Factors affecting enzyme activity
- Enzyme concentration. The activity of an enzyme increases as the concentration of the enzyme increases. ...
- Substrate concentration. An enzyme’s activity increases with the rise in substrate concentration. ...
- Effect of pH on the rate of reaction. pH has an impact on enzyme activity. ...
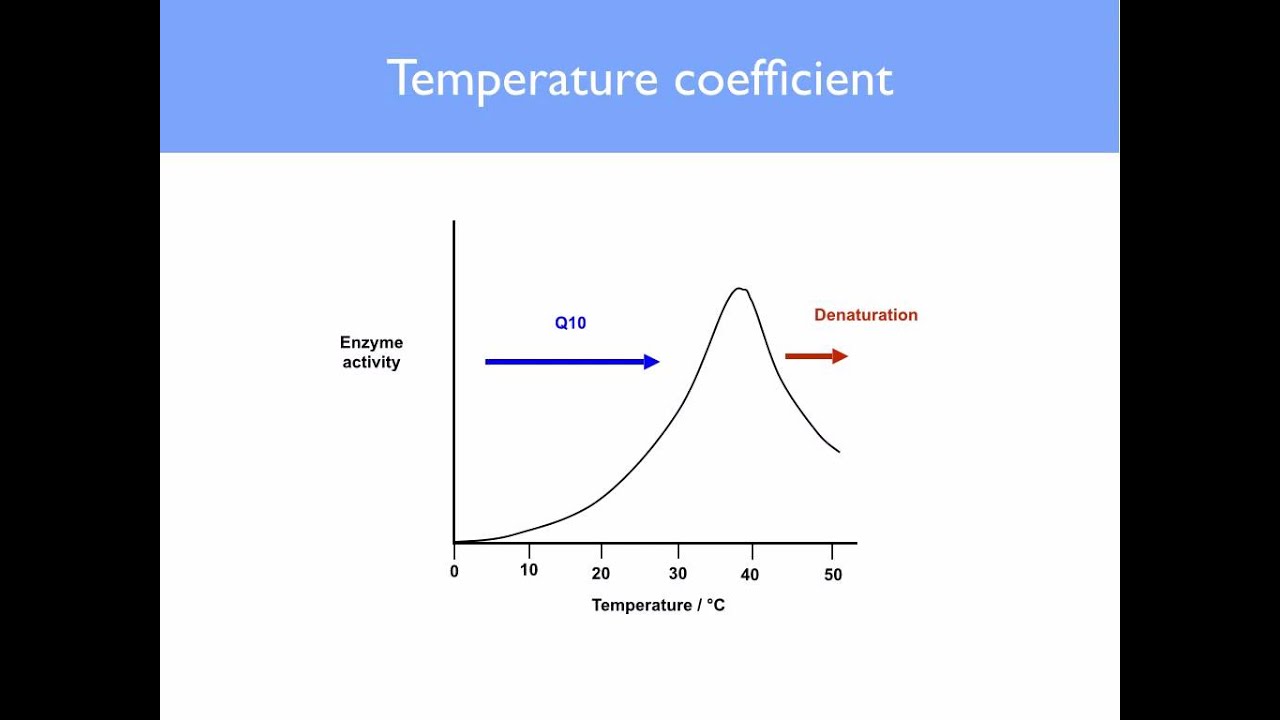
- Effects of temperature on the rate of reaction. ...
What are the 4 factors that affect enzyme activity?
May 12, 2020 · When there is a higher concentration enzyme there is more of an enzyme 'packed' into an area. There will therefore be more active sites available to catalyse the substrate so there will be a higher frequency of successful collisions in a higher concentration. Ultimately, this will increase the rate of reaction.
What are the effects of various conditions on enzyme activity?
Jan 25, 2017 · I predict that the higher the enzyme concentration, the more collisions will occur and the more enzyme-substrate complexes will form, and therefore more enzyme activity. If there are more enzymes present, then there is a higher chance of a substrate colliding, with suitable activation energy into an active zone, and products formed.
What modifies the rate of enzyme activity?
How does enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity? Enzyme concentration : Increasing enzyme concentration will speed up the reaction, as long as there is substrate available to bind to. Once all of the substrate is bound, the reaction will no longer speed up, since there will be nothing for additional enzymes to bind to.
How to improve enzyme activity?
Effect of Enzyme Concentration on Enzymatic Reaction As long as there is substrate available to bind to, increasing enzyme concentration will speed up the enzymatic reaction. Once all of the substrate is bound, the reaction will no longer speed up with the increasing enzyme concentration, since there will be nothing for additional enzymes to bind to.

What is the effect of enzyme concentration on enzyme activity?
The activity of an enzyme increases as the concentration of the enzyme increases. This is because more enzymes are available to bind to the substrate. In turn, the reaction speed increases. As long as there is a substrate to bind to, increasing enzyme concentration will speed up the reaction.
How does enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity quizlet?
How does enzyme concentration affect the direction of an enzyme reaction?
Why does enzyme activity increase when the substrate concentration increases?
How does enzyme concentration affect catalase activity?
What happens when enzyme concentration decreases?
How does enzyme concentration affect the rate of product production?
What is the relationship between substrate concentration and enzyme activity?
How does enzyme-substrate interaction affect the rate of reaction?
Enzyme-substrate complexes affect the rate of most reactions – the more enzymes there are in a solution where the substrate is in excess, the more successful the enzyme-substrate collisions so increases the rate of reaction. The of enzyme concentration and rate of reaction graph is directly proportional.
What happens when an enzyme is introduced to the correct substrate?
