How does intermolecular forces affect chromatography? There are also the intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen-bonding and dipole-dipole interactions in chromatography, which help retain the analyte to the stationary phase of your column. The stronger the intermolecular forces, the stronger and longer the compound is retained in the column.
What are intermolecular forces in chromatography?
Intermolecular forces are forces of attraction between molecules that affect the physical properties of matter. Furthermore, it also aims how these forces can be exploited to physically separate complex mixtures in chromatography.
How does solubility affect chromatography?
How does solubility affect chromatography? Solubility does not affect chromatography; differences in intermolecular forces affect chromatography. In paper chromatography, for example, you dissolve the components of a mixture in a solvent. As the solution moves along the paper, the various constituents travel at different speeds.
How do intermolecular forces affect the structure of a substance?
Strong intermolecular forces help hold the substance together, while weaker ones do not hold the molecules in the substance together as much. Water has the strongest intermolecular forces (hydrogen bonds) of all the substances used.
How do intermolecular forces affect boiling point?
Substances with strong intermolecular forces will have a higher boiling point than substances with weaker intermolecular forces. To investigate capillarity (how far up a tube a liquid rises or how far down a liquid falls) and to determine the relation between capillarity and intermolecular forces.

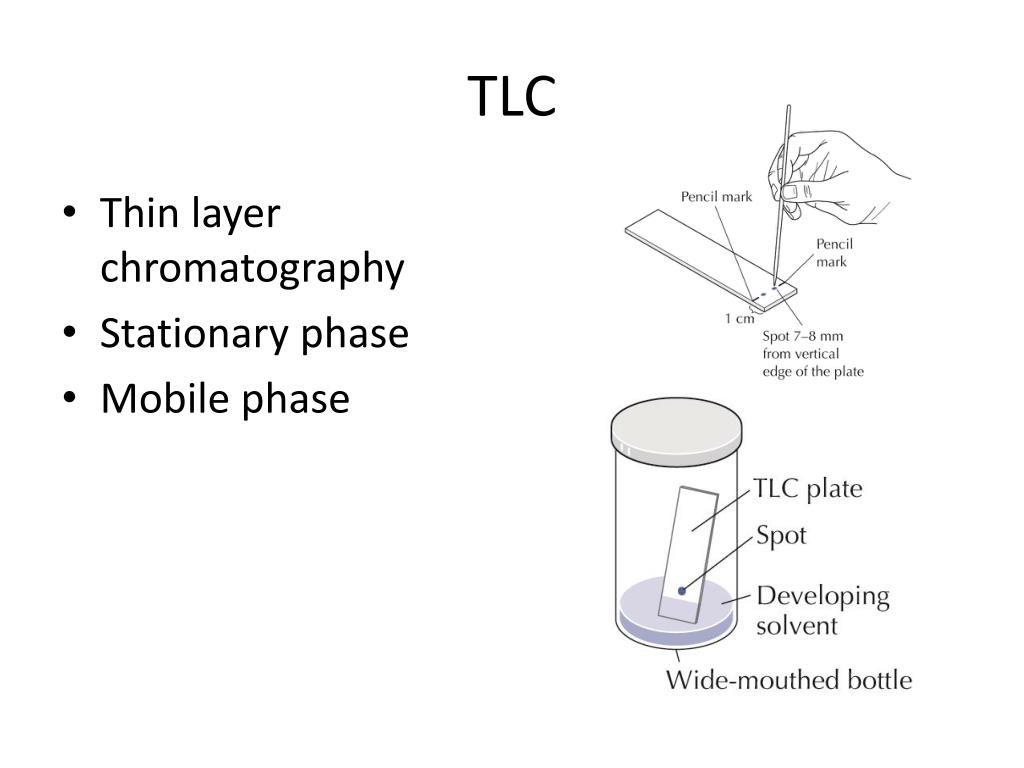
How do intermolecular forces affect TLC?
Intermolecular forces are fundamental to the separation of compounds via TLC. We have three components at play here, the stationary phase, the mobile phase, and the sample. The balance between the interactions of these components causes separation.
What are the factors affecting chromatography?
What factors affect chromatography? Retention factor values in thin layer chromatography are affected by the absorbent, the solvent, the chromatography plate itself, application technique and the temperature of the solvent and plate.
Does hydrogen bonding affect chromatography?
Hydrogen bonding has been acknowledged as a contributing factor to protein retention on ion exchangers since the mid-1950s and more recently suggested as a selectivity modifier for many mixed-mode chromatography products.
What type of intermolecular force of attraction occurs between the water and the chromatography paper?
Hydrogen bonding occurs between paper and water because of the OH from the chromatography paper and the H from the water; this strong intermolecular force accounts for the tendency of the water to travel in a capillary action opposite of gravity.
What affects the separation of mixtures in chromatography?
The different components of the mixture travel through the stationary phase at different speeds, causing them to separate from one another. The nature of the specific mobile and stationary phases determines which substances travel more quickly or slowly, and is how they are separated.
What affects the rate of separation in chromatography?
Separation depends on the relative partial pressures of the sample components above the stationary phase. Liquid chromatography uses similar packed tubular columns and usually a pump to force a liquid mobile phase through the column.
What force is involved in chromatography?
