
How does mantle convection affect the plates? As tectonic plates slowly move away from each other, heat from the mantle’s convection currents makes the crust more plastic and less dense. The less-dense material rises, often forming a mountain or elevated area of the seafloor. Eventually, the crust cracks.
What is an example of mantle convection in plate tectonics?
Based on mantle convection, each plate tectonic moves in a specific way. For example, there are divergent, convergent and transform plates. How does mantle convection drive plate tectonics?
What is the role of the mantle in plate tectonics?
Mantle convection is the main driver of plate tectonics. Under the rigid layer of rock we live on, the Earth is plastic and more dense. Because of its fluid-like properties, mantle convection can occur.
How does convection affect plate tectonics?
As mantle convection rises, it breaks apart the Earth to form mid-oceanic ridges (tensional force). When it sinks down, it breaks it apart (compressional force). These tensional and compressional forces are what drives plate tectonics. They break apart the whole lithosphere into 7 major plate tectonics and 12 or so minor ones.
What happens when the mantle rises and sinks?
As mantle convection rises, it breaks apart the Earth to form mid-oceanic ridges (tensional force). When it sinks down, it breaks it apart (compressional force). These tensional and compressional forces are what drives plate tectonics.
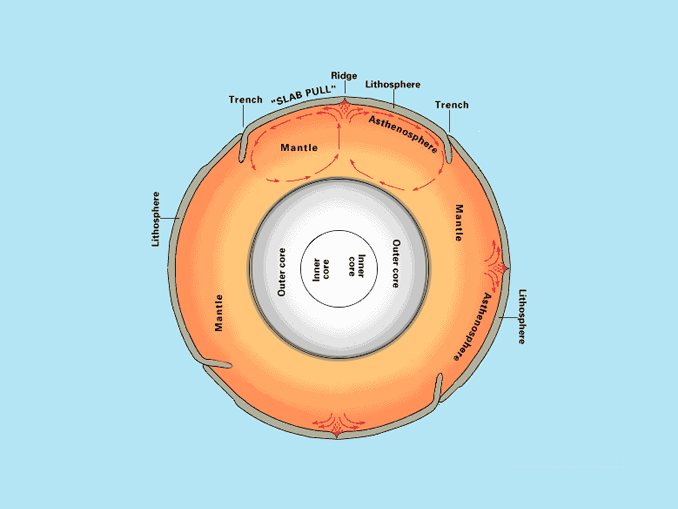
What does mantle convection affect?
Mantle convection: Thermal convection in the terrestrial planetary mantles, the rocky layer be- tween crust and core, in which hot material rises, cold material sinks and the induced flow governs plate tectonic and volcanic activity, as well as chemical segregation and cooling of the entire planet.
Does mantle convection current affect plate boundaries?
Complete answer: Convection flows drive the development of Earth's inflexible tectonic plates in the planet's liquid mantle. In spots where convection flows ascend towards the crust surface, tectonic plates move away from one another in a cycle known as seafloor spreading.
How does plate tectonics affect the mantle?
The system of ideas behind plate tectonics theory suggests that Earth's outer shell (lithosphere) is divided into several plates that glide over the Earth's rocky inner layer above the soft core (mantle). The plates act like a hard and rigid shell compared to Earth's mantle.
How does mantle convection cause subduction?
At the consumption edges of the plate, the material has thermally contracted to become dense, and it sinks under its own weight in the process of subduction usually at an ocean trench. Subduction is the descending component of mantle convection. This subducted material sinks through the Earth's interior.
Does the mantle cause the plates to move?
The plates can be thought of like pieces of a cracked shell that rest on the hot, molten rock of Earth's mantle and fit snugly against one another. The heat from radioactive processes within the planet's interior causes the plates to move, sometimes toward and sometimes away from each other.
What is the cause and effect of mantle convection?
Mantle convection occurs due to density differences from temperature and composition variations. The leftover heat from the Earth's formation and heat generated by unstable isotopes cause internal heating, producing the hot lower thermal boundary and colder upper thermal boundary.
Does mantle convection causes continental drift?
Arthur Holmes proposed that convection of the mantle is the driving mechanism for continental drift: rifts represent regions of mantle upwelling, whereas mountain ranges form where rocks sink back into the interior of the planet.
How does mantle convection cause seafloor spreading?
Seafloor spreading occurs at divergent plate boundaries. As tectonic plates slowly move away from each other, heat from the mantle's convection currents makes the crust more plastic and less dense. The less-dense material rises, often forming a mountain or elevated area of the seafloor. Eventually, the crust cracks.
Do convection currents cause plate tectonics?
Convection currents in the magma drive plate tectonics. Heat generated from the radioactive decay of elements deep in the interior of the Earth creates magma (molten rock) in the aesthenosphere. The aesthenosphere (70 ~ 250 km) is part of the mantle, the middle sphere of the Earth that extends to 2900 km.
Do convection currents cause transform boundaries?
A transform boundary is like a tear in the Earth's crust. These plates move very slowly across the surface of the Earth as though they were on a conveyor belt. The convection currents in the much hotter mantle continually move the plates about 1/2 to 4 inches per year.
Do convection currents cause convergent boundaries?
The hypothesis of convection currents suggests that flow in the mantle is induced by currents which drag and move the lithospheric plates above the asthenosphere. Convection currents rise and spread below divergent plate boundaries and converge and descend along convergent.
How do convection currents affect convergent boundaries?
