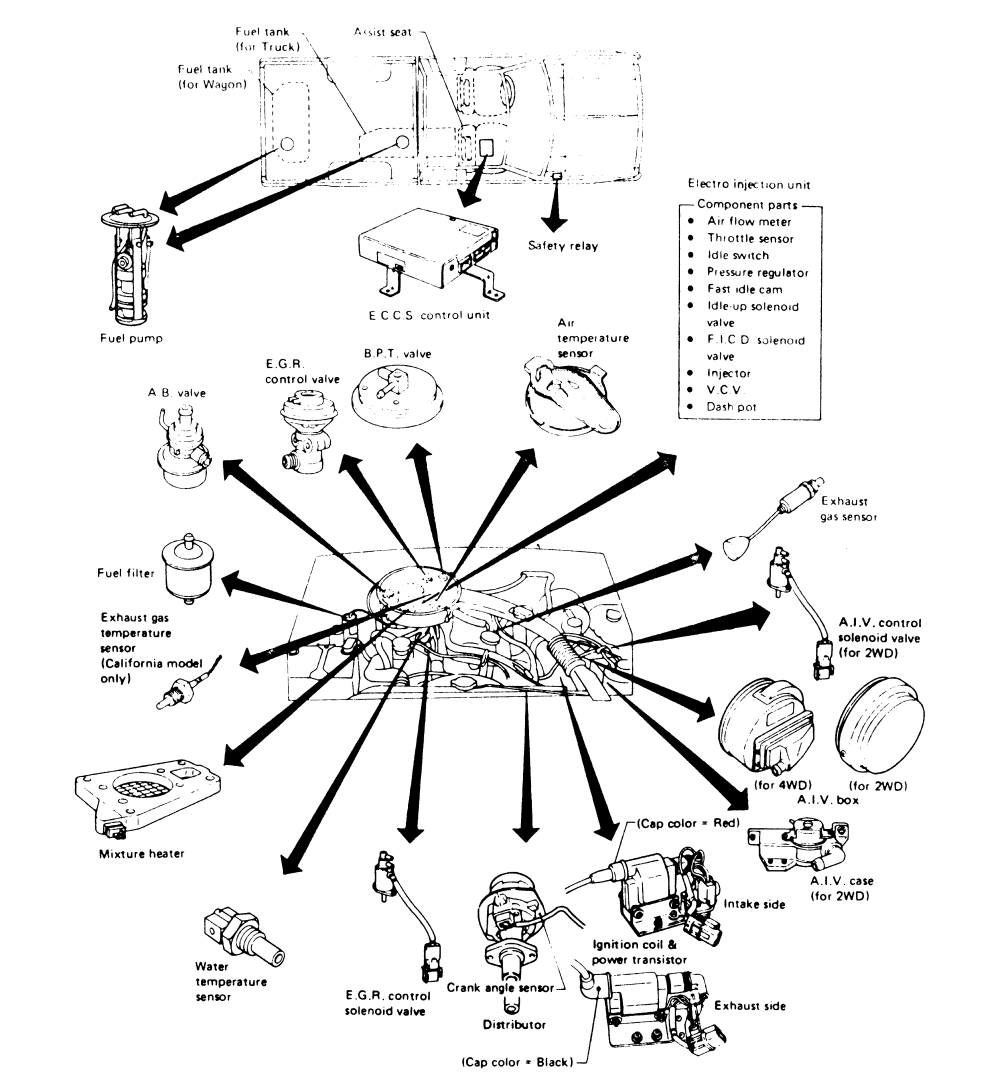
How Emission Systems Work An emission system helps control gas fumes and cleans the air Emission control systems or EVAP system as there are called have been incorporated into automobiles to prevent pollution by limiting the amount of un-burnt and evaporated gases into the atmosphere.
What does the emission control system do on a car?
Emission control system. Written By: Emission control system, in automobiles, means employed to limit the discharge of noxious gases from the internal-combustion engine and other components. There are three main sources of these gases: the engine exhaust, the crankcase, and the fuel tank and carburetor.
How do diesel emission systems work?