The four forces involved in chromatography are the London dispersion, dipole-dipole, hydrogen bonding and ion-dipole forces.
How does polarity affect paper chromatography?
Polarity of the solvent affects the speed of the chromatography process. So, we can say that, if we increase the polarity of the solvent all the other components present in the mixture move faster during the chromatography experiment.
Between what types of substances do the different intermolecular forces exist?
How forces of attraction affect properties of compoundsType of compoundIntermolecular forces presentPolar covalent compoundsDipole-dipole attraction between dipoles created by partially charged ions, London dispersion forcesNonpolar covalent compoundsLondon dispersion forces2 more rows
What are the effects of intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind two molecules together. Physical properties are affected by the strength of intermolecular forces. Melting, boiling, and freezing points increase as intermolecular forces increase. Vapor pressure decreases as intermolecular forces increase.
What would happen if there were no intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces allow us to determine which substances are likely to dissolve in which other substances and what the melting and boiling points of substances are. Without intermolecular forces holding molecules together we would not exist.
What is the relationship between strength of intermolecular forces and solubility of substances?
Main Idea: “Like dissolves like.” The stronger the intermolecular forces between solute molecule and solvent molecule, the greater the solubility of the solute in the solvent.
What are the factors that affect the movement of pigment during chromatography?
The porosity of the chromatography paper, the solvent's solubility, and the molecular size of the solute were all factors that affected pigment transport during chromatography.
What affects chromatography resolution?
To achieve satisfactory resolution, the maxima of two adjacent peaks must be disengaged. Such disengagement depends on the identity of the solute and the selectivity of the stationary and mobile phases. The second feature important to efficiency and resolution is the width of the peak.
What factors affect the separation of pigments?
The factors that are involved in the separation of the pigments in this lab are solubility, size of particles, and their attractiveness to the paper are involved in the separation of the pigments.
What are the factors that affect the column efficiency?
Factors affecting column efficiency in column chromatographyColumn chromatography is the basic and oldest separation technique for separating compounds according to their polarity. ... Column Packing: ... The particle size of the adsorbent: ... The dimension of the column: ... Solvents: ... Flow Rate: ... The temperature of the column:More items...•
Abstract
A survey is presented of column chromatography, with special emphasis on intermolecular interactions that are at the origin of selectivity in chromatographic separations.
Keywords
These keywords were added by machine and not by the authors. This process is experimental and the keywords may be updated as the learning algorithm improves.
Introduction
One well-known application of gas chromatography is its analytical capability used to obtain purely physiochemical data such as activity coefficients of solutes in various solvents, heats of solution, and enthalpies of vaporization of volatile compounds. It can also be used to demonstrate colligative properties.
Sensors and Equipment
This experiment features the following sensors and equipment. Additional equipment may be required.
What happens if a substance has weak intermolecular forces?
If a substance has weak intermolecular forces then it will evaporate easily. Substances with weak intermolecular forces also have low surface tension and do not rise as far up in narrow tubes as substances with strong intermolecular forces. Boiling points are lower for substances with weak intermolecular forces.
What happens when the attractive force between the glass walls of the tube and the substance is stronger than the intermolecular?
If the attractive force between the glass walls of the tube and the substance are stronger than the intermolecular forces in the substance, than the edges of the liquid will be pulled above the surface of the liquid. This in turn helps pull the liquid up the tube.
Which substance has the strongest intermolecular force?
Water has the strongest intermolecular forces (hydrogen bonds) of all the substances used. Glycerine and methylated spirits also have hydrogen bonds, but these intermolecular forces are slightly weaker than in water. Sunflower oil is mostly non-polar but has very long molecules which help account for the higher surface tension.
How many ml of each substance given in separate small beakers or measuring cylinders?
Place about 50 50 ml ml of each substance given in separate small beakers or measuring cylinders.
Which forces travel further up a narrow tube?
Substances with strong intermolecular forces will travel further up a narrow tube (have a greater capillarity) than substances with weaker intermolecular forces.
Does iodine dissolve in water?
You should find that the sodium chloride and potassium permanganate dissolved (at least a bit) in all the substances. The iodine did not dissolve in any of the substances. The three solvents (water, chloroform and ethanol) are all polar and have dipole-dipole forces. Sodium chloride and potassium permanganate are both ionic substances, while iodine is non-polar.
Does nail polish remover hold together?
You should also have noticed that water, oil and Glycerine tend to form a drop, while nail polish remover and methylated spirits do not . Strong intermolecular forces help hold the substance together, while weaker ones do not hold the molecules in the substance together as much.
How does paper chromatography work?
Explanation: In paper chromatography, for example, you dissolve the components of a mixture in a solvent. As the solution moves along the paper, the various constituents travel at different speeds. They separate into different spots. The separation depends on the different attractive forces between the paper and the components of the mixture.
What happens when components are strongly attracted to a solvent?
The components that are strongly attracted to the paper spend less time in the solvent and move more slowly. Thus, the components separate into separate spots, based on their different attractions to the paper.
Why do swimmers hold on longer?
The swimmers with the stronger grip can hold on longer. They spend less time being carried along the water, so they are carried to their deaths more slowly. The more time a component stays in the solvent, the faster it moves along the paper, because the solvent is moving forwards.
