Centrifugation is a method of separating molecules having different densities by spinning them in solution around an axis (in a centrifuge rotor) at high speed. It is one of the most useful and frequently employed techniques in the molecular biology laboratory.
Full Answer
What are centrifuges?
Centrifuges are common pieces of lab equipment, used to separate particles from a solution. These particles are separated according to the size, shape, density, and viscosity of the medium. The separation process depends on the rotor speed.
What is the basic principle of centrifugation?
What is the principle of centrifugation? A centrifuge operates by using the sedimentation principle: liquids separate according to their density under the influence of gravitational force (g-force). Various forms of separation, including isopycnic, ultrafiltration, gradient of mass, phase separation, and pelleting, are known.
What is the meaning of centrifugal apparatus?
An apparatus in which humans or animals are enclosed and which is revolved to simulate the effects of acceleration in a spacecraft. To rotate (something) in a centrifuge or to separate, dehydrate, or test by means of this apparatus. [French, centrifugal, from New Latin centrifugus; see centrifugal .]

What is the meaning of centrifuging in science?
Introduction. Centrifugation is a method of separating molecules having different densities by spinning them in solution around an axis (in a centrifuge rotor) at high speed. It is one of the most useful and frequently employed techniques in the molecular biology laboratory.
What is an example of centrifuging?
Some common examples of centrifugation include: The extraction of fat from milk in order to produce skimmed milk. The removal of water from moist lettuce with the help of a salad spinner. The Spin-drying of water in washing machines in order to remove water from the clothing.
What is centrifuging how is it done?
Centrifugation is a technique used for the separation of particles from a solution according to their size, shape, density, viscosity of the medium and rotor speed. The particles are suspended in a liquid medium and placed in a centrifuge tube. The tube is then placed in a rotor and spun at a define speed.
What is the use of centrifuging?
A centrifuge is used to separate particles suspended in a liquid according to particle size and density, viscosity of the medium, and rotor speed.
How does centrifuge separate mixtures?
The particles are segregated depending on their size, shape, density, and rotor speed. The suspended particles in a mixture are rotated at a high speed in a machine, called the centrifuge in order to segregate the particles from the liquid. The mixture is separated through spinning.
What can be separated by centrifugation?
Centrifugation is a process which involves the use of the centrifugal force for the sedimentation of heterogeneous mixtures with a centrifuge, used in industry and in laboratory settings. This process is used to separate two immiscible liquids. Uses: Separating chalk powder from the water.
How do you do centrifugation?
1:552:58Centrifugation - MeitY OLabs - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWater place it opposite the first centrifuge tube to balance the centrifuge. Machine then close theMoreWater place it opposite the first centrifuge tube to balance the centrifuge. Machine then close the centrifuge machine and centrifuge the milk for 13.
What are the types of centrifuges?
Generally, there are two types of centrifuges: the filtration and sedimentation centrifuges.
What is another word for centrifuge?
What is another word for centrifuge?extractorfilterseparatorsievestrainer
What is centrifugation machine?
A centrifuge is a system that separates the components of a liquid or fluid (and even gases) using the centrifugal force. It is a biological instrument used for the separation of liquid material based on its density and weight. This is done by rotating the fluid in a container at high speed.
What is a centrifuge in science, with definition?
In science, a centrifuge is a device that helps separate components of a mixture through the use of centrifugal force, by spinning. A centrifuge is...
What is centrifugation and its example?
Centrifugation is a method used to divide components of a mixture into separate isolations. Centrifugation is carried out by a centrifuge. An examp...
What is a centrifuge used for?
A centrifuge can be used to separate mixtures according to the principal of sedimentation. There are several applications of centrifuges in science...
What is the principle of centrifugation?
A centrifuge operates by using the sedimentation principle- Here the substances are separated based on their density under the influence of gravita...
How does the centrifuge separate mixtures?
The components of heterogeneous mixtures are detached by centrifugation. That comprises liquids in liquids, solids in fluids, and gases in solids a...
What is the centrifuge used for?
Centrifuges work by separating out two materials with different densities. Centrifuges are used in various laboratories to separate fluids, gases o...
What are the types of centrifugation?
For splitting ions, there are two types of centrifugal techniques: differential centrifugation and centrifugation of density gradients. It is furth...
