
An industrial furnace is a direct fired device used to provide heat for industrial processes that require heat in excess of 400° C (752° F). Through the combustion of fuels and gases, raw materials and products are heated by direct or indirect contact.
What is a furnace and how does it work?
Derived from the Latin word fornax, meaning oven, a furnace is a large heating appliance designed to evenly distribute heat throughout a building. Furnaces accomplish this by burning fuel internally to warm air, water or steam, then directing this warmth into various parts of a building to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature.
What is a blast furnace and how does it work?
The blast furnace is a huge, steel stack lined with refractory brick, where iron ore, coke and limestone are dumped into the top, and preheated air is blown into the bottom. The hot air that was blown into the bottom of the furnace ascends to the top in 6 to 8 seconds after going through numerous chemical reactions.
How does a high-efficiency furnace work?
How do High Efficiency Furnaces work? Second Heat Exchanger. Remember above, where we said that in traditional furnaces, 20% - 35% of the energy going into your furnace is wasted? Sealed Combustion Chambers. Traditional furnaces draw in cold air from the surrounding environment into the combustion chamber for it to be heated and circulated throughout your home. Multi-stage burners. ...
How to find a new furnace?
Furnaces typically have their model and serial number in an easy, accessible place. Check the inside top section of the furnace. The information you need should be located on the sidewall on a sticker or plate. If your furnace is a down flow unit, the information might be located in the lower compartment instead of the top part.

How does a furnace work step by step?
0:445:46How a Furnace Works | Repair and Replace - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe exhaust fumes are released through the flue gas vent. The blower fan then pushes air over theMoreThe exhaust fumes are released through the flue gas vent. The blower fan then pushes air over the heat exchanger. And circulates it around your home the furnace runs until the thermostat detects.
How does a refinery furnace work?
0:283:45Direct Fired Heater | Furnace | Refinery | Oil&Gas - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWe need heat energy in heater. So produce the heat energy in heater. And using the fuel gas or fuel.MoreWe need heat energy in heater. So produce the heat energy in heater. And using the fuel gas or fuel. Oil a fuel is released as a heat energy by the process of combustion.
How hot can an industrial electric furnace get?
Electric furnaces to preheat or dry components up to a variety of temperatures (50°C to 700ºC/120°F to 1,290°F).
How does a metal furnace work?
They use coiled heating elements embedded within a crucible or integrated into the walls of the heating chamber itself. These convert electrical energy into heat which is radiated through the material with outstanding degrees of thermal uniformity.
Why do refineries do burn offs?
When refineries lose power, that pressure needs to be released. The petroleum product is sent up tall stacks, where it is burned off by the stack-top flares, causing flames and heavy smoke. The burn-off is a safety mechanism that prevents chemicals from spreading through the refinery, officials said.
What are the 3 basic steps in the refining process?
All refineries have three basic steps: separation, conversion and treatment. During the separation process, the liquids and vapors separate into petroleum components called factions based on their weight and boiling point in distillation units.
How long does an industrial furnace last?
Yet, sooner or later, even the best system will reach the end of its functional life. Proactive, ongoing maintenance can significantly prolong any unit's performance, but knowing when to make a big change remains essential. Generally, a commercial HVAC system will last anywhere from 10 to 15 years.
What is the hottest furnace ever made?
Death Valley National Park's Furnace Creek Visitor Center hit an astonishing 130.0 degrees Fahrenheit (54.4°C) on Friday afternoon, July 9, 2021, beating the previous world record of 129.9 degrees Fahrenheit (54.4°C), set there on August 16, 2020.
What is the hottest furnace in the world?
For ultra high temperature requirements, MRF has several furnace capable of continuous operating at 3000°C (5430 F). Not many materials can handle these extreme temperatures, hot zones are available in Graphite or Tungsten.
How are steel furnaces powered?
The open-hearth furnace (OHF) uses the heat of combustion of gaseous or liquid fuels to convert a charge of scrap and liquid blast-furnace iron to liquid steel. The high flame temperature required for melting is obtained by preheating the combustion air and, sometimes, the fuel gas.
