Is time equal to velocity?
time = distance ÷ speed.
Does the velocity increase with time?
A velocity-time graph shows how velocity changes over time. The sprinter's velocity increases for the first 4 seconds of the race, it remains constant for the next 3 seconds, and it decreases during the last 3 seconds after she crosses the finish line.
Does velocity decrease with time?
If the displacement is constant then the velocity is inversely proportional to time so increase in velocity with decreases in time. If we increase the velocity then time will be decreases.
Why does velocity increase as time increases?
The reason why object keep increasing its velocity even though magnitude of force is decreasing is that the applied force has been converted to mechanical energy and been transformed to object. This energy keeps the object velocity increasing for some time and will eventually come to rest.
What happens to the velocity if the time interval increases?
A positive velocity indicates that the position is increasing as time increases, while a negative velocity indicates that the position is decreasing with respect to time. If the distance remains constant, then the velocity will be zero on such an interval of time.
Why is time affected by velocity?
Time dilates on moving vessels: the greater the speed, the greater the time dilation. Only when such velocities* approach light speed do such effects become significant. If, and this one of those extreme IF's, a vessel could attain light speed, time aboard the vessel would cease altogether.
Does velocity decrease with distance?
It is true in general that the more distance you travel the more your velocity increases, e.g if you start at 0 velocity v^2 = 2aS where v is ending velocity, a is acceleration and S is displacement.
Why does time decrease as speed increases?
Time slows down as you travel faster because momentum bends the fabric of spacetime causing time to pass slower.
What is the medium for both velocity and acceleration to occur?
Time is the medium for both velocity and acceleration to occur. In a certain amount of time , an object will have moved a certain distance- This distance is defined by the velocity or acceleration.
What is acceleration in science?
Acceleration is a little more complicated. It is defined as the rate of change of the object's velocity over its change in time. So "how much has the object's velocity changed in a given time interval.".
What is it called when acceleration is negative?
Or, if the acceleration is negative, it's called deceleration and describes something slowing down. For something to speed up or slow down, it has to have a certain change in velocity. Let's compare the units of the two.
Is acceleration always the same distance?
This just means that it's not always moving the same distance in a given time. If the acceleration is positive, it's actually moving more distance as time passes by. Another relationship between the two is that when velocity is constant, acceleration is zero. Why?
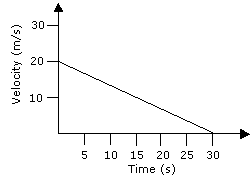
What do solved examples involving velocity vs. time graphs look like?
A windsurfer is traveling along a straight line , and her motion is given by the velocity graph below.
What does the vertical axis represent on a velocity graph?
The vertical axis represents the velocity of the object. This probably sounds obvious, but be forewarned—velocity graphs are notoriously difficult to interpret. People get so used to finding velocity by determining the slope—as would be done with a position graph—they forget that for velocity graphs the value of the vertical axis is giving the velocity.
What does the area under a velocity graph represent?
The area under a velocity graph represents the displacement of the object. To see why, consider the following graph of motion that shows an object maintaining a constant velocity of 6 meters per second for a time of 5 seconds.
Does the area under a velocity curve equal displacement?
The area under a velocity curve, regardless of the shape, will equal the displacement during that time interval.
Does the slope of a velocity graph equal acceleration?
Since is the definition of acceleration, the slope of a velocity graph must equal the acceleration of the object.
What happens when you take the slope of the velocity vs time graph?
Again, if we take the slope of the velocity vs. time graph, we get the acceleration, the rate of change of the velocity. And, if we take the area under the slope, we get back to the displacement.
What is the average velocity of a car in a drive to school?
The average velocity for the drive to school is 0.5 km/minute. We can see that the average velocity for the drive back is –0.5 km/minute. If we plot the data showing velocity versus time, we get another graph ( Figure 2.16 ):
What is the slope of a d vs t graph?
Figure 2.17 A graph is shown of the position of a jet-powered car during the time span when it is speeding up. The slope of a d vs. t graph is velocity. This is shown at two points. Instantaneous velocity at any point is the slope of the tangent at that point.
How fast is a curve?
This is a much more complicated process than the first problem. If we were to use these estimates to come up with the average velocity over just the first 30 s we would get about 191 m/s. By approximating that curve with a line, we get an average velocity of 202.5 m/s. Depending on our purposes and how precise an answer we need, sometimes calling a curve a straight line is a worthwhile approximation.
How far across the graph is 100m/s?
The average velocity we calculated here makes sense if we look at the graph. 100m/s falls about halfway across the graph and since it is a straight line, we would expect about half the velocity to be above and half below.
Why can a ball be easily manipulated with displacement?
