
Is the fluoride treatment at the dentist really worth it?
New research indicates that topical fluoride -- from toothpastes, mouth rinses, and fluoride treatments -- are as important in fighting tooth decay as in strengthening developing teeth.
Can baking soda get rid of dental fluorosis?
Yes, it is. Though excess consumption of fluoride in children can lead to fluorosis and there is always a risk of fluoride toxicity, it still helps prevent cavities. Hence, fluoride in toothpaste protects from decay and cavities. Though, if you make your own baking soda toothpaste then that doesn’t contain any fluoride.
What are the negative side effects of fluoride?
Potential downsides of fluoride include fluorosis, an increased risk of osteosarcoma, and impaired brain development in infants and children. The bottom line As with many other nutrients, fluoride...
What does fluorosis look like?
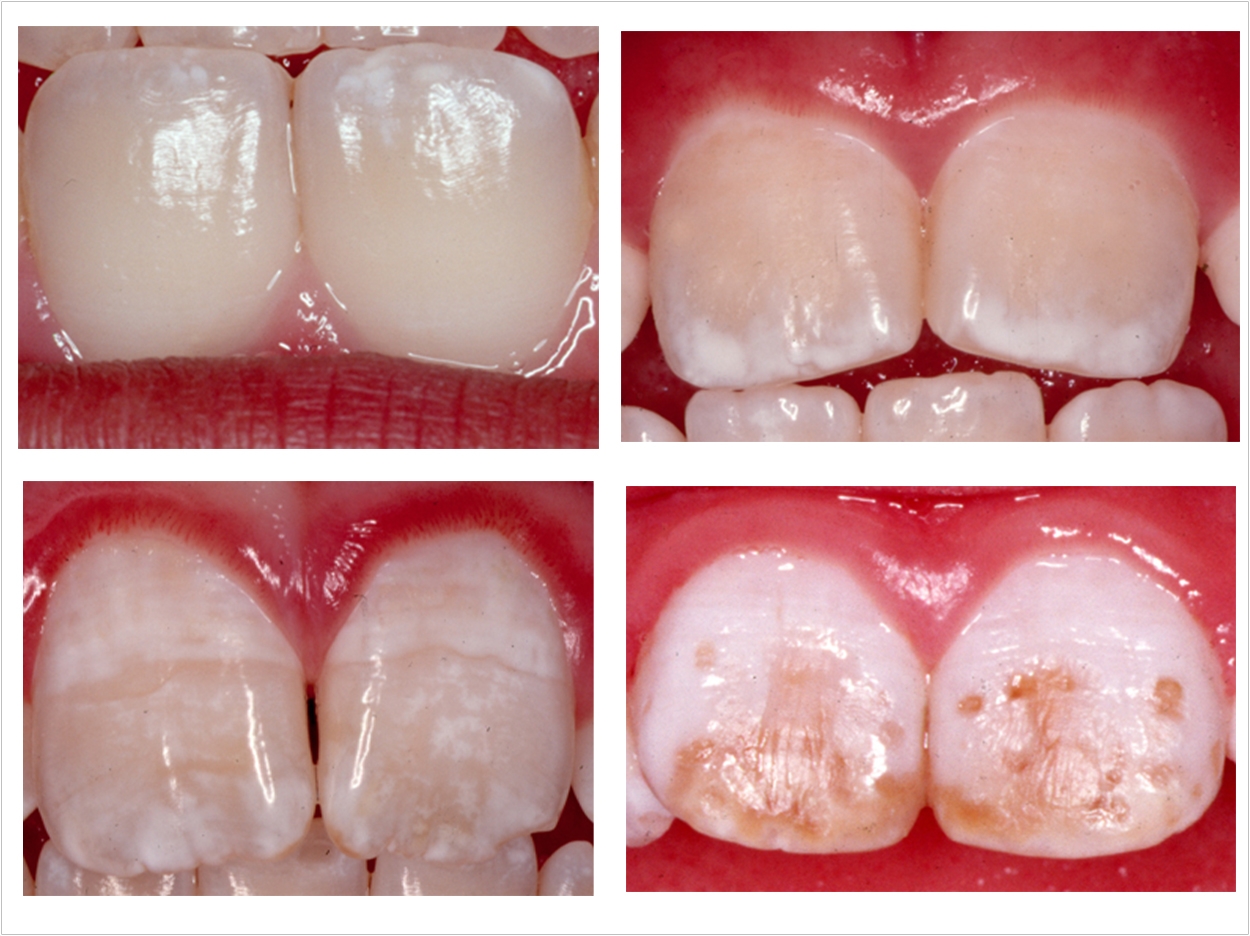
Fluorosis is a defect in tooth enamel caused by excessive fluoride in young children. It typically looks like white streaks or spots in teeth. What does Fluorosis look like? Almost all instances of Fluorosis in the United States are mild cases which look like spots or streaks of bright white in the enamel of the tooth.