What temperature does a metal furnace melt?
As the energy from the coil transfers to the metal inside the crucible, it heats the metal to its desired point. These heating points are extremely hot, as the melting point of steel is 1370 degrees Celsius, or 2500 degrees Fahrenheit.
How hot does a steel furnace get?
The hot blast temperature can be from 900 °C to 1300 °C (1600 °F to 2300 °F) depending on the stove design and condition. The temperatures they deal with may be 2000 °C to 2300 °C (3600 °F to 4200 °F).
How does an oil heating furnace work?
For an Oil Furnace System: The burner turns the oil into a fine spray, mixes it with air and ignites it in the combustion chamber (6), causing the chamber to become very hot. Air absorbs heat in the heat exchanger (7). A blower (8) sends this air through ducts (9) to heat the home.
How do refinery boilers work?
0:184:30Boiler, How it works? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe hot gas that is produced travels all over the boiler. The first heat absorption unit of theMoreThe hot gas that is produced travels all over the boiler. The first heat absorption unit of the boiler is an economizer highly pressurized water supplied by the feed water pump enters.
What is the difference between furnace and heater in refinery?
Conventional process heaters are used to preheat hydrocarbon fluids, or occasionally other compounds, for subsequent processing in other unit operations. Chemical reaction furnaces are used where a chemical process is carried out inside the furnace tubes.
How does a heat exchanger work in a refinery?
How Does a Heat Exchanger Work? Heat exchangers function by bringing a cooled fluid into close contact with a hot industrial process or piece of equipment. This allows for an exchange of the heat between the two mediums by using the principles of thermal heat conduction.
What is the area of the radiant section just before flue gas enters the shield section and into the convection?
The area of the radiant section just before flue gas enters the shield section and into the convection section called the bridgezone. A crossover is the tube that connects from the convection section outlet to the radiant section inlet.
How does a furnace burn?
Fuel flows into the burner and is burnt with air provided from an air blower. There can be more than one burner in a particular furnace which can be arranged in cells which heat a particular set of tubes. Burners can also be floor mounted, wall mounted or roof mounted depending on design. The flames heat up the tubes, which in turn heat the fluid inside in the first part of the furnace known as the radiant section or firebox. In this chamber where combustion takes place, the heat is transferred mainly by radiation to tubes around the fire in the chamber.
What is the gas that is released from a furnace?
The gases from the combustion are known as flue gas. After the flue gas leaves the firebox, most furnace designs include a convection section where more heat is recovered before venting to the atmosphere through the flue gas stack. (HTF=Heat Transfer Fluid.
How does a stack damper work?
The stack damper contained within works like a butterfly valve and regulates draft (pressure difference between air intake and air exit) in the furnace, which is what pulls the flue gas through the convection section. The stack damper also regulates the heat lost through the stack. As the damper closes, the amount of heat escaping the furnace through the stack decreases, but the pressure or draft in the furnace increases which poses risks to those working around it if there are air leakages in the furnace, the flames can then escape out of the firebox or even explode if the pressure is too great.
How does a sootblower work?
Sootblowers utilize flowing media such as water, air or steam to remove deposits from the tubes. This is typically done during maintenance with the air blower turned on. There are several different types of sootblowers used. Wall blowers of the rotary type are mounted on furnace walls protruding between the convection tubes. The lances are connected to a steam source with holes drilled into it at intervals along its length. When it is turned on, it rotates and blows the soot off the tubes and out through the stack.