Maze Game. The ball can be easily manipulated with displacement because the arena is a position space. The ball can be easily manipulated with velocity because the arena is a position space . The ball can be easily manipulated with displacement because the arena is a velocity space.
Why is km/km good?
This is good because it can tell us whether or not we have calculated everything with the correct units. For instance, if we end up with m × s for velocity instead of m/s, we know that something has gone wrong, and we need to check our math. This process is called dimensional analysis, and it is one of the best ways to check if your math makes sense in physics.
How does time relate to motion?
How does time relate to motion? We are usually interested in elapsed time for a particular motion, such as how long it takes an airplane passenger to get from his seat to the back of the plane. To find elapsed time, we note the time at the beginning and end of the motion and subtract the two. For example, a lecture may start at 11:00 A.M. and end at 11:50 A.M., so that the elapsed time would be 50 min. Elapsed time Δt is the difference between the ending time and beginning time,
What is the definition of time?
In biomechanics, the definition of time is simple— time is change, or the interval over which change occurs. It is impossible to know that time has passed unless something changes.
What is instantaneous velocity?
Instantaneous velocity v is the velocity at a specific instant or the average velocity for an infinitesimal interval.
How to find the elapsed time?
Time is measured in terms of change, and its SI unit is the second (s). Elapsed time for an event is Δt = tf – ti where tf is the final time and ti is the initial time. The initial time is often taken to be zero, as if measured with a stopwatch; the elapsed time is then just t.
How to visualize motion?
Another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. A plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful.
Is velocity a vector?
Notice that this definition indicates that velocity is a vector because displacement is a vector. It has both magnitude and direction. The standard unit for velocity is meters per second or m/s, but many other units, such as km/h, mi/h (also written as mph), and cm/s, are in common use.
Is velocity the same as distance?
Velocity. Your notion of velocity is probably the same as its scientific definition. You know that if you have a large displacement in a small amount of time you have a large velocity, and that velocity has units of distance divided by time, such as kilometers per hour.
How does time relate to motion?
How does time relate to motion? We are usually interested in elapsed time for a particular motion, such as how long it takes an airplane passenger to get from his seat to the back of the plane. To find elapsed time, we note the time at the beginning and end of the motion and subtract the two. For example, a lecture may start at 11:00 A.M. and end at 11:50 A.M., so that the elapsed time would be 50 min. Elapsed time Δ t is the difference between the ending time and beginning time,
What is the definition of time?
Every measurement of time involves measuring a change in some physical quantity. It may be a number on a digital clock, a heartbeat, or the position of the Sun in the sky. In physics, the definition of time is simple— time is change, or the interval over which change occurs. It is impossible to know that time has passed unless something changes.
What is instantaneous speed?
Instantaneous speed is the magnitude of the instantaneous velocity. Instantaneous speed is a scalar quantity, as it has no direction specified. Average speed is the total distance traveled divided by the elapsed time. (Average speed is not the magnitude of the average velocity.)
How to visualize motion?
Another way of visualizing the motion of an object is to use a graph. A plot of position or of velocity as a function of time can be very useful. For example, for this trip to the store, the position, velocity, and speed-vs.-time graphs are displayed in Figure 2.3. 4. (Note that these graphs depict a very simplified model of the trip. We are assuming that speed is constant during the trip, which is unrealistic given that we’ll probably stop at the store. But for simplicity’s sake, we will model it with no stops or changes in speed. We are also assuming that the route between the store and the house is a perfectly straight line.)
What does delta mean in math?
(As usual, the delta symbol, Δ, means the change in the quantity that follows it.)
What is the SI unit for time?
The amount of time or change is calibrated by comparison with a standard. The SI unit for time is the second, abbreviated s. We might, for example, observe that a certain pendulum makes one full swing every 0.75 s. We could then use the pendulum to measure time by counting its swings or, of course, by connecting the pendulum to a clock mechanism that registers time on a dial. This allows us to not only measure the amount of time, but also to determine a sequence of events.
How are physical quantities defined?
As discussed in Physical Quantities and Units, the most fundamental physical quantities are defined by how they are measured. This is the case with time. Every measurement of time involves measuring a change in some physical quantity. It may be a number on a digital clock, a heartbeat, or the position of the Sun in the sky. In physics, the definition of time is simple— time is change, or the interval over which change occurs. It is impossible to know that time has passed unless something changes.
How does constant velocity look like on a position-time graph?
To know about how the graph of constant velocity looks on a position-time graph, we can see below,
What kind of graph do we obtain if we plot the position-time graph of the moving truck?
Here are some consequences are given below that might help know the nature of the graph.
What is the method to find out the V-T graph?
As the name indicates, we can use a graphical method to find the velocity value.