What stage does fluorosis occur?
The development of fluorosis is highly dependent on the dose, duration, and timing of fluoride exposure. The risk of enamel fluorosis is lowest when exposure takes place only during the secretory stage, but highest when exposure occurs in both secretory and maturation stages.
Can you get fluorosis from toothpaste?
Fluorosis Causes A major cause of fluorosis is the inappropriate use of fluoride-containing dental products such as toothpaste and mouth rinses. Sometimes, children enjoy the taste of fluoridated toothpaste so much that they swallow it instead of spitting it out. But there are other causes of fluorosis.
Is fluorosis caused by water?
Fluorosis is caused by excessive intake of fluorides from multiple sources such as in food, water, air (due to gaseous industrial waste), and excessive use of toothpaste. However, drinking water is the most significant source.
How do you get rid of fluorosis on teeth?
How do you get rid of fluorosis?Teeth whitening. Your dentist applies bleaching gel to your teeth for a predetermined amount of time. ... Dental bonding. During this procedure, your dentist uses tooth-colored composite resin to cover up fluorosis stains. ... Dental veneers. ... Dental crowns. ... Enamel microabrasion.
What does fluorosis look like?
What does dental fluorosis look like? Very mild and mild forms of dental fluorosis—teeth have scattered white flecks, occasional white spots, frosty edges, or fine, lacy chalk-like lines. These changes are barely noticeable and difficult to see except by a dental health care professional.
Does teeth whitening help fluorosis?
However, even Zoom tooth whitening may not be enough to fully lighten stains caused by fluorosis. Stains caused by fluoride and certain antibiotics may respond somewhat to Zoom tooth whitening, but often require a solution like porcelain veneers for complete elimination.
How can fluorosis be prevented?
How can I prevent dental fluorosis in my children?Do not brush your child's teeth more than 2 times a day with a fluoride toothpaste,Apply no more than a pea-sized amount of toothpaste to the toothbrush, and.Supervise your child's tooth brushing, encouraging the child to spit out toothpaste rather than swallow it.More items...
Is dental fluorosis reversible?
This discoloration may or may not be noticeable to the eye. However, as fluorosis becomes more severe, tooth enamel can begin to turn yellow or brown and/or become thin and pitted. Unfortunately, dental fluorosis cannot be reversed once it develops. Current treatments simply mask the appearance of this condition.
Is dental fluorosis permanent?
Most cases of fluorosis are mild, not painful, and don't cause any permanent damage to a child's teeth. If severe fluorosis occurs, it can usually be treated through a number of cosmetic dentistry techniques such as whitening or veneers.
Which toothpaste is best for fluorosis?
All of the toothpastes we recommend also contain fluoride, per dentists' advice.Aim Cavity Protection Gel. ... Colgate Cavity Protection Fluoride Toothpaste. ... Crest Cavity Protection Cool Mint Gel. ... Quip Mint Anticavity Toothpaste. ... Arm & Hammer Dental Care Toothpaste. ... PRO-SYS Mint Fluoride Toothpaste Gel.More items...•
Can fluorosis be fixed?