How Diesel Emission Systems Work 1 Particulate Matter (PM) 2 Nitrogen Oxides (NOx) 3 Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) 4 EGR Valve 5 EGR Cooler 6 Diesel Particulate Filter (DPF) 7 Diesel Oxidation Catalyst (DOC) 8 DPF Regeneration 9 Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) 10 Diesel Exhaust Fluid (DEF) More items...
What is the evaporative emission system?
What is the Evaporative Emission System (EVAP)? The Evaporative Emission System (EVAP) is a system in your vehicle that stores fuel vapors, which then are directed into the engine to be used. Inside the fuel tank, fuel vapors build due to motion and heat.
How do cars emit air pollution?
Air pollution gases produced by cars consist of carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons, carbon dioxide and nitrogen oxide. Tailpipe emissions are measured in parts per million or PPM. What Goes Wrong? The emission system depends on a series of chemical reactions, sensors and vacuum control solenoids to operate correctly.

What makes up the emission control system?
The components of the emission control system include fuel fill cap, vapor recirculation tube, fuel tank vapor control valve, evaporative emission canister, fuel tank pressure sensor, canister vent valve, evaporative two-way valve, and the evaporative canister purge valve.
How much does it cost to fix an emission control system?
If your vehicle failed emission testing and it needs repairing, then the cost will depend on the exact cause, but the repair work typically starts around $200. Replacing your exhaust system depends on the type of car you drive, but that work starts at approximately $175.
What does it mean when your car says emissions system problem?
If your light is on, it typically means the car's emissions control system is faulty, and the vehicle is polluting the air beyond allowable federal standards. A vehicle in this condition would fail an emissions inspection or smog check. Don't confuse the check engine light with the maintenance or service light.
What does emission system mean?
emission control system, in automobiles, means employed to limit the discharge of noxious gases from the internal-combustion engine and other components. There are three main sources of these gases: the engine exhaust, the crankcase, and the fuel tank and carburetor.
Can you drive your car with emissions light on?
So, is it safe to drive with the Emissions Control Light on? Yes, as long as it is the only light that has come on, you do not have to worry about your safety.
How do I reset emissions?
2:486:01Tricks to Use to Pass an Emissions Test Every time - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo next you basically plug in your scanner to your obd2 connector. And then you have a screen likeMoreSo next you basically plug in your scanner to your obd2 connector. And then you have a screen like this so you would normally go to you erase your codes to reset your check engine light.
How long can you drive with emissions light on?
Depending on the issue that triggered the Check Engine light, you may be able to continue driving indefinitely or only for a couple of days. Covering a distance between 50 and 100 miles gives the engine computer time to recalibrate certain sensors, which may solve the problem.
What can cause emission problems?
These are six common reasons why a vehicle will fail emissions, and what can be done to fix it.You are past due for an oil change. ... You have a rich air/fuel mixture. ... You have worn spark plugs. ... You have a loose or leaking gas cap. ... Your air filter is dirty. ... Your “check engine light” is on.
Can bad gas cause emissions problems?
A loose or broken gas cap can dramatically reduce fuel efficiency and increase emissions. MAF sensor - Mass airflow sensors are a common item to go bad in vehicles.
What does yellow check engine light mean?
On some cars, a yellow check engine light means investigate the problem and a red one means stop right now. Try tightening your gas cap. This can often solve the problem. Keep in mind that it may take several trips before the light resets. Some vehicles have a separate indicator that warns of a loose gas cap.
Why is my check engine light on but my car runs fine?
Check Engine Light False Alarms Sometimes you'll notice a check engine light even though the car runs fine. There are a couple of reasons why this may be. If there is a problem with the car, it's probably the O2 sensor. This is an extremely common problem with modern cars and a relatively easy one to fix.
Is emission system covered under warranty?
Under the Federal Emissions Warranty, all emissions related parts are covered for 2 years or 24,000 miles*, with the catalyt- ic converter and engine control unit (the computer) covered for 8 years or 80,000 miles*. The Federal provisions cover light-duty vehicles up to 8,500 pounds Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR).
What can cause emission problems?