What does centrifuge mean?
A centrifuge is a system that separates the component parts of a liquid or fluid (and even gases) using centrifugal force. This is done by rotating...
How does centrifugation work?
So, for larger quantities, the process of centrifugation is carried out. In churning, the plunger is rotated and the container containing the mixture remains constant, whereas in a centrifuge, the container is made to rotate, such that centrifugal force directly acts on the components.
What is centrifuge used for?
A centrifuge is a laboratory instrument that is used, depending on mass, to isolate gases, gas or liquid. By rotating a vessel carrying material at high speed, separation is accomplished; the centrifugal force forces heavier materials to the outside of the vessel.
What is centrifugation and churning?
Ever wondered how these milk products are made? We have seen at home or in pictures, a pot full of milk being agitated with a plunger like device, usually a cylindrical stick to separate cream from milk. This process is carried out to separate cream from milk which later may be used for making butter or solid cream. This process of agitation of milk is termed as churning.
What are the two types of centrifugal techniques?
For splitting ions, there are two types of centrifugal techniques: differential centrifugation and centrifugation of density gradients. It is further possible to separate density gradient centrifugation into rate-zonal and isopycnic centrifugation.
How does a centrifuge separate mixtures?
How does centrifuge separate mixtures? The components of heterogeneous mixtures are detached by centrifugation. That comprise liquids in liquids, solids in fluids, and gases in solids and liquids. In order to transfer bulky sections to the outside of the pipe, centrifugation uses centrifugal energy.
What is the process of agitation of milk called?
This process of agitation of milk is termed as churning.
What is a centrifuge?
The term centrifuge can refer to a machine that houses a rapidly rotating container to separate its contents by density (noun) or to the act of using the machine (verb). Centrifuges are most often used to separate different liquids and solid particulates from liquids, but they may be used for gases.
What are the differences between centrifuges?
The main differences between them are the speed of rotation and the rotor design. The rotor is the rotating unit in the device. Fixed-angle rotors hold samples at a constant angle, swinging head rotors have a hinge that allows sample vessels to swing outward as the rate of spin increases, and continuous tubular centrifuges have a single chamber rather than individual sample chambers.
How does differential gravity affect the phase composition of a material?
The differential gravity affects the phase composition and other properties of the materials. Everyday Applications: Medium-size centrifuges are common in daily life, mainly to quickly separate liquids from solids. Washing machines use centrifugation during the spin cycle to separate water from laundry.
What is the force that pulls objects inward?
Centripetal force is the real physical force at work, pulling spinning objects inward. Spinning a bucket of water is a good example of these forces at work. If the bucket spins fast enough, the water is pulled inward and doesn't spill. If the bucket is filled with a mixture of sand and water, spinning it produces centrifugation.
Why do samples move in a centrifuge?
Because the sample tubes are fixed at an angle and centrifugal force acts in the horizontal plane, particles move a tiny distance before hitting the wall of the tube , allowing dense material to slide down. While many lab centrifuges have fixed-angle rotors, swinging-bucket rotors are also common.
What is industrial centrifuge?
Industrial Centrifuges are used to separate components of colloids (like cream and butter from milk), in chemical preparation, cleaning solids from drilling fluid, drying materials, and water treatment to remove sludge.
What are some techniques that can be used to separate materials?
These include filtration, sieving, distillation, decantation, and chromatography.
What are the three characteristics of centrifugation?
Centrifugability is, therefore, seen to be affected by three sludge characteristics: settleability, scrollability , and floc strength .
What are the laboratory procedures for evaluating the feasibility of industrial centrifugation?
The main laboratory procedures available in practice for evaluating the feasibility of industrial centrifugation and selecting the type and dosage of polymer required for conditioning are: (1) centrifugation by a lab centrifuge, followed by a penetrability test, and (2) measurement of floc strength (Spinosa, 1985).
How long does sludge spin in a bottle centrifuge?
Sludge spinning in a bottle centrifuge for 30 s and examination of the centrate clarity.
Is centrifuging a continuous process?