Where convection currents converge, plates move towards each other. The movement of the plates, and the activity inside the Earth, is called plate tectonics . Plate tectonics cause earthquakes and volcanoes . The point where two plates meet is called a plate boundary .
What is Figure 37?
Figure 37. Shadowgraphs of the convection planforms found for the case of rigid boundaries (a) and for the case of a stress-free upper boundary (b).
How to conserve momentum and heat during flow?
To conserve momentum and heat during flow (the continuity equations) requires the same scaling ( Hofmeister and Criss, 2018 ). Thus, for planets, which are nearly spherical, Ra must be multiplied by (1− h / Rout) 6. This correction is ~0.01 which changes the value of Ra by only two orders of magnitude. More importantly, the correction of Eq. (3.19) changes the character of non-dimensionalized mantle convection equations, which do not currently incorporate the size of the planet.
What is the relationship between mantle convection and plate tectonics?
Mantle convection and plate tectonics provide a general framework for understanding tectonophysics. Transport of heat from the interior of the earth drives solid-state convection. Plate tectonics is a direct consequence of this convection. The relative velocity between plates causes crustal deformation at the boundaries between plates.
What is the Rayleigh number for the mantle?
Evidence for whole mantle convection rests on the large magnitude of the dimensionless Rayleigh number (Ra ~10 8) for Earth’s ~3000 km thick mantle. However, the historic derivation of the Rayleigh number assumes conditions quite different from those inside the rocky Earth, which motivated Hofmeister and Criss (2018) to probe the underlying physics. This section summarizes their theoretical assessment of stability criteria and arguments for stability of the lower mantle.
What is the most important form of energy available in the mantle for convection and other dynamical processes?
In terms of magnitude, thermal energy is by far the most important form of energy available in the mantle for convection and other dynamical processes, and heat flow is far and away the largest form of energy transport in the earth's interior.
How does mantle convection work?
The process of mantle convection can be regarded as a thermal engine on a planetary scale, which transports heat from the earth's deep interior to the surface. The rate at which the solid earth evolves is dictated by the rate at which this heat transport occurs. In terms of magnitude, thermal energy is by far the most important form of energy available in the mantle for convection and other dynamical processes, and heat flow is far and away the largest form of energy transport in the earth's interior. The primary sources of thermal energy for mantle convection are three: (1) internal heating due to the decay of the radioactive isotopes of uranium, thorium, and potassium; (2) the long-term secular cooling of the earth; and (3) heat from the core. The total heat flow from the mantle is 30–35 TW (1 TW = 10 12 watts of heat flow), which amounts to roughly 75–80% of the total heat loss from the earth's interior. The remaining 20–25% of the surface heat loss is due to radioactivity in the continental crust, which does not contribute much to mantle convection. The relative importance of these three mantle heat sources is somewhat uncertain, but a reasonable estimate is that radioactive heating contributes about half of the total, secular cooling about 40% and the remaining 10% comes from the core.
What are the main sources of thermal energy for mantle convection?
The primary sources of thermal energy for mantle convection are three: (1) internal heating due to the decay of the radioactive isotopes of uranium, thorium, and potassium; (2) the long-term secular cooling of the earth; and (3) heat from the core.
What is the process of convection of the mantle?
Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the planet's surface. The Earth's surface lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere and the two form the components of the upper mantle. The lithosphere is divided into a number ...
How long does it take for a convection cycle to occur?
A single shallow convection cycle takes on the order of 50 million years, though deeper convection can be closer to 200 million years. Currently, whole mantle convection is ...
What causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface?
Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface. It seems to have been much more active during the Hadean period, resulting in gravitational sorting of heavier molten iron, nickel, and sulphides to the core and lighter silicate minerals to the mantle.
What is the slow moving motion of Earth's solid mantle caused by?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. The slow moving motion of Earth's solid mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the planet's interior to its surface. Whole-mantle convection. Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by ...
How does accretion occur in the lithosphere?
Accretion occurs as mantle is added to the growing edges of a plate, associated with seafloor spreading. This hot added material cools down by conduction and convection of heat. At the consumption edges of the plate, the ...
What is the Rayleigh number for convection?
On Earth, the Rayleigh number for convection within Earth's mantle is estimated to be of order 10 7, which indicates vigorous convection. This value corresponds to whole mantle convection (i.e. convection extending from the Earth's surface to the border with the core ). On a global scale, surface expression of this convection is ...
What causes surface volcanism?
Secondary convection may cause surface volcanism as a consequence of intraplate extension and mantle plumes. In 1993 it was suggested that inhomogeneities in D" layer have some impact on mantle convection. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface.
What is the process of rising magma?
Rising magma pushes against and along tectonic plates, which eventually moves the plates together, apart, or along each other.
What happens when the plates move?
The movement of the plates can lead to volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis and mountain-range formation . However, it does take a huge amount of movement in the mantle to move literally the heaviest rocks on Earth, so it's a very slow process, even if the consequences - volcanic eruptions, for example - seem very quick.
What happens when hot molecules move up?
As the hot molecules move up, they cool down and begin to drop. As the cool molecules move down, they heat up and begin to rise. This cycle goes on over and over again, as is known as a convection current. In the Earth, this happens in the magma in the mantle. The core heats up the magma and causes a convection current.
Where does convection occur on Earth?
In the Earth, this happens in the magma in the mantle. The core heats up the magma and causes a convection current.