Fixing Fluorosis The three favorable methods to correct fluorosis involve a bit of work and cost, but they can be successful. They are dental bonding, veneers, and deep whitening. Dental bonding: Dental bonding is the most affordable of the three, and is something you may already be familiar with.
Does fluoride make teeth yellow?
Fluorosis: Fluoride is good for teeth, but excess fluoride can cause yellow or brownish yellow spots called fluorosis. Fluoridated water, fluoride toothpaste and prescribed fluoride tablets and treatments are your biggest sources of fluoride.
How much toothpaste causes fluorosis?
Even a small 'pea-sized' amount of toothpaste containing 1,450 ppm fluoride, would contain approximately 0.36–0.72 mg fluoride, which if consumed twice a day could contribute to fluoride levels that would increase the risk of dental fluorosis in children [26].
Can fluoride cause white spots on teeth?
These white spots on your teeth have several causes. They typically appear when people are younger if they consume excessive amounts of fluoride as a child and are referred to as dental fluorosis. Although they're undesirable, they're usually harmless and begin forming before the teeth even grow in.
Can you reverse dental fluorosis?
This discoloration may or may not be noticeable to the eye. However, as fluorosis becomes more severe, tooth enamel can begin to turn yellow or brown and/or become thin and pitted. Unfortunately, dental fluorosis cannot be reversed once it develops. Current treatments simply mask the appearance of this condition.
Is dental fluorosis permanent?
Most cases of fluorosis are mild, not painful, and don't cause any permanent damage to a child's teeth. If severe fluorosis occurs, it can usually be treated through a number of cosmetic dentistry techniques such as whitening or veneers.
What is dental fluorosis?
Dental fluorosis is an abnormality caused by excessive fluoride intake. It occurs when too much fluoride is consumed while the teeth are developing...
What causes white spots on teeth from fluorosis?
Fluoride is a naturally occurring mineral that's been proven to strengthen tooth enamel and help prevent tooth decay. But it's only beneficial when...
Is fluorosis reversible?
Fluorosis damages teeth while they are developing. By the time they erupt, dental fluorosis reversal isn't possible. However, there are various cos...
When does fluorosis develop?
Fluorosis can form at any time when the teeth are developing, and this starts in the womb. Even after the teeth are fully developed, the effects of...
How is dental fluorosis diagnosed?
There are several things that can cause white marks on teeth or other changes to tooth color. As well as fluorosis, decalcification, enamel hypopla...
Can you get treatment for fluorosis on Medicaid?
Because fluorosis is treated in a number of different ways (cosmetic and medical), there is no simple way to know if the treatment will be covered...
Why do teeth get fluorosis?
Causes. Dental fluorosis is caused by a higher than normal amount of fluoride ingestion whilst teeth are forming. Primary dentine fluorosis and enamel fluorosis can only happen during tooth formation, so fluoride exposure occurs in childhood.
How is dental fluorosis growing?
Dental fluorosis has been growing in the United States concurrent with fluoridation of municipal water supplies, although disproportionately by race. A 2010 CDC report acknowledges an overall incidence of dental fluorosis of 22% from 1986-87 increased to 41% in the early 21st century, with an increase in moderate to severe dental fluorosis from 1% to 4%. The 2011-12 NHANES figures documented another 31% overall increase among American teens since the previous decade, with a total adolescent population impact of 61% afflicted. More than one in five American teens (23%) have moderate to severe dental fluorosis on at least two teeth.
What is the disorder of tooth enamel?
Dental fluorosis is a common disorder, characterized by hypomineralization of tooth enamel caused by ingestion of excessive fluoride during enamel formation.
How to diagnose fluorosis?
