How does and describe fluid mosaic model?
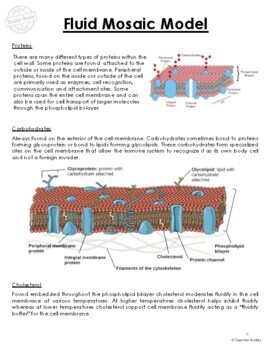
The fluid mosaic model represents the structure of a cellular membrane as a bilipid layer irregularly interspersed with protein in which the positions of individual bilipid and protein molecules are dynamic. In this model, lipids maintain flexibility and limit diffusion while proteins transport molecules through the membrane.
How do I describe the fluid mosaic model?
fluid mosaic model. A model that describes the structure of cell membranes. In this model, a flexible layer made of lipid molecules is interspersed with large protein molecules that act as channels through which other molecules enter and leave the cell.
What are fluid mosaic models used for?
The fluid mosaic model is the most acceptable model of the plasma membrane. Its main function is to separate the contents of the cell from the outside. Chemically a cell membrane is composed of four components: (1) Phospholipids (2) Proteins (3) Carbohydrates (4) Cholesterol
Why is the fluid mosaic model called Mosaic?
Why is the fluid mosaic model called Mosaic? Explanation: It is sometimes referred to as a fluid mosaic because it has many types of molecules which float along the lipids due to the many types of molecules that make up the cell membrane. The liquid part is the lipid bilayer which floats along the lipids due to the many types of molecules that make up the cell.

What is the fluid mosaic model and how was it demonstrated?
The fluid mosaic model was proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson. This model explains the structure of the plasma membrane of animal cells as a mosaic of components such as phospholipids, proteins, cholesterol, and carbohydrates. These components give a fluid character to the membranes.
What are the 3 parts of the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane. Protein, lipid, and carbohydrate components of the membrane.
Which describes the fluid mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure?
Phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins describes the fluid-mosaic model of the plasma membrane structure.
How fluid mosaic model was developed?
In 1972 the Fluid—Mosaic Membrane Model of membrane structure was proposed based on thermodynamic principals of organization of membrane lipids and proteins and available evidence of asymmetry and lateral mobility within the membrane matrix [S. J. Singer and G. L. Nicolson, Science 175 (1972) 720–731].
Which statement best describes the fluid mosaic model?
Correct answer: The fluid mosaic model states that lipids and proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer in a mosaic-like pattern; this applies to the cell membrane. Explanation: The fluid mosaic model states that amphipathic proteins are embedded in the phospholipid bilayer.
What makes the fluid mosaic model mosaic?
Cell membranes are represented according to a fluid-mosaic model, due to the fact that they are: Fluid – the phospholipid bilayer is viscous and individual phospholipids can move position. Mosaic – the phospholipid bilayer is embedded with proteins, resulting in a mosaic of components.
Why fluid mosaic model is most accepted?
The fluid mosaic model is the most acceptable model of the plasma membrane. Its main function is to separate the contents of the cell from the exterior....Chemical makeup.ComponentsLocationFunctionsCholesterolBetween phospholipids and phospholipid bilayersIt helps the plasma membrane to retain its fluidity.3 more rows
What evidence supports the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model is supported and has been further developed by measurements with modern techniques, including nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, X-ray and neutron scattering, and computer simulations. Details with molecular resolutions have now been revealed.
What causes the mosaic pattern in membranes?
The membrane proteins and lipids of the membrane can move laterally around the membrane, much like buoys in water, or sideways throughout the membrane. Such movement causes a constant change in the "mosaic pattern" of the plasma membrane. The mosaic pattern results from the many different components of the bilayer.
How many layers are in the fluid mosaic model?
When cellular membranes form, phospholipids assemble into two layers because of these hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. The phosphate heads in each layer face the aqueous or watery environment on either side, and the tails hide away from the water between the layers of heads, because they are hydrophobic.
Which of the following cell parts is described as a fluid mosaic?
Cell-membraneCell-membrane was described by the “fluid mosaic model". It describes the cell membrane as a two-dimensional liquid that restricts the lateral diffusion of the membrane components.
1. What are the Factors Affecting the Fluidity of the Plasma Membrane?
Three main factors influence cell membrane fluidity:Temperature: The temperature affects phospholipids. When it’s cold the phospholipid molecules a...
2. Who Proposed the Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane?
Plasma membrane is the cell membrane that separates the interior and exterior components of the cell from the surroundings. The cell wall is on the...
3. What are the Molecules That can go Through the Cell Membrane?
There are 5 major categories of molecules found in the cellular environment. These can travel across the cell membrane:Small, nonpolar molecules su...
4. Explain the Fluid Mosaic Model of the Plasma Membrane.
The Fluid mosaic model was proposed by Singer and Nicolson in 1972. As stated in this model, the quasi-fluid nature of lipids allows lateral moveme...
