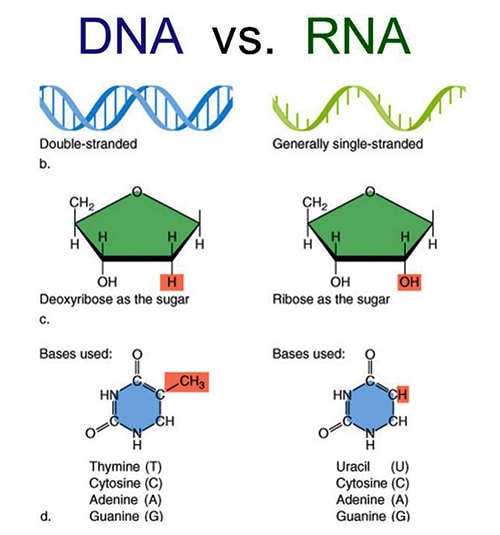
Summary of Differences Between DNA and RNA
- DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, while RNA contains the sugar ribose. ...
- DNA is a double-stranded molecule, while RNA is a single-stranded molecule.
- DNA is stable under alkaline conditions, while RNA is not stable.
- DNA and RNA perform different functions in humans. ...
What are the 4 main differences between DNA and RNA?
Main Differences Between DNA and RNA. DNA is a double-stranded helix structure with long chains of nucleotides. Whereas, RNA molecules are single-stranded helix structures with shorter chains of nucleotides. The bases present in DNA are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine. RNA also shares the same bases, but instead of Thymine is contains ...
How would you differentiate RNA from DNA?
What Are The Differenced Between DNA and RNA?
- Structure and Size. One of the notable differences between DNA and RNA is physical structure. ...
- Sugar Structure. Remember that both have sugar structures. ...
- Nitrogenous Bases. DNA has four nitrogenous bases that include adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. ...
- Location and Occurrence. ...
- General Functions. ...
- Types. ...
What are two ways RNA is different from DNA?
What is the main difference between DNA and RNA?
- like RNA SINGLE STRAND have many type (mRNA , tRNA ,rRNA ,prokaryotic RNA) in the prokaryotic cell and eukaryotic cell
- in prokaryotic cell RNA in the cell free without nucleus.and replicated with themselvies
- in eukaryotic all RNA INSIDE THE NUCLEUS.and replicated by templet strand of DNA
What are the roles of DNA and RNA?
- mRNA carries genetic information copied from the DNA in codons
- tRNA helps to decipher the mRNA. Each type of amino acid has its own tRNA. The tRNA carries the amino acid to the polypeptide chain
- mRNA is ribosomal RNA and helps to form ribosomes. Ribosomes are what assemble the polypeptide chains.
What are 4 differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA has four nitrogenous bases - Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Thyamine. RNA also has four nitrogenous bases, Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine and Uracil.
What are 3 ways DNA differs from RNA?
So, the three main structural differences between RNA and DNA are as follows: RNA is single-stranded while DNA is double-stranded. RNA contains uracil while DNA contains thymine. RNA has the sugar ribose while DNA has the sugar deoxyribose.
How do DNA and RNA differ quizlet?
RNA is different than DNA because it has: ribose for the sugar, uracil instead of thymine, and it is single-stranded. DNA is different than RNA because it has: deoxyribose for the sugar, thymine instead of uracil, and it is double stranded.
How are RNA and DNA alike and different?
Nucleotides simply refer to nitrogenous bases, pentose sugar together with the phosphate backbone. Both DNA and RNA have four nitrogenous bases each—three of which they share (Cytosine, Adenine, and Guanine) and one that differs between the two (RNA has Uracil while DNA has Thymine).
How does RNA differ from DNA Quizizz?
RNA contains sucrose while DNA contains glucose. DNA contains deoxyribose while RNA contains ribose. Two other differences between RNA and DNA involve... the fact that one is composed of purines while the other is composed of pyrimidines.
What are the 5 differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its own.
What are the four ways that RNA differs from DNA quizlet?
Terms in this set (4) DNA has the bases adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine. RNA has the bases adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine. 2.
What is the difference between DNA and RNA nucleotides?
A DNA nucleotide contains deoxyribose sugar, whereas an RNA contains the sugar ribose in every nucleotide. The nitrogenous bases in DNA can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. Unlike DNA, RNA contains a uracil nitrogenous base instead of thymine.
What is the DNA and RNA?
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA) are complex molecular structures that control all hereditary characteristics of cells and thus of organisms. DNA is the master blueprint for life and constitutes the genetic material in all free-living organisms.
What are 5 differences between DNA and RNA?
