
How does the liver work?
What is the hepatic portal vein?
What is the blood supply of the liver?
Which artery enters the hepatoduodenal ligament?
Which artery gives rise to the left gastric artery?
Where is lymph produced in the liver?
What is referred pain?
See 4 more
About this website
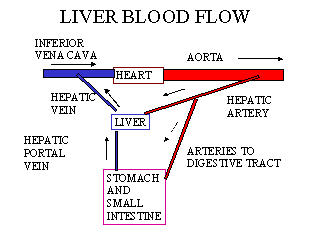
How does blood flow from the liver?
Blood leaves the liver through the hepatic veins. This blood is a mixture of blood from the hepatic artery and from the portal vein. The hepatic veins carry blood to the inferior vena cava—the largest vein in the body—which then carries blood from the abdomen and lower parts of the body to the right side of the heart.
How does blood enter and leave the liver?
Blood enters the liver through the hepatic artery and the portal vein. The blood from the hepatic artery carries oxygen and helps support liver growth. The portal vein carries blood and nutrients from the intestine and delivers them to the liver cells (hepatocytes), which perform specific liver functions.
How much blood flow does the liver get?
between 800 and 1200 mL/minTotal hepatic blood flow ranges between 800 and 1200 mL/min, which is equivalent to approximately 100 mL/min per 100 g liver wet weight[4]. Although the liver mass constitutes only 2.5% of the total body weight, the liver receives nearly 25% of the cardiac output.
How often does blood pass through the liver?
Every two and a half minutesThe liver's blood supplies The liver is a reddish brown colour because it is saturated in blood. Every two and a half minutes a gallon of blood passes through the liver's complicated network of arteries, veins and capillaries.
Why does blood go to the liver first?
Nutrient-rich blood leaves the gastrointestinal tract and is first brought to the liver for processing before being sent to the heart. Here, carbohydrates and amino acids can be stored or used to make new proteins and carbohydrates.
Does liver get blood from heart?
The hepatic artery provides the remaining one third of blood. This oxygen-rich blood comes from the heart and provides the liver with about half of its oxygen supply.
Does all blood go through liver?
All the blood leaving the stomach and intestines passes through the liver. The liver processes this blood and breaks down, balances, and creates the nutrients and also metabolizes drugs into forms that are easier to use for the rest of the body or that are nontoxic.
Which organ gets the most blood flow?
Logic of the KidneyHighest blood flow per unit organ weight.Little or no anastomoses beyond the large segmental renal artery.Large functional arteriovenous shunt.
Which organ receives the most blood?
the liverAt any moment in time, the majority of the body's blood will be contained within the cardiovascular system. In terms of which organ has the most blood pumped into it however, the liver gets the greatest share of the body's circulating blood by comparison with all other organs.
How much blood does the liver filter in a day?
At any given time your liver contains about 10 percent of your body's total blood volume, and it filters 1.4 liters of blood per minute.
Does blood get filtered in the liver?
The liver filters or detoxifies the blood. Almost all the blood in your body passes through the liver. As blood passes through the liver, it breaks down substances, such as prescription or over-the-counter drugs, street drugs, alcohol, and caffeine.
How much blood does the liver filter every minute?
A healthy liver filters about 1.7 litres of blood per minute. It contains 300 billion specialized cells. As far back as 400 BC, the importance of bile was recognized.
Does the liver regulate blood flow?
The liver is not capable of directly controlling portal blood flow. Yet, as will be discussed, the liver can have very significant indirect effects to regulate portal blood flow via mechanisms impacting on blood flow to the splanchnic organs that drain into the portal vein.
How many blood vessels supply the liver?
The walls of large blood vessels, like the aorta and the vena cava, are supplied with blood by vasa vasorum. This term translates to mean "vessel of a vessel." Three types of vasa vasorum exist (1) vasa vasorum internae, (2) vasa vasorum externae, and (3) venous vasa vasorae.
