
What are some interesting facts about the integumentary system?
Nails are keratinous external appendages of the integumentary system.
- The nails grow on the hands and the feet, under a white shaped region called the lunula.
- The protein keratin makes up the nail and the cuticle which covers the nail root.
- The nails on the hands grow at a rate of approximately 0.5 mm per week, whereas those on the toes grow at a much slower rate.
What are three functions of the integumentary system?
integumentary system function 3 this system helps keep the body from drying out, provides a natural sunscreen, and acts as storage for fatty tissues necessary for energy, with the aid of sunshine it provides vitamin d, also provides sensory input and unpleasant sensations involving pressure and temperature
What is included in the integumentary system?
Your integumentary system consists of the following glands:
- Sudoriferous glands: These are the glands that secrete sweat through your skin. ...
- Sebaceous glands: These glands produce sebum (oil) and give your face its oil.
- Ceruminous glands: These are the glands in your ear that secrete ear wax.
- Mammary glands: These are the glands on a person’s chest. ...
What are the examples of the integumentary system?
The integumentary system is made up of several organs and structures including the skin, hair, nails, glands, and nerves. The primary function of the integumentary system is to protect the inside of the body from elements in the environment—like bacteria, pollution, and UV rays from the sun. The skin and its associated structures also retain ...
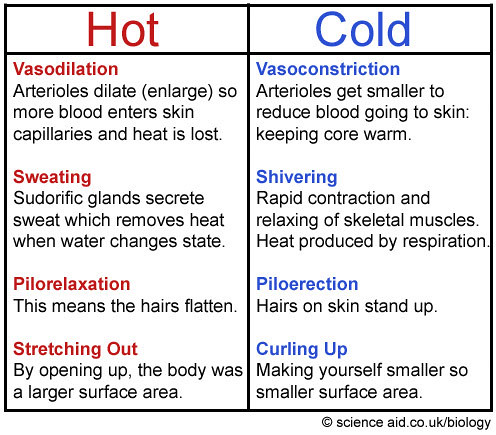
How does sweating affect the body?
Show Answer. Sweating cools the body when it becomes warm. When the body temperature rises, such as when exercising on a hot day, the dermal blood vessels dilate, and the sweat glands begin to secrete more sweat. The evaporation of the sweat from the surface of the skin cools the body by dissipating heat.
Where is the Meissner corpuscle located?
In this micrograph of a skin cross-section, you can see a Meissner corpuscle (arrow), a type of touch receptor located in a dermal papilla adjacent to the basement membrane and stratum basale of the overlying epidermis. LM × 100. (credit: “Wbensmith”/Wikimedia Commons)
How much sweat does the body produce?
If the body becomes excessively warm due to high temperatures, vigorous activity (Figure 2), or a combination of the two, sweat glands will be stimulated by the sympathetic nervous system to produce large amounts of sweat, as much as 0.7 to 1.5 L per hour for an active person. When the sweat evaporates from the skin surface, the body is cooled as body heat is dissipated.
What is the effect of sweat glands on bacteria?
Another factor affecting the growth of pathological bacteria is alkaline conditions.
Why is vitamin D important for bones?
Vitamin D is essential for normal absorption of calcium and phosphorous , which are required for healthy bones. The absence of sun exposure can lead to a lack of vitamin D in the body, leading to a condition called rickets, a painful condition in children where the bones are misshapen due to a lack of calcium, causing bowleggedness.
What is the skin's first line of defense against abrasive activity?
It also is the first line of defense against abrasive activity due to contact with grit, microbes, or harmful chemicals.
How does skin flora protect the host?
The skin flora can protect the human host by preventing transient pathogenic organisms from colonizing the skin surface, either by competing for nutrients, secreting chemicals against them , or stimulating the skin’s immune system .
What is brain facts?
Disclaimer: BrainFacts.org provides information about the field's understanding of causes, symptoms, and outcomes of brain disorders. It is not intended to give specific medical or other advice to patients. Visitors interested in medical advice should consult with a physician.
What happens when your heart slows down?
When the heart suddenly slows, blood flow to other organs will also drop. If blood flow to the brain drops too much, victims of heatstroke will faint. This is an adaptive technique — it’s much easier for the heart to pump blood to the brain when you’re flat on the ground.
What is the function of the hypothalamus?
In the brain, the hypothalamus controls this reflex. It also plays roles in hormone secretion, sleep, and other functions. The hypothalamus receives input from temperature receptors in the skin and internal organs, including the gut. Even at rest in a temperate environment, your hypothalamus remains vigilant.
What happens if you don't pump blood to the brain?
If blood isn’t pumped to key organs, especially the brain, then you’re in trouble. Cardiac arrhythmias leading to cardiac arrest seem to be what kills most people who die of exposure.
What does 10 degree shift mean?
A 10-degree temperature shift could mean the difference between grabbing a light jacket or rolling up your sleeves on a nice day. Your body is even more vigilant about regulating and tracking its internal temperature.
How much temperature does the body regulate?
You’re not conscious of it. The average healthy human body maintains an internal temperature of around 37 degrees Celsius (98.5 degrees Fahrenheit), though individuals can vary slightly. The body makes tiny shifts and changes that keep it at a healthy temperature depending on the environment and ...
What happens if you don't drink water in the desert?
If this water is not replenished by drinking, which could happen in a desert environment, then blood volume will decrease. This leads to reduced cardiac output and reduced blood flow to the brain.