The adequate diagnosis of fluorosis can be diagnosed by visual clinical examination. This requires inspection of dry and clean tooth surfaces under a good lighting. There are individual variations in clinical fluorosis manifestation which are highly dependent on the duration, timing, and dosage of fluoride exposure.There are different classifications to diagnose the severity based on the appearances. The clinical manifestation of mild dental fluorosis is mostly characterised a snow flaking appearance that lack a clear border, opaque, white spots, narrow white lines following the perikymata or patches as the opacities may coalesce with an intact, hard and smooth enamel surface on most of the teeth. With increasing severity, the subsurface enamel, all along the tooth becomes more porous. Enamel may appear yellow/ brown discolouration and/ or many and pitted white-brown lesions that look like cavities. They are often described as “mottled teeth”. Fluorosis does not cause discolouration to the enamel directly, as upon eruption into the mouth, affected permanent teeth are not discoloured yet. In dental enamel, fluorosis causes subsurface porosity or hypomineralizations, which extend toward the dentinal-enamel junction as the condition progresses and the affected teeth become more susceptible to staining. Due to diffusion of exogenous ions (e.g., iron and copper), stains develop into the increasingly and abnormally porous enamel.
What does enamel look like?
Enamel may appear yellow/ brown discolouration and/ or many and pitted white-brown lesions that look like cavities. They are often described as “mottled teeth”. Fluorosis does not cause discolouration to the enamel directly, as upon eruption into the mouth, affected permanent teeth are not discoloured yet.
What causes a tooth to be more susceptible to staining?
In dental enamel, fluorosis causes subsurface porosity or hypomineralizations, which extend toward the dentinal-enamel junction as the condition progresses and the affected teeth become more susceptible to staining.
How common is fluorosis in adolescents?
Fluorosis is extremely common, with 41% of adolescents having definite fluorosis, and another 20% "questionably" having fluorosis according to the Centers for Disease Control. As of 2005#N#[update]#N#surveys conducted by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research in the USA between 1986 and 1987 and by the Center of Disease Control between 1999 and 2004 are the only national sources of data concerning the prevalence of dental fluorosis. Before the 1999-2004 study was published, CDC published an interim report covering data from 1999 to 2002.
Why do children get fluorosis?
Dental fluorosis is caused by taking in too much fluoride over a long period when the teeth are forming under the gums. Only children aged 8 years and younger are at risk because this is when permanent teeth are developing; children older than 8 years, adolescents, and adults cannot develop dental fluorosis.
How to find out if your water is fluoridated?
If you live in a state that participates in CDC’s My Water’s Fluoride, you can find out your water system’s fluoridation status online. If you are on a public water system, you can call the water utility company and request a copy of the utility’s most recent Consumer Confidence Report.
How to clean teeth for kids?
You should clean your child’s teeth as soon as the first tooth appears by brushing without toothpaste with a small, soft-bristled toothbrush and plain water.
How does fluoride work?
Fluoride works both while the teeth are developing and every day after the teeth have emerged through the gums. Fluoride consumed during tooth development can also result in a range of visible changes to the enamel surface of the tooth. These changes have been broadly termed dental fluorosis. What is dental fluorosis?
What is the condition that causes enamel to change?
Dental fluorosis is a condition that causes changes in the appearance of tooth enamel. It may result when children regularly consume fluoride during the teeth-forming years, age 8 and younger. Most dental fluorosis in the U.S. is very mild to mild, appearing as white spots on the tooth surface that may be barely noticeable and do not affect dental function. Moderate and severe forms of dental fluorosis , which are far less common, cause more extensive enamel changes. In the rare, severe form, pits may form in the teeth. The severe form hardly ever occurs in communities where the level of fluoride in water is less than 2 milligrams per liter.
What is the term for a tooth with white spots?
Moderate and severe forms of dental fluorosis —teeth have larger white spots and, in the rare, severe form, rough, pitted surfaces.
How much fluoride is in water?
In some regions of the United States, public water systems and private wells contain a natural fluoride concentration of more than 2 mg/L; at this concentration, children 8 years and younger have a greater chance for developing dental fluorosis, including the moderate and severe forms. These children should have an alternative source of drinking water that contains fluoride at the recommended level.
What is the condition called when you have high levels of fluoride in your mouth?
These changes are a condition called dental fluorosis.
How to find out fluoride in water?
If you live in a state that participates in the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)’s My Water’s Fluoride program, you can learn of your water system’s fluoride status online. If you use a public water system, you can speak with your water utility company to request a copy of its most recent Consumer Confidence Report .