Which organ has the greatest blood flow per 100g of tissue?
Renal blood flow comprises 20–25% of the cardiac output, i.e., the perfusion rate per tissue mass exceeds that of any other organ.
Chapter 65 – Liver: Anatomy and Blood Supply | Anesthesia Key
Abstract The liver is the largest solid organ in the body (the skin is overall the largest organ) and receives a large volume of blood. At rest, the liver receives around 25% of the cardiac output (approximately 1500 mL/min). Unlike other organs, the liver receives a dual blood supply. Chapter 65 Liver: Anatomy and Blood…
Liver blood flow: Physiology, measurement, and clinical relevance
Visit the post for more. Hepatic Artery. The hepatic artery normally supplies about 25% of the total blood flow to the liver, or 30 mL/min per 100 g of liver tissue; however, it provides 30% to 50% of the liver’s oxygen requirement because of the greater oxygen content found in arterial blood.
Liver Blood Vessel - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
Cecilia G. Ethun, Shishir K. Maithel, in Blumgart's Surgery of the Liver, Biliary Tract and Pancreas, 2-Volume Set (Sixth Edition), 2017 Anatomy and Classification. Precise knowledge and mastery of the surgical anatomy of the liver, blood vessels, and biliary channels is essential to perform partial hepatectomy (see Chapter 2).The liver is divided into sections (previously called sectors) that ...
National Center for Biotechnology Information
National Center for Biotechnology Information
What is the hepatic venous system?
The hepatic venous system is the systemic drainage tract of the entire splanchnic circulation. A total liver blood flow (LBF) of 1.5 L/min is considered the normal value in the average male, but the range can be quite wide (1 to 2 L/min). Although the free pressure in a hepatic vein is 1 to 2 mm Hg, the wedged hepatic venous pressure, which is useful for estimating sinusoidal pressure, may be an indicator of portal venous pressure (Boyer et al, 1977). The sinusoidal pressure is estimated to be slightly higher than that of the vena cava, or 2 to 4 mm Hg (Eipel et al, 2010). Hepatic venous blood is normally about two-thirds saturated with oxygen, but this may be markedly reduced during periods of low delivery of oxygen to the liver, when oxygen is extracted by hepatocytes. In resting states, the liver accounts for approximately 20% of the total oxygen consumption of the body.
Why is propofol used in vivo?
Propofol and other high extraction ratio drugs are sometimes used as an in vivo probe to investigate hepatic blood flow. Indeed, after completion of enzyme maturation, changes in clearance for high extraction ratio drugs can be assumed to mainly reflect changes in hepatic blood flow.
What is the mean blood pressure in the hepatic artery?
The mean blood pressure in the hepatic artery is approximately 90 mm Hg and that in the portal vein is approximately 10 mm Hg, resulting in a sinusoidal capillary pressure of 2–3 mm Hg.
Where does blood flow to the hepatic sinuses?
In accordance with macroscopic blood flow, approximately two-thirds of the intrahepatic blood supply ultimately comes from the portal venules, whose inlets are controlled by sphincters—afferent or inlet sphincters—composed of sinusoidal endothelial cells. For the remaining third of blood supply, arterial blood flow to the sinusoids is intermittent and determined by independently contractile smooth muscle sphincters in the walls of hepatic arterioles and their arteriolosinusoidal branches. Blood flowing into a group of sinusoids could therefore be arterial, venous or mixed, depending on sphincteric activity of entering venular and arteriolar channels and the distance of the originating sinusoid from the portal tract along the penetrating venule.
What is the total hepatic blood flow?
Total hepatic blood flow in normal adults under resting conditions is between 1500 and 1900 mL/min, or approximately 25% of cardiac output. 91 Of this, about two-thirds is supplied by the portal vein and the remainder by the hepatic artery.
What is the normal hepatic blood flow during pregnancy?