Unlike filter pressing, centrifuging is a continuous process. Its performance on coagulant sludge depends to a considerable degree on polyelectrolyte conditioning of the sludge; polyelectrolyte usage is high and usually in the range 2–6 kg/t of dry solids (Piggott, 1992). The feed to the centrifuges should be maintained at <3% w/v to ensure good mixing of polyelectrolyte with the solids. Coagulant sludge can be dewatered to about 15–25% w/w depending on the nature of the raw water, softening sludge to about 40–50% w/w. Overall solids recovery is normally better than 95% (98–99%). Centrate (i.e. the effluent) water quality from a centrifuge is usually poor with a suspended solids concentration in the range 300–1000 mg/l. It may be spread on land or discharged to a sewage treatment works. The advantages of centrifuging are its enclosed operation and therefore its clean appearance, fast start-up and shutdown; quick adjustment of operating variables; continuous operation if necessary, ready automation and therefore suitability for unmanned operation; low capital cost-to-capacity ratio; and high installed capacity to building area ratio. Disadvantages are low cake dry solids, high demand for energy (about 0.07 kWh/kg dry solids), high polyelectrolyte consumption and poor centrate quality.
Can you test sludge suitability to centrifugation?
It is difficult to define a parameter for assessing the sludge suitability to centrifugation in a laboratory test. As a matter of fact, it is not possible to reproduce on a laboratory scale all the conditions actually occurring in an industrial centrifuge.
What is centrifugation in science?
Centrifugation is a mechanical process that utilizes an applied centrifugal force field to separate the components of a mixture according to density and/or particle size. The principles that govern particle behaviour during centrifugation are intuitively comprehensible.
What is the purpose of centrifugation?
Centrifugation is a very common technique to separate solid particles dispersed in liquid medium, e.g., blood cells and plasma. The liquid sample is placed in a special vial or holder, which is rotated very fast. Sample components are separated due to the centrifugal force, based on their density difference.
How is centrifugation used in biotechnology?
Centrifugation can be thought of as a settling tank driven by controlled centrifugal forces. It is used to separate bacterial cells prior to their disruption and product-containing liquids from cells, cellular debris and other particulates [4–6 ]. Centrifugation can be run either intermittently or continuously. Large-scale centrifugation is carried out as a continuous process to enable handling of large volumes. Decanter and disk stack centrifuge designs are used in bioprocessing. Decanter centrifuges are typically used with the highest solids concentrations and when the largest particles need to be isolated. Disk stack centrifuges are more commonly used in biotechnology processes to handle relatively high concentrations of insoluble materials, but the resulting effluent may still contain some particulates that need to be removed prior to purification. This is particularly relevant when separating fragile cells that require lower g-forces. Therefore, centrifugation is often followed by another clarification step such as normal flow filtration (see below).
Why is centrifugation used in sample preparation?
Sample components are separated due to the centrifugal force , based on their density difference. Centrifugation is commonly used in combination with a variety of sample preparation techniques. Centrifugation can also be used to separate emulsions (such as milk) and immiscible solvents (e.g., in combination with LLE).
What are centrifuges used for?
Today, centrifuges are routinely used in a variety of disciplines ranging from large-scale commercial applications to laboratory-scale scientific research. The number of centrifuge designs and configurations used in the mineral, petrochemical, chemical, medical, pharmaceutical, municipal/industrial waste, dairy, food, polymer, energy and agricultural industries (to name a few) seem almost as numerous as the applications themselves. An in-depth description of centrifuge designs and applications is, therefore, well beyond the scope of this treatise. Instead, this article will present the reader with an introduction to the theory of centrifugation, an overview of the various types of centrifugal separations, and a description of selected rotor/centrifuge designs and their more common applications.
What are the factors to consider when selecting a centrifuge?
Factors to consider when selecting a centrifuge include potential for product loss due to shear forces; hygiene; compatibility with feedstream chemistry, which is especially important for centrifuge seals; and mimimizing processing time when product is in contact with harmful proteases or other substances that may cause degradation or aggregation.
What is the process of rotating a sample at high speed to separate solids suspended in a liquid?
Centrifugation is a technique that, by rotating the sample at high speed, separates solids suspended in a liquid (or liquids of different densities).
What Does A Centrifuge Do?
Centrifuges separate heterogeneous mixtures into their various components – liquids in liquids, solids in liquids, and liquids in gases, based on the different densities of the components. One of the most common uses is to separate red blood cells and other blood components from whole blood.
What is a laboratory centrifuge?