DNA is a double-stranded molecule that has a long chain of nucleotides. RNA is a single-stranded molecule which has a shorter chain of nucleotides. DNA replicates on its own, it is self-replicating. RNA does not replicate on its own.
What are three ways RNA differs from DNA quizlet?
RNA is different from DNA is three ways: (1) the sugar in RNA is ribose not dioxyribose; (2) RNA is generally single-stranded and not double-stranded; and (3) RNA contains uracil in place of thymine.
How does RNA differ from DNA Quizizz?
RNA contains sucrose while DNA contains glucose. DNA contains deoxyribose while RNA contains ribose. Two other differences between RNA and DNA involve... the fact that one is composed of purines while the other is composed of pyrimidines.
What are the 3 types of RNA?
Three main types of RNA are involved in protein synthesis. They are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). rRNA forms ribosomes, which are essential in protein synthesis. A ribosome contains a large and small ribosomal subunit.
What is the composition of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA are nearly identical polymers of nucleotides, except for the base pairs. DNA contains thymine while the same is substituted with uracil...
Where are DNA and RNA found?
DNA is located in the nucleus of a cell and in the mitochondria. Meanwhile, RNA is found in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and also in ribosomes.
How does propagation occur in DNA and RNA?
DNA is capable of self-replication but RNA cannot self-replicate instead, it is synthesized from DNA (DNA transcription) when required.
What is the similarity between DNA and RNA?
Three out of the four nitrogenous bases in DNA and RNA are the same (cytosine, adenine, guanine). They both possess a phosphate backbone to which t...
Why is DNA a better genetic material than RNA?
The deoxyribose sugar of DNA contains one less oxygen-containing hydroxyl group. DNA is a more stable nucleic acid. RNA, on the other hand, contain...
What is the composition of DNA and RNA?
DNA and RNA are nearly identical polymers of nucleotide, except for the base pairs. DNA contains thymine while the same is substituted with uracil in RNA.
How does propagation occur in DNA and RNA?
DNA is capable of self-replication but RNA cannot self-replicate and instead, it is synthesized from DNA (DNA transcription) when required.
Why is DNA a better genetic material than RNA?
DNA is a more stable nucleic acid. RNA, on the other hand, contains a ribose sugar and is more reactive than DNA. Therefore, DNA is a better genetic material than RNA.
What is the name of the nucleic acid that is used to make proteins?
In cells, DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is the nucleic acid that functions as the original blueprint for the synthesis of proteins. DNA contains the sugar deoxyribose, phosphates and a unique sequence of the nitrogenous bases adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T).
How are genes formed?
Genes are formed by the order of the nitrogenous bases present in the DNA which is crucial for protein synthesis. The RNA is another nucleic acid that translates genetic information into proteins from DNA.
What are the building blocks of life?
But at the molecular level, all life is fundamentally made up of the same building blocks – DNA and RNA. One of the primary differences between DNA and RNA is that DNA is double-stranded while RNA is single-stranded.
Which pair of bases is located on one strand?
The bases located on one strand pair up with the bases on the other strand, as in – guanine pairs with cytosine and adenine pair s with thymine.
What are the bases of DNA?
Bases. The nitrogen bases in DNA are the basic units of genetic code, and their correct ordering and pairing is essential to biological function . The four bases that make up this code are adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C).
What is the sugar in DNA called?
Both DNA and RNA are built with a sugar backbone, but whereas the sugar in DNA is called deoxyribose (left in image), the sugar in RNA is called simply ribose (right in image).
What is the process of bringing amino acids to the protein factories?
Transfer RNA ( tRNA) is responsible for bringing amino acids, basic protein building blocks, to these protein factories, in response to the coded instructions introduced by the mRNA. This protein-building process is called translation.
What is the purpose of DNA?
DNA encodes all genetic information, and is the blueprint from which all biological life is created. And that’s only in the short-term. In the long-term, DNA is a storage device, a biological flash drive that allows the blueprint of life to be passed between generations 2. RNA functions as the reader that decodes this flash drive.
How many strands does DNA have?
DNA consists of two strands, arranged in a double helix. These strands are made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a phosphate, a 5-carbon sugar molecule and a nitrogenous base. RNA only has one strand, but like DNA, is made up of nucleotides. RNA strands are shorter than DNA strands.
What is the most important molecule in cell biology?
December 18 2020. | by Ruairi J Mackenzie, Editor for Technology Networks. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic acid (RNA) are perhaps the most important molecules in cell biology, responsible for the storage and reading of genetic information that underpins all life. They are both linear polymers, consisting of sugars, phosphates and bases, ...
What are the different types of RNA?