Influence of Pregnancy. Normal hepatic blood flow in women is 1500 liter/min/1.73m 2, which is about 34% of the cardiac output. During pregnancy, hepatic blood flow remains unchanged but because of the increased plasma volume and cardiac volume output, the flow represents 28% of cardiac output.
What is shock liver?
The clinical entity known as shock liver has long been recognized, typically related to cardiogenic or hemorrhagic shock ( Birgens et al, 1978 ). Hepatic dysfunction caused by hypoperfusion is manifested pathologically by centrilobular necrosis and clinically by abdominal pain, cholestatic jaundice, and marked elevation of serum aminotransferases. Three phases of liver injury attributed to ischemia were proposed by Champion and colleagues (1976), whereby the initial hepatic dysfunction would resolve as long as no additional insults (e.g., sepsis) were incurred. Gottlieb and colleagues (1983) showed that hepatic dysfunction in humans after trauma was related to a reduced hepatic blood flow rate as much as 70% of resting levels. Hepatic blood flow was markedly reduced after injury, and although total splanchnic oxygen delivery was decreased, oxygen consumption remained normal as a result of increased hepatic extraction.
What is the liver made of?
Liver tissue is made up of lots of smaller units of liver cells called lobules. Many canals carrying blood and bile run between the liver cells. Blood coming from the digestive organs flows through the portal vein to the liver, carrying nutrients, medication and also toxic substances.
What happens when blood sugar is low?
If someone’s blood sugar levels are too low, the liver breaks down glycogen and releases sugar into the blood. As well as sugar, the liver also stores vitamins and minerals (iron and copper), and releases them into the blood when needed.
What is the liver's main function in fat metabolism?
In fat metabolism the liver cells break down fats and produce energy. They also produce about 800 to 1,000 ml of bile per day. This yellow, brownish or olive green liquid is collected in small ducts and then passed on to the main bile duct, which carries the bile to a part of the small intestine called the duodenum.
How does the liver work?
Once they reach the liver, these substances are processed, stored, altered, detoxified, and passed back into the blood or released in the bowel to be eliminated. In this way the liver can, for example, remove alcohol from your blood and get rid of by-products from the breakdown of medications.
What is the role of the liver in the metabolism of proteins?
The liver also plays an important role in the metabolism of proteins: liver cells change amino acids in foods so that they can be used to produce energy, or make carbohydrates or fats. A toxic substance called ammonia is a by-product of this process.
How does the liver help with glucose?
In the metabolism of carbohydrates, the liver helps to ensure that the level of sugar in your blood (blood glucose) stays constant. If your blood sugar levels increase, for example after a meal, the liver removes sugar from blood supplied by the portal vein and stores it in the form of glycogen.
What is IQWiG health information?
IQWiG health information is written with the aim of helping people understand the advantages and disadvantages of the main treatment options and health care services. Because IQWiG is a German institute, some of the information provided here is specific to the German health care system.
What are the terminal branches of the hepatic artery?
Inside the liver, the branches of the hepatic artery dichotomously divide and in the terminal portal tracts they are terminal branches (arterioles). The diameter of the arteriol is 10-15 μm, its wall contains elastic fibers, sometimes - smooth muscle fibers in the form of bundles. Thus, arterioles can form precapillary sphincters. On the periphery of the portal field, the hepatic arterioles perforate the border plate and flow directly into the sinusoids. The walls of the sinusoids are lined with endothelium. Sinusoids are located between the beams (trabeculae) of hepatocytes. The branches of the hepatic artery give their blood to sinusoids both on the periphery and in the center of the lobules.
What is the center of the hexagonal hepatic lobe?
The center of the hexagonal hepatic lobe is the hepatic (central) vein , and on the periphery there is a portal field. The parenchyma of the lobes is formed by radially arranged beams (trabeculae) of hepatocytes, converging to the central (hepatic) vein. Between the beams there are sinusoids, through which the mixed arterio-venous blood flowing from the portal vein and the hepatic artery flows.