What is the fluid mosaic model and what does it tell us?
The fluid mosaic model is a model of the cell membrane that explains how the components are able to move freely, laterally in the bilayer, and that...
Who proposed fluid mosaic model of cell membrane?
S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson proposed the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane in 1972 to describe its molecular structure.
Why is it called the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model describes the main characteristics of the plasma membrane. First, the membrane is fluid with the molecules moving and the me...
What is fluid mosaic?
The fluid mosaic model is one way of understanding biological membranes, consistent with most experimental observations. This model states that the components of a membrane such as proteins or glycolipids, form a mobile mosaic in the fluid-like environment created by a sea of phospholipids. There are restrictions to lateral movements, and subdomains within the membrane have specific functions.
When was the fluid mosaic model refined?
Other Models for Membrane Structure. The fluid mosaic model was refined in the early 1980s, by two scientists called Mouritsen and Bloom to create the ‘mattress model’ for membrane structure.
How is the fluid nature of the lipid matrix forming the membrane illustrated?
The fluid nature of the lipid matrix forming the membrane was first illustrated by an experiment where membranes with different compositions were artificially fused. The proteins of both cells redistributed themselves across the entire fused membrane in less than an hour.
When were cell membranes first visualized?
More than 25 years after the lipid bilayer model was proposed, cell membranes were first visualized in the 1950s. The initial observations seemed to suggest that the lipid membrane was coated on either side by thin sheets of proteins. However, in 1972, two scientists, Singer and Nicolson, refined this to create the fluid mosaic model.
Why is the fluid mosaic model called such?
The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is called such because the cell membrane is made of different parts working together, like a mosaic is made of many tiles. The different parts of the cell membrane include:
What is fluid mosaic?
The fluid mosaic model is a model of the cell membrane. The cell membrane separates the interior of the cell, called the cytoplasm, from the external environment. The cell membrane regulates what enters and exits the cell, called selective permeability. The fluid mosaic model describes the fluid and flexible nature of the cell membrane and also the components it is made from. The different components, such as proteins and phospholipids, float laterally in the membrane. The table below summarizes the different components:
Who proposed the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane?
S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson proposed the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane in 1972 to describe its molecular structure.
What is the fluid mosaic model?
The fluid mosaic model explains various observations regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. According to this biological model, there is a lipid bilayer (two molecules thick layer consisting primarily of amphipathic phospholipids) in which protein molecules are embedded. The lipid bilayer gives fluidity and elasticity to the membrane.
How to determine fluid properties of biological membranes?
The fluid property of functional biological membranes had been determined through labeling experiments, x-ray diffraction, and calorimetry. These studies showed that integral membrane proteins diffuse at rates affected by the viscosity of the lipid bilayer in which they were embedded, and demonstrated that the molecules within the cell membrane are dynamic rather than static.
How fast do lipids diffuse?
Diffusion occurs at a high speed, with an average lipid molecule diffusing ~2 µm, approximately the length of a large bacterial cell, in about 1 second. It has also been observed that individual lipid molecules rotate rapidly around their own axis. Moreover, phospholipid molecules can, although they seldom do, migrate from one side of the lipid bilayer to the other (a process known as flip-flop). However, flip-flop might be enhanced by flippase enzymes. The processes described above influence the disordered nature of lipid molecules and interacting proteins in the lipid membranes, with consequences to membrane fluidity, signaling, trafficking and function.
What are the models of biological membranes?
Previous models of biological membranes included the Robertson Unit Membrane Model and the Davson-Danielli Tri-Layer model. These models had proteins present as sheets neighboring a lipid layer, rather than incorporated into the phospholipid bilayer. Other models described repeating, regular units of protein and lipid. These models were not well supported by microscopy and thermodynamic data, and did not accommodate evidence for dynamic membrane properties.
What is asymmetric membrane?
Membrane asymmetry. Additionally, the two leaflets of biological membranes are asymmetric and divided into subdomains composed of specific proteins or lipids, allowing spatial segregation of biological processes associated with membranes.
What is the most acceptable model of the plasma membrane?
The fluid mosaic model is the most acceptable model of the plasma membrane. Its main function is to separate the contents of the cell from the outside.
Which scientist proposed the idea that all membranes in the cell have the same structure?
1957 – J. David Robertson, based on electron microscopy studies, establishes the "Unit Membrane Hypothesis". This, states that all membranes in the cell, i.e. plasma and organelle membranes, have the same structure: a bilayer of phospholipids with monolayers of proteins at both sides of it.
Why is the fluid mosaic model called fluid mosaic model?
The phospholipid molecules and the molecules of cholesterol are linked together. This keeps the cell membrane intact and cohesive. This is why it is called fluid mosaic model.
Which protein forms channels to allow the movement of large molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane?
Integral Proteins: These proteins form channels to allow the movement of large molecules and ions across the hydrophobic layer of the membrane.