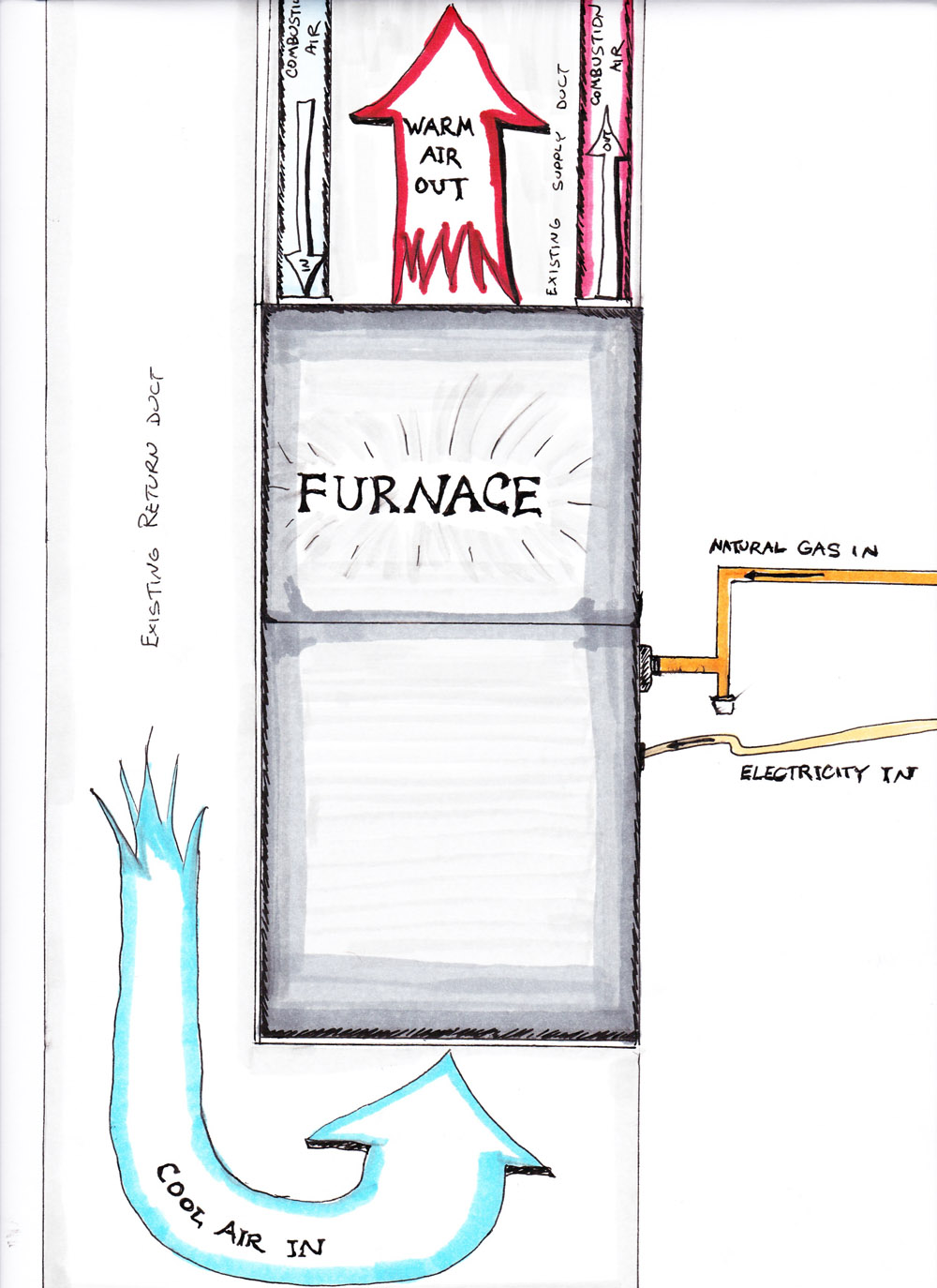
How does a furnace generate heat?
Heat is generated by an industrial furnace by mixing fuel with air or oxygen, or from electrical energy. The residual heat will exit the furnace as flue gas.
What is an industrial furnace?
An industrial furnace, also known as a direct heater or a direct fired heater, is a device used to provide heat for an industrial process, typically higher than 400 degrees celsius. They are used to provide heat for a process or can serve as reactor which provides heats of reaction. Furnace designs vary as to its function, heating duty, ...
What is a gas cleaning system?