Laboratory centrifuges are widely used in different applications, including clinical, research, and academia. They handle a wide variety of tasks such as separation, purification, and isolation of organelles, cells, and cell components for further observation.
How much does a centrifuge cost?
Centrifuge costs vary widely depending on the size, type, and features of the unit. Average prices by type are: 1 Benchtop – $1,000 to $5,000 2 Large Capacity / High Speed – $10,000 to $25,000 3 Ultracentrifuge – $10,000 to $50,000
Why is it important to consider the rotor of a centrifuge?
Beyond the type of centrifuge itself, it’s also important to consider the centrifuge rotor, as the rotor design influences what the machine can do and how much it costs.
What is sedimentation in a centrifuge?
Sedimentation refers to the tendency for particles in suspension to settle out of the medium where they are entrapped and come to rest against a barrier. The centrifuge uses centrifugal acceleration to separate the particles out of the solution. If the solution has a higher density than the solvent, the particles will sink to the bottom of the tube.
How fast can an ultra centrifuge spin?
Ultra centrifuges are optimized to spin at very high speeds, capable of reaching as high as 1,000,000 g (9,800 kilometers per second or 6,089 miles per second). These kinds of centrifuges are classified as either preparative or analytical.
How does a centrifuge work?
How A Centrifuge Works. A centrifuge uses a motor to spin liquid samples at high speed. There are different types of centrifuges, which vary in size and sample capacity. Centrifugal force moves the dense components to the outside of the container allowing the solids to settle completely and rapidly.
What is centrifuging in science?
n. 1. An apparatus consisting essentially of a compartment spun about a central axis to separate contained materials of different specific gravities, or to...
What is a centrifuge?
A machine that separates substances of different densities by rotating them at very high speed. The denser substances are thrown farther outward than the less dense ones. A centrifuge can be used to separate cream from milk, or bacteria from a fluid.
What is the meaning of "centrifuged"?
tr.v.cen·tri·fuged, cen·tri·fug·ing, cen·tri·fug·es. To rotate (something) in a centrifuge or to separate, dehydrate, or test by means of this apparatus.
What is the definition of a rotating machine?
(Mechanical Engineering) any of various rotating machines that separate liquids from solids or dispersions of one liquid in another, by the action of centrifugal force
What is a centrifuge?
Artwork: Centrifugal force makes an object fly outward as you spin it in a circle around your head... or does it?
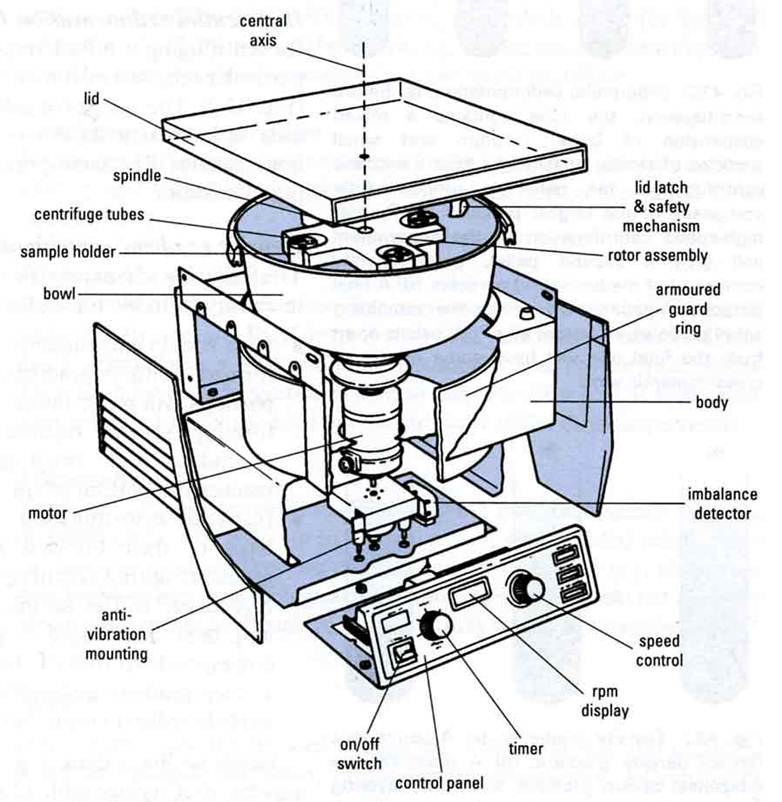
How does a laboratory centrifuge work?