How to prevent tooth decay?
Dental fluorosis is more likely to occur when the following sources of fluoride are consumed to prevent tooth decay: 1 Drinking water with fluoride 2 Fluoride toothpaste and mouth rinses, especially if ingested by young children 3 Dietary prescription fluoride supplements in tablets or drops, mainly if prescribed to children already drinking fluoridated water
What happens if you eat too much fluoride?
When children consume too much fluoride over a long period when the teeth are developing under the gums, fluorosis is likely to occur.
What is enamel microabrasion?
Enamel microabrasion treats white spots on teeth with dental fluorosis. During this treatment, a dentist removes a small amount of enamel from the teeth. This procedure may reduce the appearance of white spots.
How to clean a baby's teeth?
You should clean your baby’s teeth as soon as the first tooth erupts by brushing with a small, soft-bristled toothbrush. The AAPD recommends using a tiny amount of fluoridated toothpaste (the size of a grain of rice) on the toothbrush when brushing baby's teeth.
How old should a child be to brush their teeth?
If you have children aged from two to six years of age, you should apply no more than a pea-sized amount of toothpaste when they brush their teeth. You should also monitor their teeth brushing at this age, encouraging your child to spit out the toothpaste instead of swallowing it. Until around the age of six, children cannot control their swallowing reflex well and often ingest a lot of the toothpaste from their brush.
What is Dental Fluorosis?
Dental fluorosis is a common defect of tooth enamel caused by ingestion of too much fluoride during the first 8 years of life when enamel is formed . 1
How To Prevent Dental Fluorosis?
If you or your child has dental fluorosis, consider it a blessing in disguise.
What happens if your child's teeth are white?
If you observe that your child’s teeth have white streaks, spots, or discoloration- immediately eliminate fluoride exposure. Dental fluorosis typically signals the first sign of fluoride toxicity and the development of more severe health effects caused by fluoride ( 3 ). As the effects of fluoride do not start and stop at the teeth.
What are the effects of fluoride on teeth?
In essence, dental fluorosis acts as a red flag to the development of fluoride induced health effects that are not as easily seen with the naked eye: 1 Skeletal Fluorosis: broken bones, arthritis, reduced mobility. 2 Pineal Gland Calcification: poor sleep, lower melatonin. 3 Fluoride’s Brain Effects: lowered IQ, autism, ADHD.
How serious is fluoride?
The seriousness of fluoride toxicity depends on the amount of fluoride, age, individual response, weight, degree of physical activity, nutrition, and bone growth. 5
Does toothpaste cause fluorosis?
Since then, with the combination of fluoride containing toothpaste, mouthwash and other sources of fluoride, dental fluorosis has become common.
Is dental fluorosis a red flag?
In essence, dental fluorosis acts as a red flag to the development of fluoride induced health effects that are not as easily seen with the naked eye:
What is Dental Fluorosis?
Dental fluorosis or brown tooth staining is a tooth defect indicated by an increase in porosity of the enamel. This mineralization defect occurs on the tooth surface, also known as hypomineralization. Hypomineralization is a result of excessive fluoride ion exposure during the developmental stage; critical ages are one through four years of age up to the age of eight. Fluorosis is no longer a risk when teeth are fully erupted.
What is the best treatment for fluorosis?
These options include; micro abrasion, bleaching with custom fitted teeth whitening trays and carbamide peroxide whitening gel, bonding or filling restorations, veneers (cost varies but may be the best option for moderate to severe cases), and crowns. Tooth Bleaching and micro abrasion treatments are used for superficial staining, whereas the restorative approach is used for the more unaesthetic situations.
What is the difference between tooth bleaching and micro abrasion?
Tooth Bleaching and micro abrasion treatments are used for superficial staining , whereas the restorative approach is used for the more unaesthetic situations. Bleaching dental fluorosis staining can initially cause the white spotting to be brighter.
Is fluorosis a risk factor?
There are no known risk factors associated with dental fluorosis that will affect the health of the tooth. Known risks are limited to the ascetic appearance of the tooth and the embarrassment incurred by the person.