Cleaning systems involve semi-dry acid gas-cleaning plants, flue gas desulphurization plants (which strip SO2 from exhausts and convert it to gypsum), 8 and various other types of wet process gas-cleaning plants, and enhanced all-dry scrubbing systems. Table 3.3 provides a range of exhaust gas applications.
What temperature is a flue gas?
Depending on the combustion or melting process involved, the flue gases can be quite mild, or alternatively explosive and aggressive, with temperature ranging from 65°C to well over 600°C.
What is an incinerator?
An incinerator is a combustion device that uses a closed flame technology to incinerate or destroy waste materials. These devices are not classified as industrial furnaces because they are not necessarily permitted to make any useful product. Incinerator regulations date back to 1980 and are found in 40 CFR Part 264/265, Subpart O. The types of standards for incinerators are similar to those for industrial furnaces; however, incinerators are not necessarily engaged in “energy recovery” but rather waste destruction. Because of this unique aspect of incineration, many of the more toxic wastes, for example, D/F wastes, are only burned in incinerators. The EPA recognized the human health risk involved in burning these wastes and similar to industrial furnaces, incinerators typically have to meet the DRE of four nines (99.99%) for POHCs. In addition, many incinerators burn and destroy D/F waste and because of this they have to meet the most stringent standard of a DRE of six nines (99.9999%) when burning these materials.
What are hazardous wastes?
Hazardous wastes have long been burned both as a means of disposal and as a source of energy. Utilities such as Duke Power and Northern Indiana Public Service Co. have burned tar-laden dirt from manufactured gas plants in both pulverized coal and cyclone boilers. Many utilities are permitted to burn their own waste oils. Manufacturing industries have burned their own wastes as well. Over the past 30 years, hazardous wastes have entered the blending fuels arena, being supplied to cement kilns and industrial boilers. This practice has led to the promulgation of the Boiler and Industrial Furnace (BIF) regulations by the USEPA. Most significantly, this practice has been used by cement kilns and other industries as a means of reducing fuel costs as a component of product manufacturing costs.
What is the temperature of an industrial furnace?
Industrial furnaces using fossil fuels are characterized by heat losses from flue gases with a temperature of 500 °C and above.
How much power does a hard coal furnace have?
The thermal efficiency of the furnace is 80%, the one of the stove 70%. The industrial furnace is assumed to be fuelled with the average Western European hard coal supply mix, the stove either with coke or with briquettes.
How does a semi dry gas absorber work?
During the semi-dry gas-cleaning process, a liquid, usually a lime slurry, is injected into the flue gas by means of one or more spray nozzles at the top of an absorption tower. The slurry then reacts with the pollutants. Some of the liquid will evaporate into the gas stream, and it is possible with careful flow control to arrange that the effluent at the bottom of the absorber is effectively dry.
How is Furnace Energy Efficiency Measured?
The energy efficiency of your furnace is dependent on its Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), which basically tells you how much of your fuel is used for heating and how much is lost due to combustion (usually out of your vents).
What is a furnace problem?
When there is a problem with your furnace, it is usually the thermostat ( control system ), gas valve/thermocouple/heat exchanger ( heat source ), or the blower/air handler/ductwork ( distribution system ). In any case, a trained and qualified HVAC technician will be able to fix the problem quickly and effectively.
How does a furnace start?
Your furnace starts when it receives a signal from the thermostat that tells it to turn on. Depending on the temperature you set, when the thermostat detects the air temperature dropping below that number, it activates the furnace.
What is the percentage of AFUE in a furnace?
The remaining 10% is lost. High-efficiency furnaces have AFUE percentages above 90%. Think of AFUE as the gas mileage of your furnace.
What happens when the thermostat detects the air temperature dropping below the number?
Depending on the temperature you set, when the thermostat detects the air temperature dropping below that number, it activates the furnace. When the thermostat sends its signal to the furnace, the furnace gas valve opens and ignites the burner component beneath the combustion chamber.
How does a gas valve work?