What is the diameter of Mesenterica superior?
Mesenterica superior, its largest tributaries are v. corvnaria ventriculi and v. Mesenterica inferior. The length of the portal vein is 6-8 cm, diameter up to 1.2 cm; it does not have valves, it collects blood from the unpaired organs of the abdominal cavity. At the level of the gates of the liver, the portal vein divides into the right branch, ...
Where does blood flow from the terminal hepatic venules?
From the terminal hepatic venules blood enters the sublobular and collective veins, then into the right median and left hepatic veins that flow into the lower hollow vein below where it passes through the opening in the tendon part of the diaphragm into the thoracic cavity.
Which venous vessel perforates the parenchymal border plate and runs into the hepatic sinus?
The terminal venule perforates the parenchymal border plate and runs into the hepatic sinusoids, which thus contain mixed arterial venous blood.
What is the pressure in the portal vein?
Normally, the pressure in the portal vein is 5-10 mm Hg. Or 70-140 mm.vod.st.
Which muscle blocks the hepatic veins?
At the point of confluence in the inferior vena cava, the hepatic veins are blocked by the annular muscle.
What is the liver?
The liver is located in the upper right part of your belly (abdomen). Most of it is protected by your ribs. It is a vital organ that has many jobs. The liver: 1 Makes bile, a substance that helps your body absorb fat 2 Makes proteins and blood-clotting factors that your body needs. 3 Controls sugar (glucose) in the blood and stores extra sugar 4 Works with your stomach and intestines to digest food 5 Controls production and removal of cholesterol 6 Stores vitamins and minerals 7 Removes poisonous (toxic) substances from your blood, as well as many prescription and over-the-counter medicines 8 Regulates other organs, such as the kidneys 9 Is part of the immune system, which helps your body fight infection
Where does blood flow?
Blood flows through the liver. All the blood that flows from the intestines, stomach, and spleen is filtered through the liver. The blood flows into the liver through the hepatic portal vein. It filters through the liver in a system of smaller and smaller veins.
Which vein carries blood from the liver to the heart?
Inferior vena cava. A large vein that carries blood from the liver, intestines, legs, and kidneys to the heart. Hepatic veins. Blood vessels that carry blood out of the liver to the inferior vena cava. Hepatic artery. A blood vessel that carries blood with a fresh supply of oxygen into the liver from the heart.
What happens when blood passes through the liver?
As blood passes over liver cells, these cells process nutrients in the blood. This processing makes products like proteins and sugars that your body can use. Blood is carried out of the liver through the hepatic veins to the heart.
What is the function of the liver?
The liver: Makes bile, a substance that helps your body absorb fat. Makes proteins and blood-clotting factors that your body needs. Controls sugar (glucose) in the blood and stores extra sugar. Works with your stomach and intestines to digest food. Controls production and removal of cholesterol.
What part of the intestine is bile?
Duodenum. The first part of the small intestine. When bile leaves the liver, it flows through the bile ducts into the duodenum. Here, bile starts mixing with food to help digest fat.
Which organ carries blood from the spleen to the portal vein?
An organ that filters blood. It also helps keep your body healthy and free of infection, as part of the immune system. Splenic vein. A blood vessel that carries blood from the spleen to the portal vein. Hepatic portal vein. A blood vessel that carries blood containing nutrients and oxygen from the digestive tract and spleen into the liver.
Why is there insufficient blood flow in the liver?
Inadequate blood flow—into or out of the liver—may result from heart failure or disorders that make blood more likely to clot (clotting disorders). In clotting disorders, a clot may block the portal vein or a hepatic vein, slowing or blocking blood flow. Disorders with blockages in blood flow include.
What is liver failure?