These are six common reasons why a vehicle will fail emissions, and what can be done to fix it.You are past due for an oil change. ... You have a rich air/fuel mixture. ... You have worn spark plugs. ... You have a loose or leaking gas cap. ... Your air filter is dirty. ... Your “check engine light” is on.
How much does it cost to fix evaporative emission control system?
In general, you should expect to pay around $200- - $400 for your EVAP system leak repairs, but you should confirm that this is the case where you live. The price breakdown for different vehicles is listed below. These prices will vary depending on where you live and the specific repairs your EVAP system needs.
What does it mean when the exhaust light comes on?
In many vehicles, an exhaust light (or emissions light) is used to warn the driver of exhaust-related problems. This allows the driver to take action before more damage occurs. When an irregularity is detected in the exhaust system, the exhaust light will turn on, and a fault code will be saved to your car's computer.
What does emissions system problem mean on a 2016 Honda Pilot?
What Does Honda Emissions System Problem Mean On a Honda Pilot? An emission system warning light indicates a problem with the mixture of fuel to air in the engine. In the Honda Pilot, the fuel injectors can go bad between 40,000-60,000 miles. An oxygen sensor near the catalytic converter may need replacing as well.
Why are emission systems important?
An emission system helps control gas fumes and cleans the air. Emission control systems or EVAP system as there are called have been incorporated into automobiles to prevent pollution by limiting the amount of un-burnt and evaporated gases into the atmosphere.
How does a mass air flow sensor work?
A mass air flow sensor monitors airflow that enters the engine by measuring resistance across a hot wire that is cooled when different amounts of air pass over it. This feedback data trim adjustments to further help clean emission outputs by not allowing excess fuel to enter the engine during excessive throttle input.
What is an EGR valve?
An EGR valve stands for exhaust gas recirculation which is use to allow engine exhaust to enter the intake manifold . This recalculation cools combustion temperatures and lowers emissions. Many cars have done away with this valve by being able to control valve timing which achieves the same objective.
What is a catalytic converter?
A catalytic converter is designed to convert partially burned gases to completely burned gases. This is done when the converter becomes hot unitizing a thermo reaction due to the catalyst material inside the unit. Some cars use an electric air pump which injects air into the exhaust system just after the exhaust ports of the cylinder head to help heat up the catalyst and optimize efficiency.
Why do we need oxygen sensors?
An oxygen sensor is designed to monitor engine exhaust gases and send this information to the main computer PCM so adjustments can be made to the fuel mixture controlling un-burnt fuel. Because these sensors are emerged in hot exhaust gases they have a high failure rate and must be replaced to keep the system working correctly.
Where is the EVAP solenoid located?
An EVAP solenoid is controlled by the main engine computer and located near the intake manifold. This solenoid is connected to the charcoal canister using a vacuum hose to draw raw gas vapor from the fuel tank and into the charcoal canister.
What is a gas cap?
A gas cap seals liquid fuel and fumed gases from escaping the fuel tank. This cap is designed with an automatic tightening mechanism to support the minimum tension the cap must be installed at while sealing against the tank filler neck using an O ring seal.
What is an emission control system?
Emission control system, in automobiles, means employed to limit the discharge of noxious gases from the internal-combustion engine and other components. There are three main sources of these gases: the engine exhaust, the crankcase, and the fuel tank and carburetor. The exhaust pipe discharges burned and unburned hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, ...
What are the sources of emissions in an automobile?
There are three main sources of these gases: the engine exhaust, the crankcase, and the fuel tank and carburetor. The exhaust pipedischarges burned and unburned hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, oxides of nitrogenand sulfur, and traces of various acids, alcohols, and phenols. The crankcaseis a secondary source of unburned hydrocarbons and, to a lesser extent, carbon monoxide. In the fuel tank and (in older automobiles) the carburetor, hydrocarbons that are continually evaporating from gasolineconstitutea minor but not insignificant contributing factor in pollution. A variety of systems for controlling emissionsfrom all these sources have been developed.
How does an exhaust system work?