When an enzyme is introduced to the correct substrate, an enzyme-substrate complex will occur and the substrate will either be broken down, built up, or altered.
How does casein break down milk?
In this experiment, milk protein casein is introduced to different concentrations of the protein enzyme trypsin, which breaks down the casein by the process of hydrolysis. The original cloudiness of the milk, caused by casein, slowly fades depending on the concentration of protease trypsin, the rate of which is measured by a colourimeter.
How does cystic fibrosis affect the pancreas?
In cystic fibrosis, the pancreatic duct becomes blocked by abnormally sticky and viscous mucus, impairing the release of digestive enzymes. The lower concentration of enzymes within the small intestine reduces the rate of digestion. Food is not fully digested, so not all the nutrients can be absorbed into the bloodstream. As a consequence, the faeces contain a higher proportion of undigested food, so energy is lost (malabsorption). An additional complication occurs when the pancreatic enzymes become trapped behind the mucus blocking the pancreatic duct. These enzymes damage the pancreas itself. Cysts of hard, damaged fibrosed tissue form within the pancreas.*
When the tertiary structure forms, the amino acid chain becomes a fully functioning protein?
When the Tertiary Structure forms, the amino acid chain becomes a fully functioning protein as bonds between R groups form a 3D structure. The order of the R groups in the original amino acids determines the 3D structure in which it becomes.
Which glands secrete enzymes?
Gland secrete digestive enzymes into the lumen of the gut, where they act as catalysts to speed up the extracellular breakdown of food molecules. Exocrine glands outside the gut, e.g. The pancreas produces a wide range of enzymes. Enzymes are also built into the membranes of the gut wall.
What is the purpose of the experiment in casein?
The aim of this experiment is to investigate the effect of an increase in concentration of protease (in this experiment, trypsin), on the rate of hydrolysis of the milk protein, casein.
What happens to enzymes when concentration increases?
However, with the increase of enzyme concentration, the effectiveness of the active sites also increases, so these active sites will convert the substrate molecules into products. This basically means that if the concentration of the enzyme is to be increased, there needs to be an excess of substrate, in other words, ...
How to study the effect of increasing the enzyme concentration upon the reaction rate?
In order to study the effect of increasing the enzyme concentration upon the reaction rate, the substrate must be present in an excess amount; i.e., the reaction must be independent of the substrate concentration.
What happens when the substrate is bound?
Once all of the substrate is bound, the reaction will no longer speed up with the increasing enzyme concentration, since there will be nothing for additional enzymes to bind to.
How does an enzyme work?
Enzyme is a catalytic protein which can speed up the chemical reaction without being altered in the reaction process. In the reaction process, there is no bond formed between the enzyme and the substrate, so the enzyme goes back to its original shape and can be used again. The enzyme binds to the substrate through the active site to form an enzyme-substrate complex. They are very specific in the reaction and also to the substrate they are binding with. When the shape of the substrate matches the active site of the enzyme, the function of the enzyme is correct, and their functioning is dependent on its three-dimensional structure. They make the reaction easier to occur by reducing the activation energy and activating more molecules, thus carrying out the catalyst.
When the shape of the substrate matches the active site of the enzyme, the function of the enzyme is correct?
When the shape of the substrate matches the active site of the enzyme, the function of the enzyme is correct, and their functioning is dependent on its three-dimensional structure. They make the reaction easier to occur by reducing the activation energy and activating more molecules, thus carrying out the catalyst.
Why is concentration important in chemical reactions?
Effect of Enzyme Concentration. The concentration of the enzyme is important in chemical reaction as it is needed to react with the substrate. Often a small amount of enzyme can consume a large amount of substrate.
When is an enzyme assay satisfied?
It is satisfied only when the reaction is zero-order.
How does increasing enzyme concentration affect the speed of a reaction?
Enzyme concentration: Increasing enzyme concentration will speed up the reaction, as long as there is substrate available to bind to. Once all of the substrate is bound, the reaction will no longer speed up, since there will be nothing for additional enzymes to bind to.
What determines the amount of enzyme present in a reaction?
Enzyme Concentration. The amount of enzyme present in a reaction is measured by the activity it catalyzes. The relationship between activity and concentration is affected by many factors such as temperature, pH, etc.
Why does increasing substrate concentration increase the rate of reaction?
This is because more substrate molecules will be colliding with enzyme molecules, so more product will be formed.
How does the rate of a chemical reaction increase?
Conclusions: The rate of a chemical reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases . Enzymes can greatly speed up the rate of a reaction. However, enzymes become saturated when the substrate concentration is high.
What happens when enzyme concentration increases?
Additionally, what happens when enzyme concentration increases? By increasing the enzyme concentration, the maximum reaction rate greatly increases. Conclusions: The rate of a chemical reaction increases as the substrate concentration increases. Enzymes can greatly speed up the rate of a reaction. However, enzymes become saturated when the substrate concentration is high.
Why is the rate of enzyme activity greater when the enzyme concentration is inserted to 100%?
If the enzyme concentration is inserted to 100%ml then rate of the enzyme activity will be greater because the reaction is dependent on the enzyme concentration. The greater the number of enzyme there wills the more enzymes to bind with the substrate.
What factors affect the rate at which enzymatic reactions proceed?
Several factors affect the rate at which enzymatic reactions proceed - temperature, pH, enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, and the presence of any inhibitors or activators.
What causes enzymes to denature?
Extreme pH values can cause enzymes to denature. Enzyme concentration: Increasing enzyme concentration will speed up the reaction, as long as there is substrate available to bind to. Once all of the substrate is bound, the reaction will no longer speed up, since there will be nothing for additional enzymes to bind to.