How does molecular geometry determine the polarity of a molecule? In molecules with more than one bond, both shape and bond polarity determine whether or not the molecule is polar. Molecules in which all of the atoms surrounding the central atom are the same tend to be nonpolar if there are no lone pairs on the central atom.
How does molecular geometry determine the polarity of a molecule?
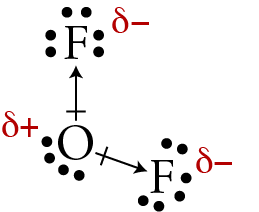
So, the geometry of the molecule determines the direction that the bond dipole vectors point. The polarity of the molecule results from adding up all these individual bond dipoles.
Does polarity depend on geometry?
In a polar molecule, electron density is unevenly distributed throughout the molecule, resulting in regions of partial negative charge and regions of partial positive charge. Molecular polarity depends on both individual bond polarities and molecular geometry, the latter of which we can predict using VSEPR theory.
What factors affect polarity of a molecule?
The shape of a molecule and the polarity of its bonds determine the OVERALL POLARITY of that molecule. A molecule that contains polar bonds, might not have any overall polarity, depending upon its shape.
What molecular geometries can you considered as polar?
Lewis Structures and the Shapes of MoleculesFormula3D Structure Shape Polarity1.CH4tetrahedral nonpolar2.NH3trigonal pyramidal polar3.H2Obent polar4.H3O+trigonal pyramidal charged2 more rows
What determines the polarity of a bond?
The difference in electronegativity between two atoms determines how polar a bond will be. In a diatomic molecule with two identical atoms, there is no difference in electronegativity, so the bond is nonpolar or pure covalent.
What increases polarity?
Bond polarity and ionic character increase with an increasing difference in electronegativity. The electronegativity (χ) of an element is the relative ability of an atom to attract electrons to itself in a chemical compound and increases diagonally from the lower left of the periodic table to the upper right.
How to determine the polarity of a molecule?
The overall polarity of molecules with more than one bond is determined from both the polarity of the individual bonds and the shape of the molecule. Each bond’s dipole moment can be treated as a vector quantity, having a magnitude and direction. Therefore the molecular polarity is the vector sum of the individual bond dipoles.
What is the difference between electron group geometry and molecular geometry?
VSEPR makes a distinction between electron group geometry, which expresses how electron groups (bonding and nonbonding electron pairs) are arranged, and molecular geometry, which expresses how the atoms in a molecule are arranged. However, the two geometries are related. There are two types of electron groups: any type of bond—single, double, ...
How to find the sum of the dipole arrows?
Let’s examine this method for a molecule of water. 1. First draw the Lewis electron dot diagram for water and determine its molecular shape. Water has four electron groups, but only two atoms attached to the central atom so it is bent. 2. Draw in dipole arrows for all polar covalent bonds, starting the arrow at the more electropositive atom, and ending at the more electronegative atom. 3. Connect the dipole arrows tail-to-head. 4. Draw a new line connecting the tail of the first vector. This is the net molecular dipole. 5. Now superimpose the net molecular dipole arrow onto the molecule. An alternative method to determine the vector sum of dipole arrows is known as the vector component method. Let’s examine this method again for a molecule of water. The first two steps remain the same as the tail-to-head method: 1. First draw the Lewis electron dot diagram for water and determine its molecular shape. Water has four electron groups, but only two atoms attached to the central atom so it is bent.
Why is a molecule with four electron groups around the central atom but only one electron group bonded to another?
A molecule with four electron groups around the central atom but only one electron group bonded to another atom is linear because there are only two atoms in the molecule. Double or triple bonds count as a single electron group. CH 2 O has the following Lewis electron dot diagram.
Why does the central C atom have three electron groups around it?
The central C atom has three electron groups around it because the double bond counts as one electron group. The three electron groups repel each other to adopt a trigonal planar shape: (The lone electron pairs on the O atom are omitted for clarity.)
How many electron groups are in a molecule?
A molecule with four electron groups around the central atom orients the four groups in the direction of a tetrahedron, as shown in Figure 9.4 “Tetrahedral Geometry.” If there are four atoms attached to these electron groups, then the molecular shape is also tetrahedral. Methane (CH 4) is an example.
When two electron groups are 180 degrees apart, what is the shape of the molecule?
When the two electron groups are 180° apart, the atoms attached to those electron groups are also 180° apart, so the overall molecular shape is linear. Examples include BeH 2 and CO 2: A molecule with three electron groups orients the three groups as far apart as possible.
VSEPR
Chemists use the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model to predict the shape of different molecules. The model is based on the fact that electrons will repel one another. As a result of this repulsion, the constituent atoms in a molecule will be as far apart from one another as possible.
Shape and Bond Angle
In order to easily and accurately determine the shape of a molecule chemists created a VSEPR chart that allows us to find the shape of an element on the basis of its bonds and lone pairs.
Polarity
This distinction might seem pedantic, but it is crucial when determining the polarity of a molecule. In the previous lesson on bonds, polar bonds result from two atoms with differing electronegativity values. While a polar molecule must possess polar bonds the arrangement of those bonds is also important.