Is calcium harmful to the human body?
Too much calcium in the blood (over 2500 mg) may cause calcium toxicity. It can develop into abnormal deposits of calcium in tissues, which is harmful for the body. Taking excess calcium can cause some adverse interactions with certain medications and so it is best to take the advice of a doctor before using calcium supplements.
How to increase calcium in body naturally?
Some good choices are:
- Skim or non-fat milk
- Dairy products like yogurt and cheese
- Dark leafy greens like spinach, kale, turnips and collard greens
- Fortified cereals
- Fortified orange juice
- Sardines
- Blackstrap Molasses
- Soybeans and other soy products
How does calcium effect the body?
Your body needs calcium for muscles to move and for nerves to carry messages between your brain and every part of your body. Calcium also helps blood vessels move blood throughout your body and helps release hormones that affect many functions in your body.
What job does calcium do in the body?
Calcium in the bones is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with the help of Vitamin D. Maintaining an adequate amount of this vitamin in the body is just as essential to healthy bone development as calcium is. The skin makes vitamin D from the ultra-violet rays in sunlight, and the body stores the vitamin for later use.
See more

Why do vegetarians have less calcium?
Vegetarians might absorb less calcium than omnivores because they consume more plant products containing oxalic and phytic acids [ 1 ]. Lacto-ovo vegetarians (who consume eggs and dairy) and nonvegetarians have similar calcium intakes [ 45, 46 ]. However, vegans, who eat no animal products and ovo-vegetarians (who eat eggs but no dairy products), might not obtain sufficient calcium because of their avoidance of dairy foods [ 47, 48 ]. In the Oxford cohort of the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition, bone fracture risk was similar in meat eaters, fish eaters and vegetarians, but higher in vegans, likely due to their lower mean calcium intake [ 49 ]. It is difficult to assess the impact of vegetarian diets on calcium status because of the wide variety of eating practices and thus should be considered on a case by case basis.
What are the health risks of high calcium levels?
Excessively high levels of calcium in the blood known as hypercalcemia can cause renal insufficiency, vascular and soft tissue calcification, hypercalciuria (high levels of calcium in the urine) and kidney stones [ 1 ].
How many people have osteoporosis?
Osteoporosis, a disorder characterized by porous and fragile bones, is a serious public health problem for more than 10 million U.S. adults, 80% of whom are women. (Another 34 million have osteopenia, or low bone mass, which precedes osteoporosis.)
What foods have oxalic acid?
Foods with high levels of oxalic acid include spinach, collard greens, sweet potatoes, rhubarb, and beans. Among the foods high in phytic acid are fiber-containing whole-grain products and wheat bran, beans, seeds, nuts, and soy isolates [ 1 ]. The extent to which these compounds affect calcium absorption varies.
How much calcium does the human body absorb?
Humans absorb about 30% of the calcium in foods, but this varies depending upon the type of food consumed [ 1 ]. Other factors also affect calcium absorption including the following: Amount consumed: the efficiency of absorption decreases as calcium intake increases [ 1 ].
What is the RDA for nutrition?
These values, which vary by age and gender, include: Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA): Average daily level of intake sufficient to meet the nutrient requirements of nearly all (97%–98%) healthy individuals; often used to plan nutritionally adequate diets for individuals.
How much calcium is in calcium carbonate?
For example, calcium carbonate is 40% calcium by weight, whereas calcium citrate is 21% calcium. Fortunately, elemental calcium is listed in the Supplement Facts panel, so consumers do not need to calculate the amount of calcium supplied by various forms of calcium supplements.