Artwork: Inside a typical high-speed laboratory centrifuge. From US Patent 2,699,289: High-speed centrifuge by Robert R. Allen, Custom Scientific Instruments Inc., patented January 11, 1955, courtesy of US Patent and Trademark Office.
How big is centripetal force?
If the velocity is changing, it's accelerating (even if its speed is constant). If it's accelerating, a force must be acting—sometimes a very big force. All these statements follow directly from the laws of motion.
How does a centrifugal governor work?
It's a pair of weights on moving arms fastened to a spinning shaft. As the shaft spins faster, the weights fly outward and the arms move out. That closes a valve that lets less steam into the engine, slowing down the machine. As the machine slows, the shaft also spins more slowly, so the governor weights drop back down , the steam valve opens up again , and the engine speeds up once again. The rising and falling governor weights keep the engine working at a roughly constant speed.
What force is there when something is moving in a circle?
So look at the situation carefully and figure out where the inward pushing or pulling force is coming from. That's the centripetal force. If some part of the object is flying outward, that's not because there's centrifugal force: it's because there's no centripetal force to make it go in a circle.
Why do astronauts spin in a circle?
There's no special reason why they spin round in a circle; that's pretty much irrelevant. What's being tested is their ability to withstand very high forces—and the easiest way to experience that is at the end of a centrifuge beam. You might feel a bit dizzy at the end but, hey ho, this is rocket science after all!
How does centrifugal force get your clothes dry?
So "centrifugal force gets your washing dry because it makes the water fly out " becomes "Centripetal force between your clothes and the inside of the drum pushes them around in a circle. There's nothing to give the water the same kind of push because it can slip straight through the drum holes. The clothes experience centripetal force, the water doesn't. The clothes go round in a circle, the water goes in a straight line—straight through the holes. And that's what gets your washing dry."
What is a centrifuge?
Uses of Centrifuge. Centrifuges are devices that can be employed to place objects in a rotational motion with respect to a fixed axis. This results in the application of a force on the object which is perpendicular to the axis of the rotation.
Why are centrifuges used in space?
Such centrifuges are designed in order to help train and evaluate astronauts and pilots for flying under high-g conditions. Another important application of such centrifuges is to simulate the feeling of a gravitational force on humans. Such an application may be viable in space missions of relatively long durations. Furthermore, the simulated gravity produced by these centrifuges may also help reduce (or prevent altogether) the decalcification of bones and muscle atrophy, both of which are common side effects of being exposed to free fall for long durations of time.
Why do we use centrifuges in laundry?
Such centrifuges are widely employed by laundry services that handle relatively large loads of laundry. In order to remove the excess water in the washed clothes, special types of centrifuges are incorporated into domestic laundry machines. In the field of soil mechanics, centrifuges are employed in order to match the soil stresses ...
When was the first centrifuge invented?
The first ever human centrifuge was created in the year 1933 .
What is the purpose of a disc stack centrifuge?
The oil sands industry is known to employ centrifuges in order to separate small quantities of residual solids and water from asphalt (sometimes referred to as bitumen). Such specially designed centrifuges are commonly known as disc stack centrifuges.

Invention and Early History of The Centrifuge
How A Centrifuge Works
- A centrifuge gets its name from centrifugal force—the virtual force that pulls spinning objects outward.Centripetal force is the real physical force at work, pulling spinning objects inward. Spinning a bucket of water is a good example of these forces at work. If the bucket spins fast enough, the water is pulled inward and doesn't spill. If the buc...
Types and Uses of Centrifuges
- The types of centrifuges are all based on the same technique but differ in their applications. The main differences between them are the speed of rotation and the rotordesign. The rotor is the rotating unit in the device. Fixed-angle rotors hold samples at a constant angle, swinging head rotors have a hinge that allows sample vessels to swing outward as the rate of spin increases, a…
Related Techniques
- While centrifugation is the best option for simulating high gravity, there are other techniques that may be used to separate materials. These include filtration, sieving, distillation, decantation, and chromatography. The best technique for an application depends on the properties of the sample being used and its volume.