Why is the plasma membrane important?
It helps the plasma membrane to retain the fluidity. It is present between the phospholipids and prevents the compaction of hydrophilic tails at low temperatures and their expansion at high temperatures.
What is the fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane?
The fluid mosaic model of the cell membrane is how scientists describe what the cell membrane looks and functions like , because it is made up of a bunch of different molecules that are distributed across the membrane. If you were to zoom in on the cell membrane, you would see a pattern of different types of molecules put together, also known as a mosaic. These molecules are constantly moving in two dimensions, in a fluid fashion, similar to icebergs floating in the ocean. The movement of the mosaic of molecules makes it impossible to form a completely impenetrable barrier.
What is a cell drawing?
A drawing showing a part of a cell membrane magnified to see the molecules that it is comprised of.
Why are phospholipids semi-permeable?
For this reason, and the ability of proteins to help with transport across the membrane, cell membranes are called semi-permeable.

Fluid Mosaic Model Definition
Development of The Fluid Mosaic Model
- This model was developed over many years, through painstaking work of scientists across the world. It began with the hypothesis that the membrane was made of a lipid bilayer, where membrane phospholipid self-assembled into a dual layer, with the non-polar, hydrophobic tails facing each other. The hydrophilic ‘head’ regions face the cytosol and the extracellular region. Th…
Functions and Components of Biological Membranes
- The main function of cell membranes is to demarcate the inner and outer regions of the cell. Within the cell, membranes of organelles perform the same function for subcellular structures. This function comes along with a caveat – the cell needs to actively communicate with the external environment, exchange materials, while also retaining important nutrients and keeping …
Other Models For Membrane Structure
- The fluid mosaic model was refined in the early 1980s, by two scientists called Mouritsen and Bloom to create the ‘mattress model’ for membrane structure. They demonstrated the fact that while earlier experiments had suggested that the entire membrane is fluid and allows free diffusionof proteins, there are in fact, subdomains within each membrane. For instance, when a t…
Related Biology Terms
- Amphipathic Molecules– Molecules containing polar hydrophilic regions and non-polar hydrophobic regions.
- Antigen– Any molecule capable of producing an immune response.
- Signal Transduction– Transmission of information, in the form of electrical or chemical signals, from the exterior of the cell to the interior.
- Amphipathic Molecules– Molecules containing polar hydrophilic regions and non-polar hydrophobic regions.
- Antigen– Any molecule capable of producing an immune response.
- Signal Transduction– Transmission of information, in the form of electrical or chemical signals, from the exterior of the cell to the interior.
- Sphingolipids– Fatty acid derivatives of a molecule called sphingosine. Often seen in membrane lipid rafts.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these statements about the structure of membranes is true? A. Made primarily of cholesterol molecules B. Glycoproteins on the cell surface are necessary for immune recognition C. Lipid rafts were predicted by early models of cell membrane structure D.All of the above 2. Which of these are features of the fluid mosaic model of cell membranes? A. Lipid bilayer forme…
Overview
The fluid mosaic model explains various observations regarding the structure of functional cell membranes. According to this biological model, there is a lipid bilayer (two molecules thick layer consisting primarily of amphipathic phospholipids) in which protein molecules are embedded. The phospholipid bilayer gives fluidity and elasticity to the membrane. Small amounts of carbohydr…
Subsequent developments
Additionally, the two leaflets of biological membranes are asymmetric and divided into subdomains composed of specific proteins or lipids, allowing spatial segregation of biological processes associated with membranes. Cholesterol and cholesterol-interacting proteins can concentrate into lipid rafts and constrain cell signaling processes to only these rafts. Another form of asymmetry was shown by the work of Mouritsen and Bloom in 1984, where they propos…
Experimental evidence
The fluid property of functional biological membranes had been determined through labeling experiments, x-ray diffraction, and calorimetry. These studies showed that integral membrane proteins diffuse at rates affected by the viscosity of the lipid bilayer in which they were embedded, and demonstrated that the molecules within the cell membrane are dynamic rather than static.
Restrictions to bilayer fluidity
There are restrictions to the lateral mobility of the lipid and protein components in the fluid membrane imposed by the formation of subdomains within the lipid bilayer. These subdomains arise by several processes e.g. binding of membrane components to the extracellular matrix, nanometric membrane regions with a particular biochemical composition that promote the formation of lipid rafts a…
Historical timeline
• 1895 – Ernest Overton hypothesized that cell membranes are made out of lipids.
• 1925 – Evert Gorter and François Grendel found that red blood cell membranes are formed by a fatty layer two molecules thick, i.e. they described the bilipid nature of the cell membrane.
• 1935 – Hugh Davson and James Danielli proposed that lipid membranes are layers composed by proteins and lipids with pore-like structures that allow specific permeability for certain molecules. Then, they sugge…