The gas valve works with the thermostat to regulate the amount of gas that flows into your furnace. If your gas valve is working fine, but the furnace isn’t turning on, check to make sure your pilot light is on.
What is furnace 101?
Welcome to Furnace 101, where we teach you the basics of your furnace and how it works to provide heating to your home.
Why do furnaces quench?
Quenching furnaces feature an enclosed heating chamber to prevent low-temperature processes, such as phase transformations. The furnace’s controlled, rapid cooling hardens the material. This furnace process aims to avoid uneven heating and overheating, but the tempering technique may be performed after quenching to increase toughness.
Why use a tempering furnace?
To access the best balance of strength and elasticity, tempering furnaces are often used in conjunction with quenching furnaces. It is crucial that these furnaces maintain uniform temperature levels throughout the chamber to achieve the desired material characteristics. Both gas and electric heating types of these furnaces offer indirect fuel contact.
How long do oil furnaces last?
Most new oil-fired furnaces have AFUE ratings of 80 to 90 percent and are popular in areas with limited access to natural gas. With a lifespan of 30 years, oil furnaces tend to be less expensive than gas furnaces, but oil (often imported) is more expensive than gas and prices can be volatile. Oil furnaces require an on-site storage tank. In terms of maintenance, oil-fired furnaces develop deposits of soot and carbon on the heat exchanger surfaces which require periodic removal to maintain efficiency. In addition, the nozzle on the burner unit may need to be replaced as well as the oil filters used to remove impurities from the fuel prior to the oil being vaporized and ignited.
How do furnaces heat up?
Furnaces in industrial settings heat up materials using fuel and combustion gases. The material may be in direct contact with the fuel and its gases ( blast furnaces ), indirect contact with the fuel but still in direct contact with the gases (reverberatory), or indirect contact with both fuel and gases (muffle furnaces). Nevertheless, the goal remains the same — attaining a high level of heat.
What is a wood burning furnace?
Wood-burning furnaces are a viable option for heating homes in areas where firewood is plentiful and affordable. Wood is burned in a firebox and the heat is circulated through ductwork in the same manner used in oil and gas furnaces. Wood burning furnaces have to be fuelled manually and the fire has to be tended, meaning these are impractical if you want the house to be heated while you are absent for an extended period. Wood furnaces are therefore often part of a combination furnace where an oil or gas burner functions as a backup heat source.
What percentage of homes use gas furnaces?
Gas-Fired Furnaces. Gas-fired furnaces are used in about 57 percent of American homes, making gas the most commonly-used heating fuel. While gas furnaces are more expensive than oil furnaces, paying for the installation of a municipal gas line may add to the costs. New gas furnaces have an AFUE rating of 89 to 98 percent.
How does a furnace generate heat?
Furnaces provide heat to homes and other buildings by blowing heated air through ducts that deliver warmth to different rooms . The heat energy that fuels a furnace may be generated through fuel combustion, electricity, and other means. Considerations include the cost of the furnace itself, the cost of the fuel used, venting requirements, and the Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE), which indicates the efficiency of the furnace’s combustion. The first part of this article will explore different types of furnaces classified by the fuel or method by which heat energy is generated:
What is a cupola furnace?
A cupola melting furnace typically comprises a vertical heating chamber in a shaft-like arrangement, which is filled with layers of combustible matter such as coke and limestone. Inlets allow air into the chamber to facilitate combustion while a working door enables easy access to the lowest portion of the cupola. This is where raw materials are reduced to a molten mixture that can be periodically extruded through the drop-bottom spout.
How does an induction furnace work?
Induction melting furnaces operate on a radically different principle to the cupola version. They use coiled heating elements embedded within a crucible or integrated into the walls of the heating chamber itself. These convert electrical energy into heat which is radiated through the material with outstanding degrees of thermal uniformity.
What is a melting furnace?
Melting furnaces are used to overheat solid materials until they liquefy. Often, thermal processing equipment is used to alter the surface or internal characteristics of materials by carefully elevating their temperature. In the case of metals, this typically increases ductility at the expense of both hardness and strength.