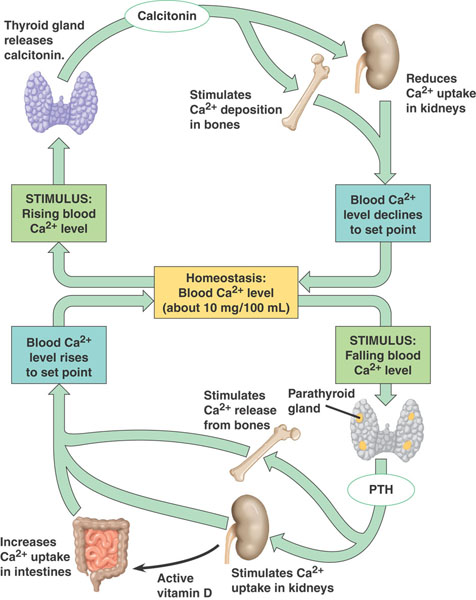
What hormones are released when calcium levels drop?
In response to decreased blood calcium levels, the parathyroid glands release parathyroid hormone (PTH) which stimulates osteoclasts to liberate calcium from bone and into blood. PTH also encourages the digestive system to absorb more calcium and the kidneys to retain more calcium in blood.
Why is ATP not replaced?
Because cross bridge detachment and calcium active transport is ATP driven, calcium leakage from the sarcoplasmic reticulum causes attachment of cross bridges, and lack of ATP prevents detachments.
Which bone has a large medullary cavity?
The diaphysis in long bones has a large medullary cavity, whereas the epiphyses do not. Compare how nutrients reach individual osteocytes in compact bone and in spongy bone. In spongy bone, nutrients reach osteocytes by diffusing through the canaliculi from capillaries in the endosteum surrounding the trabeculae.
What is the difference between a diaphyseal and an epiphyseal bone?
Diaphyseal bone is composed almost entirely of compact bone (except in irregular and short bones), while the epiphyses are composed almost entirely of spongy bone . The epiphyses are on the ends of the bone; the diaphysis is the "shank" of the bone.
How much calcium enters the bones each day?
Up to 0.5 g of calcium may enter or leave the bones each day, depending on the negative feedback hormonal mechanism and gravitational forces. Compare the function of the organic materials in the bone matrix with the function of the inorganic materials in the matrix.
Why does my child have rickets?
The child most likely has rickets, a condition caused by poor diet, especially one deficient in vitamin D. The parents were told to increase her intake of calcium and vitamin D and to make sure that she gets some sunshine every day.
Why is succinylcholine used in ECT?
Because the muscles contract, the shape, size, and strength of the muscles are maintained as well as joint mobility. A patient is admitted for electroconvulsive treatment (ECT). The physician orders the neuromuscular blocking agent succinylcholine to reduce trauma by relaxing skeletal muscles.
Why do parathyroid glands become overactive?
The parathyroid glands may become overactive when one is enlarged or when a noncancerous growth forms on one. Having overactive parathyroid glands is called hyperparathyroidism. This may be the most common cause of hypercalcemia. Hyperparathyroidism is usually diagnosed in people aged between 50 and 60.
What happens if your parathyroid gland is overactive?
Overactive parathyroid glands or an underlying health condition can disrupt the balance of calcium. If calcium levels become too high, a person may be diagnosed with hypercalcemia. This condition can impede bodily functions, and may specifically be associated with: poor bone health. kidney stones.
Why is hypercalcemia bad?
The term hypercalcemia refers to having too much calcium in the blood. For some, the cause is an overactive parathyroid gland, certain medications, too much vitamin D, or underlying health conditions, including cancer. Calcium plays an essential role in the body.
Why does my bone feel weak?
Bone pain and muscle weakness. Hypercalcemia can cause the bones to release too much calcium , leaving them deficient. This abnormal bone activity can lead to pain and muscle weakness.
Which gland controls calcium levels in the blood?
The parathyroid gland controls calcium levels in the blood. Calcium levels in the blood are mostly controlled by the parathyroid glands. These four tiny glands sit behind the thyroid. When the body needs calcium, the parathyroid glands secrete a hormone. This hormone signals:
How much calcium is absorbed in the body?
Only 10–20 percent of the calcium in the diet is usually absorbed, while the rest is passed in stools. However, excessive amounts of vitamin D cause the body to absorb more calcium, leading to hypercalcemia.
How to prevent kidney stones?
Drinking plenty of water. Staying hydrated may lower blood calcium levels, and it can help to prevent kidney stones.