What are the three types of RNA? 1 Messenger RNA ( mRNA) copies portions of genetic code, a process called transcription, and transports these copies to ribosomes, which are the cellular factories that facilitate the production of proteins from this code. 2 Transfer RNA ( tRNA) is responsible for bringing amino acids, basic protein building blocks, to these protein factories, in response to the coded instructions introduced by the mRNA. This protein-building process is called translation. 3 Finally, Ribosomal RNA ( rRNA) is a component of the ribosome factory itself without which protein production would not occur 3.
What is DNA?
To begin with, we must start with probably the best known of the three macromolecules (“big molecules”) we will be looking at today: DNA.
What type of RNA is used to build protein?
Other types of RNA, such as transfer RNA ( tRNA) and ribosomal RNA ( rRNA ), help the ribosome actually build the protein. Once the protein is built, the mRNA’s job is over and it will degrade. Again, this is a general look at what mRNA actually does.
What are the different types of RNA?
As you might guess, this is a simplified version of what actually happens in the cells. To get a better idea of what is actually going on with RNA, here are some vocabulary words that provide more details on the concepts surrounding RNA: 1 DNA 2 transcription 3 ribosome 4 protein 5 amino acid 6 protein synthesis 7 mRNA (we’ll be getting to this one) 8 tRNA 9 rRNA
How does RNA help the ribosomes?
There, RNA helps the ribosomes properly build the correct proteins that the body needs .
Why is DNA important to life?
These base pairs are the reason why DNA is so important to life: the ordering of the base pairs results in a specific genetic code called a gene. DNA consists of many genes and is itself organized into structures known as chromosomes, of which humans have 23 pairs.
What are some words that describe RNA?
transcription. ribosome. protein. amino acid. protein synthesis. mRNA (we’ll be getting to this one) tRNA.
What is RNA made of?
RNA stands for “ribonucleic acid.” RNA is a large molecule made from a single strand of DNA, and one of its main roles is to transfer the instructions needed to make proteins.
How does tRNA work?
2. tRNAs bring the proper amino acids into the ribosome. 3. Each tRNA has an anticodon that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions the start codon to attract its anticodon. 4. Ribosome attaches the amino acids and forms a peptide bond between the 1st and 2nd amino acids.
Why is RNA polymerase important?
RNA polymerase is important because its ability to copy a single DNA sequence into RNA makes it possible for a single gene to produce hundreds or even thousands of RNA molecules.
How is RNA different from DNA?
RNA is different from DNA is three ways: (1) the sugar in RNA is ribose not dioxyribose; (2) RNA is generally single-stranded and not double-stranded; and (3) RNA contains uracil in place of thymine.
Which molecule carries the coded message that directs the process?
The mRNA molecule carries the coded message that directs the process. The tRNA delivers exactly the right amino acid called for by each codon on the mRNA. The tRNA are adaptors that enable the ribosome to read the mRNA's message accuarately and to get the translation just right.
What is RNA made of?
Tap card to see definition 👆. Like DNA, RNA is made up of a 5-carbon surgar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. Click again to see term 👆. Tap again to see term 👆. Nice work!
What is the term for the assembly of amino acids into proteins?
Protein synthesis, or the assembly of amino acids into proteins.
Where does mRNA attach to?
4. The mRNA attaches to a ribosome subunit.
Why can a tRNA anticodon pair with more than one mRNA codon?
Because each amino acid is coded for by just one codon. a. Because the 5' base on the tRNA anticodon has some flexibility (wobble); thus, some tRNA anticodons can pair with more than one mRNA codon. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms differ in how they process genetic information.
What happens to the 9 most recently added nucleotides in the newly synthesized RNA strand?
Within the transcription bubble, the 9 most recently added nucleotides in the newly synthesized RNA strand temporarily form a helix with the template DNA strand . How might transcription be affected if helix formation did not occur?
How many bases are there in the anticodon?
d. There is some flexibility in pairing between all 3 bases of the codons and all 3 bases of the anticodon
What is the difference between initiation of transcription and initiation of DNA replication?
Initiation of transcription differs form initiation of DNA replication in several ways. One difference is that initiation of transcription does not require
What is the translation of genes into mRNA?
In eukaryotes, genes are transcribed into RNA which is used to assemble polypeptides. c. In prokaryotes, translation occurs before genes are transcribed into mRNA. In eukaryotes, genes are transcribed into mRNA which is then translated into polypeptides.
How many base sequences are present in bacterial promoters?
Two 6- base sequences are present in bacterial promoters : TATAAT ( located 10 nt upstream from the start site) and TTGACA (located 35 nt upstream from the start site). What is the significance of the fact that these two base sequences are different?
What is missense mutation?
A missense mutation has altered the ribosome-binding sequence at the 5' end of the mRNA. a. A small deletion has removed the nucleotides that code for the signal sequence at the amino terminus of the protein. A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell.