.
What is difference between tendon and ligament?
A tendon serves to move the bone or structure. A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
What do you mean by aponeurosis?
aponeurosis, a flat sheet or ribbon of tendonlike material that anchors a muscle or connects it with the part that the muscle moves. The aponeurosis is composed of dense fibrous connective tissue containing fibroblasts (collagen-secreting spindle-shaped cells) and bundles of collagenous fibres in ordered arrays.
What is the function of an aponeurosis?
Their primary function is to join muscles and the body parts they act upon, whether bone or other muscles. They have a shiny, whitish-silvery color, are histologically similar to tendons, and are very sparingly supplied with blood vessels and nerves. When dissected, aponeuroses are papery and peel off by sections.
Which is an example of an aponeurosis quizlet?
An aponeurosis is a broad sheet of dense connective tissue that connects a muscle to another muscle or to bone. An example of an aponeurosis is the galea aponeurotica, the origin of the frontalis. Skeletal muscles are covered by three continuous layers of connective tissue.
What is an example of aponeurosis?
Aponeuroses are found throughout the human body. Tendons and aponeuroses play a role in attaching muscles to a bone. Some examples of aponeurosis in humans are epicranial aponeurosis, abdominal aponeurosis and the plantar aponeurosis. The abdominal aponeurosis is also referred to as rectus sheath.
What is difference between tendon and ligament?
A tendon serves to move the bone or structure. A ligament is a fibrous connective tissue that attaches bone to bone, and usually serves to hold structures together and keep them stable.
Does aponeurosis connect muscle to muscle?
An aponeurosis is a type of connective tissue found throughout the body. Aponeuroses provide an attachment point for muscles to connect to bone, and can also envelope muscles and organs, bind muscles together, and bind muscles to other tissues. They are important for muscle movement and posture.
What do you mean by aponeurosis?
aponeurosis, a flat sheet or ribbon of tendonlike material that anchors a muscle or connects it with the part that the muscle moves. The aponeurosis is composed of dense fibrous connective tissue containing fibroblasts (collagen-secreting spindle-shaped cells) and bundles of collagenous fibres in ordered arrays.
What is an example of aponeurosis?
Aponeuroses are found throughout the human body. Tendons and aponeuroses play a role in attaching muscles to a bone. Some examples of aponeurosis in humans are epicranial aponeurosis, abdominal aponeurosis and the plantar aponeurosis. The abdominal aponeurosis is also referred to as rectus sheath.
Key Difference
The main difference is that Aponeurosis connects the muscles of the body to other muscles which necessitate help, while the tendons serve as a link between the muscles and the bones. Both these structures individually perform functions that are associated with muscles, which contribute to the optimal functioning of the body.
Aponeurosis
These are ribbon or flat sheets of tendon-like substances anchoring muscles or connecting them with the part that muscles move.
Tendon
Tough, whitish cords with differing thickness and length, lacking elasticity.
Key Differences Between Aponeurosis And Tendon
The table below depicts the differences between Aponeurosis And Tendon.
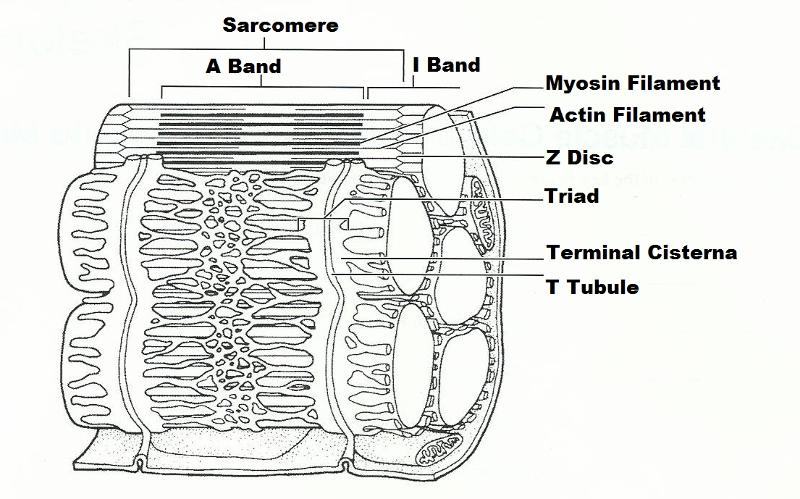
What are myofibrils made of?
myofibrils are composed of repeating contractile elements known as
What is the difference between aponeuroses and tendons?
Aponeuroses are thick membranes that separate muscles from one another. They are tough and resilient. Tendons are similar, in both function and composition, only they serve to connect muscles to bones. Both aponeuroses and tendons are capable of resisting considerable tension.
What is connective tissue?
connective tissue ensheathing a bundle of muscle cells.
Which fibers attach muscle to bone?
cord of collagen fibers that attaches muscle to bone.
Which type of tissue attaches muscles to the coverings of adjacent muscles?
broad fibrous sheets of connective tissue that attach muscles to the coverings of adjacent muscles
What is connective tissue?
Connective tissue ensheathing a bundle of muscle cells
What is the term for a band of white fibrous connective tissue?
A aponeurosis is a sheet of white fibrous connective tissue; a tendon is a band or cord of the same tissue.
What is the name of the neuron that simulates skeletal muscle?
A motor neuron and all the skeletal muscle cells it simulates
Where is the banded apperance found?
A long filamentous organelle with a banded apperance found within muscle cells