The recirculated exhaust gases serve to lower the temperature of combustion, a condition that favours lower production of nitrogen oxides as combustion products (though at some loss of engine efficiency). In a typical air-injection system, an engine-driven pump injects air into the exhaust manifold, where the air combines with unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide at a high temperature and, in effect, continues the combustion process. In this way a large percentage of the pollutants that were formerly discharged through the exhaust system are burned (though with no additional generation of power).
How does a fuel tank reduce emissions?
Today those emissions are greatly reduced by sealed fuel-tank caps and the so-called evaporative control system, the heart of which is a canister of activated charcoal capable of holding up to 35 percent of its own weight in fuel vapour. In operation, fuel-tank vapours flow from the sealed fuel tank to a vapour separator, which returns raw fuel to the tank and channels fuel vapour through a purge valve to the canister. The canister acts as a storehouse; when the engine is running, the vapours are drawn by the resultant vacuum from the canister, through a filter, and into the combustion chamber, where they are burned.
What is the EGR system?
To control exhaust emissions, which are responsible for two-thirds of the total engine pollutants, two types of systems are used: the air-injection system and the exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) system. In EGR a certain portion of exhaust gases are directed back to the cylinder head, where they are combined with the fuel-air mixture and enter ...
How does computer controlled combustion improve combustion efficiency?
Improvements in combustion efficiencyare effected by computerized control over the whole process of combustion. This control ensures the most efficient operation of the systems described above. In addition, computer-controlled fuel-injection systems ensure more precise air-fuel mixtures, creating greater efficiency in combustion and lower generation of pollutants.
What gases are converted into water vapour?
As the exhaust gases are passed through the packed beads or the honeycomb, the metals act as catalysts to induce the hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides in the exhaust to convert to water vapour, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen.
How does emissions trading work?
Emissions trading programs work by first setting an environmental goal: a national, or sometimes regional, limit on the overall amount of pollution that sources are allowed to emit into the environment. This environmental goal is a critical part of an emissions trading program.
How does the EPA use emissions trading?
Successful emissions trading programs require sources to monitor the pollution they emit through very accurate methods, such as continuous emissions monitoring systems, and report those data. One way that emissions trading programs provide transparency and accountability is by making data available to the public. This adds another level of scrutiny to the data and encourages compliance with the programs. For example, the data collected from power plants in EPA’s emissions trading programs are available through the Air Markets Program Data (AMPD) system and on the Power Plant Emission Trends page. EPA also releases an annual progress report that presents data on emissions and compliance, allowance market activity, and environmental results under emissions trading programs.
What are emissions trading allowances?
Affected sources, such as power plants, that are included in an emissions trading program receive allowances that authorize a certain amount of pollution. For example, in EPA’s Acid Rain Program, each allowance authorizes a source to emit one ton of sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ). Depending on the program, sources receive allowances in different ways, such as free allocations or auctions. Once an affected source has an allowance, the source can decide whether to use it for compliance, trade it in the allowance market, or save that allowance for compliance in the future.
What is the environmental goal of emissions trading?
Is intended to protect public health and the environment and sustain that protection into the future, ...
What is the emission limit?
Emission limit: total amount of tons that affected sources within a state or group of states collectively must meet to achieve the environmental goals of the program.
How to remove pollution from smokestack?
Install pollution control technology, such as a scrubber to remove pollution before it comes out of the smokestack.
How did pollution control technology help reduce emissions?
In the early days (1990s), changing piston designs, altering injector spray angle or switching to electronically controlled injection systems helped curb a lot of emissions, but not all of them. As a result, higher injection pressures and especially high-pressure common-rail systems were turned to in order to meet PM requirements. Then came the aforementioned EGR systems, which helped drop NOx levels. Further PM and NOx-fighting technologies such as the diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC), diesel particulate filter (DPF), active and passive regeneration, selective catalytic reduction (SCR) and diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) were soon to follow.
What is the cause of diesel smog?