Is dental fluorosis on the rise?
Dental fluorosis is on the rise. The CDC and NIDR compared the number of children reported by dentist as suffering from dental fluorosis back in 1987 to the number reported in 2002. Data can be seen in the table to the right. Their collective data suggest that there has been an 80% increase.
How does fluoride affect enamel?
In dental enamel, fluorosis causes subsurface hypomineralizations or porosity , which extend toward the dentinal-enamel junction as severity increases. This subsurface porosity is most likely caused by a delay in the hydrolysis and removal of enamel proteins, particularly amelogenins, as the enamel matures. This delay could be due to the direct effect of fluoride on the ameloblasts or to an interaction of fluoride with the proteins or proteinases in the mineralizing matrix. The specific mechanisms by which fluoride causes the changes leading to enamel fluorosis are not well defined; though the early-maturation stage of enamel formation appears to be particularly sensitive to fluoride exposure. The development of fluorosis is highly dependent on the dose, duration, and timing of fluoride exposure. The risk of enamel fluorosis is lowest when exposure takes place only during the secretory stage, but highest when exposure occurs in both secretory and maturation stages. The incidence of dental fluorosis is best correlated with the total cumulative fluoride exposure to the developing dentition. Fluoride supplements can contribute to the total fluoride exposure of children, and if the total fluoride exposure to the developing teeth is excessive, fluorosis will result.
What is the term for the alterations in the mineralization process?
Fluorosis occurs when fluoride interacts with mineralizing tissues, causing alterations in the mineralization process. In dental enamel, fluorosis causes subsurface hypomineralizations or porosity, which extend toward the dentinal-enamel junction as severity increases. This subsurface porosity is mo …
Overview
Mechanism
Teeth are the most studied body tissues to examine the impact of fluoride to human health. There are a few possible mechanisms that have been proposed. It is generally believed that the hypomineralization of affected enamel is mainly due to in-situ toxic effects of the fluoride on the ameloblasts in the enamel formation, and not caused by the general effects of fluoride on the calcium metabolism, or by the poisoning effects that suppress the fluoride metabolism. Howeve…
Diagnosis
The adequate diagnosis of fluorosis can be diagnosed by visual clinical examination. This requires inspection of dry and clean tooth surfaces under a good lighting. There are individual variations in clinical fluorosis manifestation which are highly dependent on the duration, timing, and dosage of fluoride exposure.There are different classifications to diagnose the severity based on …
Classification
The two main classification systems are described below. Others include the tooth surface fluorosis index (Horowitz et al. 1984), which combines Deans index and the TF index; and the fluorosis risk index (Pendrys 1990), which is intended to define the time at which fluoride exposure occurs, and relates fluorosis risk with tooth development stage.
Causes
Dental fluorosis is caused by a higher than normal amount of fluoride ingestion whilst teeth are forming. Primary dentine fluorosis and enamel fluorosis can only happen during tooth formation, so fluoride exposure occurs in childhood. Enamel fluorosis has a white opaque appearance which is due to the surface of the enamel being hypomineralised.
The most superficial concern in dental fluorosis is aesthetic changes in the permanent dentitio…
Management
Dental fluorosis may or may not be of cosmetic concern. In some cases, there may be varying degrees of negative psychosocial effects. The treatment options are:
• Mild cases: Tooth bleaching
• Moderate cases: Enamel microabrasion (outer affected layer of enamel is abraded in an acidic environment)
Epidemiology
Fluorosis is extremely common, with 41% of adolescents having definite fluorosis, and another 20% "questionably" having fluorosis according to the Centers for Disease Control. As of 2005 surveys conducted by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research in the USA between 1986 and 1987 and by the Center of Disease Control between 1999 and 2004 are the only national sources of data concerning the prevalence of dental fluorosis. Before the 1999-2004 st…
Prevention
Dental fluorosis can be prevented by lowering the amount of fluoride intake to below the tolerable upper limit. This can be achieved by consuming de-fluorinated water and improving the general nutritional status of the people.