How to achieve homogeneous molten mixture?
To achieve a homogeneous molten mixture, the melting furnace must be capable of generating and maintaining the requisite temperatures over a sustained period. There are several melting furnace architectures capable of performing this process.
Why use a helically wound induction coil?
Helically-wound induction coils engineered from refractory heating metals and ceramics improve service longevity and enable good compatibility with additional controls. Thermal cycling can be automated and additional controls can be implemented to reduce the generation and emission of toxic metal vapors in metal melting furnaces.
Why do metals need furnaces?
In the case of metals, this typically increases ductility at the expense of both hardness and strength. This requires an industrial furnace capable of generating and maintaining temperatures below that of the material’s melting point.
What happens when a furnace melts?
A melting furnace, by comparison, generates overhot temperatures that exceed the metal’s melting point and cause decomposition of its physical structure which leads to liquefaction. This phase transition is utterly dependent on both temperature and pressure.
Why does my induction furnace hum?
An operating induction furnace usually emits a hum or whine (due to fluctuating magnetic forces and magnetostriction ), the pitch of which can be used by operators to identify whether the furnace is operating correctly or at what power level.
What is the advantage of an induction furnace?
The advantage of the induction furnace is a clean, energy-efficient and well-controllable melting process compared to most other means of metal melting. Most modern foundries use this type of furnace, and now also more iron foundries are replacing cupolas with induction furnaces to melt cast iron, as the former emit much dust and other pollutants.
Why is the temperature of a material not higher than required to melt it?
Since no arc or combustion is used , the temperature of the material is no higher than required to melt it; this can prevent loss of valuable alloying elements.
How many tons of metal can be melted in a furnace?
Power supplies range from 10 kW to 42 MW, with melt sizes of 20 kg to 65 tons of metal respectively.
What frequency is used to melt metal?
Operating frequencies range from utility frequency (50 or 60 Hz) to 400 kHz or higher, usually depending on the material being melted, the capacity (volume) of the furnace and the melting speed required. Generally, the smaller the volume of the melts, the higher the frequency of the furnace used; this is due to the skin depth which is a measure of the distance an alternating current can penetrate beneath the surface of a conductor. For the same conductivity, the higher frequencies have a shallow skin depth—that is less penetration into the melt. Lower frequencies can generate stirring or turbulence in the metal.
How does a coil work?
The coil creates a rapidly reversing magnetic field that penetrates the metal. The magnetic field induces eddy currents, circular electric currents, inside the metal, by electromagnetic induction. The eddy currents, flowing through the electrical resistance of the bulk metal, heat it by Joule heating. In ferromagnetic materials like iron, the ...
Is there a disposable refractory lining?
There is a disposable refractory lining used during casting, depending on alloy mixture.
Chapter Two – How Industrial Furnaces Work
Chapter Three – Types of Industrial Furnaces
- Furnaces serve the dual purposes of providing heat and assisting in production. Industrial uses of furnaces tend to center around the annealing, melting, tempering, and carburizing of metals. Though these are critical functions of furnaces, they serve far more purposes and come in designs to fit those differing functions. Residential furnaces are simple devices designed to pro…
Chapter Four – Methods For Heating Furnaces
- Heat is generated in a furnace using a variety of methods, including the burning of a fuel or the conversion of electricity to heat. The most common type of furnace is fuel powered due to the expense of electricity. Though various forms of fuel are the most economical, there are processes where electricity has an advantage over fuels. How a furnace is powered makes a difference in it…
Chapter Five – Furnace Regulations
- The major concern with industrial furnaces is their emissions, which are regulated by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The federal New Source Performance Standards (NSPS) have stipulations regarding the size, function, and construction of industrial furnaces. The emissions of greatest concern are listed as Hazardous Air Pollutants (HAP). Furnace operation…
Conclusion
- An industrial furnace is a direct fired device used to provide heat for industrial processes that require heat in excess of 400° C (752° F).
- Through the combustion of fuels and gases, raw materials and products are heated by direct or indirect contact.