Nitrogen oxides (NOx) are a direct result of the high operating temperatures diesels are capable of and are a primary ingredient in smog. They form when nitrogen is released during combustion and conjoined with oxygen. Various oxides of nitrogen are produced when extreme in-cylinder heat is present, namely nitrogen dioxide and nitric oxide, which means a fine balance between NOx (achieved with lower in-cylinder temps) and PM (achieved with complete combustion/high in-cylinder temps) is paramount if a modern diesel engine is to keep both pollutants at reasonable levels.
What is SCR in EGR?
Going beyond what EGR systems are capable of, SCR has become the most effective technology in getting NOx levels low enough to meet the current, stringent standard. The NOx problem that can’t be solved in-cylinder is dealt with in the exhaust aftertreatment system by injecting urea-based diesel exhaust fluid (DEF) upstream of an SCR catalyst. During this process, harmful NOx is chemically converted in harmless nitrogen.
What is an EGR valve?
The component responsible for controlling the flow rate of exhaust gases destined to reenter the intake stream is the EGR valve. There are two types of EGR valves, cold-side and hot-side, and the type of activation varies from pneumatically to hydraulically to electrically (the latter being most common today). Cold-side EGR valves direct exhaust gases into the intake after they’ve left the EGR cooler (s). A hot-side EGR valve performs its flow duties before the EGR cooler (s). Use of a hot-side EGR valve is believed to help cut down on the kind of soot and grime buildup that leads to valve failure (i.e. sticking).
What is a DOC in diesel exhaust?
In modern diesel exhaust aftertreatment systems, the DOC’s job is to provide the extreme heat that’s necessary to convert soot accumulation into the fine ash that remains trapped in the DPF. By oxidizing diesel fuel supplied to it from the engine, the DOC provides the means of increasing DPF temperature, which effectively incinerates the soot buildup within the DPF, breaking the soot down into the finer, noncombustible particles (i.e. ash) that remain.
What is an EGR cooler?
An air-to-liquid heat exchanger , the EGR cooler uses circulated engine coolant to lower the temperature of the exhaust gases passing through it. On engines such as the 6.4L Power Stroke and 6.7L Power Stroke, there are two EGR coolers at work.
What is the first pollutant on the EPA radar?
The first pollutant on the EPA’s radar was particulate matter (PM). In a diesel engine, PM is the result of unburned fuel, as in fuel that isn’t completely used during the combustion process and is allowed leave the cylinder through the exhaust valves, flow through the exhaust system and out the tail pipe in the form of black smoke. Mechanical (i.e. older) fuel systems with less precise injection events occurring in-cylinder were notorious for producing PM. PM itself is a complex makeup of sulphates, carcinogenic compounds, elemental carbon and heavy metals.
How does the EVAP system work?
As was mentioned, the EVAP system prevents fuel vapors from entering the atmosphere. The system does this by trapping the vapors in a vapor canister, then “purging” the vapors into the engine when conditions are correct.
What are the components of an EVAP system?
The primary components found in a typical EVAP system include the following: Vapor Canister. This component, which is also known as a charcoal canister, stores fuel vapors from the gas tank.
How does a purge valve work?
Opening the purge valve creates a vacuum that pulls fresh air through the vapor canister. The fresh air picks up the fuel vapors and delivers them to the engine to be burned during the normal combustion process.
Why is the vapor canister closed?
Normally, the vapor canister is open to the atmosphere to allow fresh air to enter. The canister is only closed when the EVAP monitor is run (more on that later).
How many operations does an EVAP system have?
But the good news is that the system’s functions can be broken down into three primary operations: storing fuel vapors, purging fuel vapors, and self-monitoring. The EVAP system has three primary operations: storing fuel vapors, purging fuel vapors, and self-monitoring. Storing Fuel Vapors.
Where are fuel vapors stored in an EVAP?
Storing Fuel Vapors. The vapor canister is the focal point of the EVAP system. When the engine is off, fuel vapors from the gas tank are stored in the canister. The canister contains activated charcoal, which traps the vapors until the engine is running, and conditions are correct for a vapor purge.
What type of leak detection system does a Chrysler have?
Depending on the year and model, it may have either an older-style Leak Detection Pump (LDP) system, a Natural Vacuum Leak Detection (NVLD) system, or an Evaporative System Integrity Monitor (ESIM).