- The active site possesses a specific geometrical shape and chemical signals that allow the specific recognition and binding between an enzyme and a substrate.
- An active site will allow the specific substrate to bind whose shape complements the shape of an active site. ...
- The active site of an enzyme catalyzes many chemical or biological pathways.
How does an enzyme's active site relate to its substrate?
- The active site possesses a specific geometrical shape and chemical signals that allow the specific recognition and binding between an enzyme and a substrate.
- An active site will allow the specific substrate to bind whose shape complements the shape of an active site. ...
- The active site of an enzyme catalyzes many chemical or biological pathways.
What is the difference between enzyme and active site?
enzymes. …of the enzyme, called the active site, binds to the substrate. The active site is a groove or pocket formed by the folding pattern of the protein. This three-dimensional structure, together with the chemical and electrical properties of the amino acids and cofactors within the active site, permits only a…
What is the role of active site of an enzyme?
| active site
- Definition. The active site of an enzyme is the region that binds substrate molecules. ...
- The role of enzymes. Enzymes catalyze countless chemical reactions. ...
- Features that Determine Active Site Specificity. ...
- Active Site Binding Theories. ...
- Examples of Enzymes. ...
What do you mean by active site of the enzyme?
The active site of an enzyme is the region where specific substrates bind to the enzyme, catalyzing the chemical reaction. Substrate binding site along with the catalytic site form the active site of the enzyme. The enzyme binds with a specific substrate in order to catalyze a chemical reaction that changes the substrate in some way.

What is the relationship between substrate and enzyme activity?
The relationship between rate of reaction and concentration of substrate depends on the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate. This is usually expressed as the Km (Michaelis constant) of the enzyme, an inverse measure of affinity.
What is the relationship between an active site and a substrate quizlet?
A substrate binds to an enzyme at the active site, which has a complementary shape, and the substrate is converted to product.
What is the relationship between an enzyme reactants active site and substrate and products?
In some reactions, a single-reactant substrate is broken down into multiple products. In others, two substrates may come together to create one larger molecule. Two reactants might also enter a reaction, both become modified, and leave the reaction as two products. The enzyme's active site binds to the substrate.
What is the relationship between substrate and the product?
Substrates are the starting material of the reaction whereas products can be obtained at the end of the reaction. The difference between substrate and product is that the substrate is the starting material of a chemical reaction whereas product is the compound obtained after the completion of the reaction.
How does an enzyme interact with its substrate quizlet?
As temperature rises the enzyme and substrate molecules move faster, collisions will happen more frequently so substrate molecules will enter the active site more frequently. Also when they do collide they will have sufficient activation energy to react. It is easier for bonds to be broken so the reaction can occur.
What is a substrate in relation to an enzyme?
In biochemistry, the substrate is a molecule upon which an enzyme acts. Enzymes catalyze chemical reactions involving the substrate(s). In the case of a single substrate, the substrate bonds with the enzyme active site, and an enzyme-substrate complex is formed.
Why is the active site of an enzyme important?
An active site contains a binding site that binds the substrate and orients it for catalysis. The orientation of the substrate and the close proximity between it and the active site is so important that in some cases the enzyme can still function properly even though all other parts are mutated and lose function.
What happens when enzymes bind to a substrate?
When binding to a substrate, enzymes may undergo an induced fit. This is the change in enzyme shape to accommodate and bind to a substrate. Although it's true all substrates are specific for their enzymes, you can imagine this is just like a little tweak to the enzyme-substrate complex to make the reaction occur.
What happens to amino acids in the active site of an enzyme?
In the active site, amino acids of the enzyme protein will bind to the substrate. The substrate fits perfectly into the active site of an enzyme, meaning that enzymes are specific for their substrates and not any others. Lactase cannot break down any other disaccharide besides lactose.
How does lactase start its reaction?
Lactase starts its reactions by binding to its substrate. A substrate is the substance or molecule on which an enzyme functions. So, the substrate for lactase is lactose. Together with enzymes, substrates form an enzyme-substrate complex. Enzymes like lactase are block-like, globular proteins with pockets.
What is the active site of lactase?
These pockets contain the active site, which is the area of an enzyme where the substrate binds and the chemical reaction takes place. In the active site, amino acids of the enzyme protein will bind to the substrate.
How do enzymes help break molecules apart?
Enzymes can break molecules apart, build or add molecules, and even rearrange them. In lowering the activation energy of a reaction, enzymes decrease the barrier to starting a reaction. It's important to note, however, that the change in energy remains the same between the start and end of a chemical reaction.
What is an enzyme?
Lesson Summary. In summary, enzymes are proteins that lower the activation energy of a chemical reaction.
Why are enzymes important in chemical reactions?
The presence of enzymes is analogous to decreasing the size of the hill in your backyard. Enzymes make things easier for your cell and help chemical reactions occur.
Why do substrates bind to the active site of an enzyme?
Substrates bind to the active site of the enzyme in order to specifically accelerate a particular chemical reaction. The active site of an enzyme comprises a substrate binding site and a catalytic site.
Why does an enzyme bind to a specific substrate?