Liver failure is a condition that occurs when a large portion of the liver becomes damaged and unable to function. Sometimes liver failure develops quickly, over several days (acute liver failure); other times, it develops slowly, over months or years (chronic liver failure). There are numerous causes of liver failure. Which of the following is NOT a common cause of liver failure?
What is the disorder where blood clots block blood flow?
Disorders with blockages in blood flow include. Budd-Chiari syndrome, which results when blood clots block blood flow from the liver. Portal vein thrombosis, which is a blockage or narrowing of the portal vein (the blood vessel that brings blood to the liver from the intestines) by a blood clot.
Where does blood come from in the liver?
Blood Supply of the Liver. Blood leaves the liver through the hepatic veins. This blood is a mixture of blood from the hepatic artery and from the portal vein. The hepatic veins carry blood to the inferior vena cava—the largest vein in the body—which then carries blood from the abdomen and lower parts of the body to the right side of the heart.
Why does the liver need blood from two blood vessels?
Receiving blood from two blood vessels helps protect the liver: If one of these blood vessels is damaged , the liver can often continue to function because it receives oxygen and nutrients from the other blood supply.
Which blood vessel provides oxygen to the liver?
The liver receives the oxygen and nutrients it needs in blood that comes from two large blood vessels: Portal vein. Hepatic artery. The portal vein provides about two thirds of the blood. This blood contains oxygen and many nutrients brought to the liver from the intestines for processing. The hepatic artery provides the remaining one third ...
What causes a vascular enlarged liver?
If the problem is blood flow out of the liver, blood backs up in the liver, causing congestion which can result in an enlarged liver .
How does the liver work?
It functions by receiving blood from the alimentary canal, the accessory organs of the digestive tract, and the spleen and subsequently filtering it. The blood supply of the liver is delivered through the portal vein and the hepatic artery . The hepatic artery brings oxygenated blood to the hepatic tissues, while the portal vein collects ...
What is the hepatic portal vein?
The hepatic portal vein is formed by the merger of the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein. The veins that contribute to the splenic vein include the inferior mesenteric vein and its branches, the pancreatic veins, the left gastroepiploic vein and the short gastric veins. Hepatic portal vein (ventral view)
What is the blood supply of the liver?
The blood supply of the liver is delivered through the portal vein and the proper hepatic artery. The proper hepatic artery (arises from the celiac trunk via common hepatic artery) brings oxygenated blood to the hepatic tissues, while the portal vein collects the deoxygenated blood from the abdominal contents and filters it, eliminating toxins and processing the nutrients it collects during absorption from the alimentary canal. The portal venous system will be discussed below, so for now, the pathway of the proper hepatic artery, which contributes approximately 30% towards the hepatic blood supply will be mentioned.
Which artery enters the hepatoduodenal ligament?
The common hepatic artery veers retroperitoneally to the right and enters the hepatoduodenal ligament of the liver. It then divides into the gastroduodenal and proper hepatic arteries, which supply the stomach and duodenum as well as the liver respectively. Common hepatic artery (ventral view)
Which artery gives rise to the left gastric artery?
Hepatic artery proper (ventral view) The celiac trunk branches off the abdominal aorta at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebra and gives rise to the left gastric artery, the splenic artery and the common hepatic artery.
Where is lymph produced in the liver?
The lymph that is produced by the liver is collected mainly by the hepatic nodes which are situated around the porta hepatis. From there the fluid is carried to the celiac nodes which are part of the intestinal lymphatic trunks and merge directly into the thoracic duct, when the cisterna chyli is anatomically not present.
What is referred pain?
Referred pain is visceral pain perceived as somatic pain through the dermatomes of the skin which are innervated by the cutaneous nerves of the spinal vertebrae T5 to L3. It is essentially information that is carried by visceral afferent fibers via the thoracic and lumbar splanchnic nerves. The liver and the gallbladder are governed by the sixth to the ninth thoracic spinal nerves and present as referred pain in the epigastric region of the abdomen, as well as to the right hypochondrium.