The enzyme binds with a specific substrate in order to catalyze a chemical reaction that changes the substrate in some way. The substrate is smaller in size than its enzyme. The substrate is perfectly oriented inside the enzyme by the active site. One or more substrate binding sites can be found in an enzyme.
What is the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
These amino acid chains fold into their 3D structures, producing the active form of enzymes. This folding creates a pocket in the enzyme called active site. Substrates specifically bind to the active site of the enzyme, increasing the rate of the biochemical reactions that occur in the body.
What is the inactive form of an enzyme called?
The polypeptide or protein part of the enzyme complex is referred to as the apoenzyme. The inactive form of the apoenzyme in the originally synthesized structure is known as the proenzyme or zymogen. Several amino acids are removed from the zymogen in order to convert the polypeptide part into an apoenzyme.
What are the molecules that enzymes act on?
The molecules that enzymes act upon are called substrates. Different molecules that are created by the action of an enzyme upon a particular substrate are called products. Enzymes catalyze biochemical reactions by lowering its activation energy. The catalysis of reaction by an enzyme increases the rate of that particular reaction in the cell.
What is the primary structure of an enzyme?
The activity of an enzyme primarily depends on its amino acid sequence of the protein chain. Enzymes are synthesized as a linear sequence of amino acids called its primary structure. The primary structure spontaneously folds into a 3D structure that is composed of alpha helices and/or beta sheets called secondary structure. The secondary structure of the enzyme folds again into a compact 3D structure called the tertiary structure. The tertiary structure of the enzyme exists in its inactive form.
How are biochemical reactions in living cells catalyzed?
Biochemical reactions in living cells are catalyzed by enzymes. The enzymes are synthesized in their inactive form which subsequently converts into the active form. The activity of an enzyme is determined by the amino acid sequence of the primary structure. Substrates bind to the active site of the enzyme in order to specifically accelerate ...
Where is the active site of an enzyme?
The active site is found deep inside the enzyme, which resembles a hole or small depression. An active site is a region combining the specific substrate molecule with the enzyme and thus catalysing the reaction. As we know the enzyme is “ Highly specific ” molecule, its specificity is due to the active site that allows the binding ...
How does an enzyme's active site lower the activation energy?
Therefore, we can conclude that an enzyme’s active site lowers the activation energy by increasing the rate of reaction. The substrate’s energy level is higher than that of a product but lower than the transition state of the substrate.
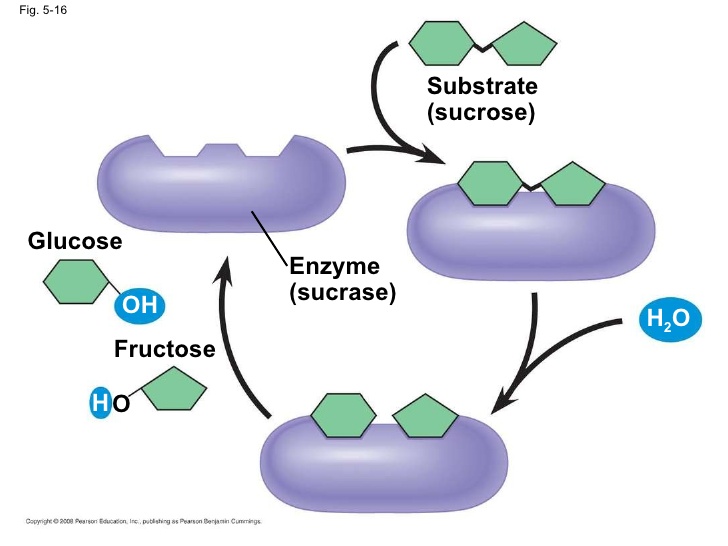
What happens when sucrose is a substrate?
Then, a reaction between sucrase and sucrose takes place. The reaction will change the sucrose’s structural conformation called “ Transition state of the Sucrose ”. The change in sucrose’s structural configuration leads to the conversion of the E-S complex into the E-P complex. At last, glucose and fructose are released as products form the sucrase enzyme.
What is the binding activity of an enzyme?
Binding Activity: The binding activity is a property of the enzyme’s active site, which increases the binding affinity of the substrate towards an enzyme. Catalytic activity: It is a property of an enzyme’s active site, which aids in the catabolic reaction of the enzyme and substrate to yield product by reducing the activation energy.
Why is enzyme specific?
As we know the enzyme is “ Highly specific ” molecule, its specificity is due to the active site that allows the binding of a particular substrate. The amino acid residues are present around the active site, which holds the substrate molecule in the right position during biochemical reactions. The substrate molecule shows a high binding affinity ...
What happens to the substrate in an enzyme catalyzed reaction?
In an enzyme-catalyzed reaction, the substrate will attach to the enzyme’s active site. A specific substrate will bind to the active site of an enzyme. As a result, an “ Enzyme-substrate complex ” forms. In the E-S complex, the substrate on enzyme activity will convert into a product. At last, the products get released, and the enzyme becomes free.
How many amino acids are in an active site?
About 10-15 amino acid residues combine to form an active site. The active site possesses a specific geometrical shape and chemical signals that allow the specific recognition and binding between an enzyme and a substrate. An active site will allow the specific substrate to bind whose shape complements the shape of an active site.
