
How Does UV Light Affect Plants?
- Higher Flower Quality, Potency, & Weight. Some studies have shown that UVA and UVB light can enhance the production of terpenes and flavonoids in plants.
- Increased Resistance To Stress & Disease. Furthermore, growers notice an increased resistance to stress and disease when supplementing with UVA and UVB spectrums.
- Faster Germination. ...
How does UV-B radiation affect plant growth?
Studies have also shown that UV-B radiation can cause damage to DNA and affect photosynthesis, respiration, water management, growth and development. 1. UV-B Radiation: From Environmental Stressor to Regulator of Plant Growth- Vijay Pratap Singh, Samiksha Singh, Sheo Mohan Prasad and Parul Parihar
What are the effects of radiation on plants?
Once DNA is tampered with, an organism can develop dangerous mutations. [1] How Plants Are Affected Directly The effects of high levels of radiation on organisms include: [2] chromosomal aberrations, defined as visually observable changes in chromosome structure.
How does UV light help plants grow?
It helps plants grow in several ways and also may improve the overall potency and quality of your flower. But, only certain types of UV light are really beneficial to plants. Both UVB and UVA are essential parts of life on earth, but UVC is not. It gets filtered out by the ozone layer, and never really makes it to our plants naturally outdoors.
How does UV radiation affect the cell membrane?
Proteins, membrane lipids, and other essential substances in the cell can also be altered through exposure to UV-B radiation, resulting in protein degradation and lipid peroxidation. These damages influence genetic makeup and affect protein synthesis, enzyme activities, and gene expression.
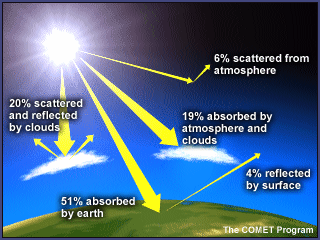
What are the effects of UV radiation on plants?
Under high Photosynthetic active radiation, UV-B light increases the net plant photosynthesis in several plant species. Higher production of flavonoids can be induced under both UV-B and high PAR in young and old plant leaves. UV-A radiation has a positive effect on the photosynthesis when plants are exposed to UV-B.
Is UV radiation good for plants?
Ultraviolet light is extremely important for plant growth. In safe doses, ultraviolet light helps plants and crops produce essential plant oils which not only enhance the flavour and smell of fruit but also helps the plants protect themselves from excessive ultraviolet exposure; acting as their own natural sunblock.
How do plants survive UV radiation?
Plants respond when exposed to UVR UV absorbing compounds accumulate in the epidermal cells of leaves and act as selective sunscreens to reduce the penetration of UVR into the leaf tissue. At the same time, they do not affect the penetration of visible light, which is essential for photosynthesis.
Do plants react to UV light?
What Kind of Light Do Plants Need to Grow? Contrary to popular belief, plants do not need ultraviolet (UV) light to grow. Plants require blue and red light, which are not a part of the UV color spectrum. Blue light encourages chlorophyll production, which helps the plants create strong and healthy stems and leaves.
How does radiation affect plants growth?
We found that chronic exposure to ionizing radiation impacted early-stage development of wild plants by reducing the ability of seeds to germinate or delaying their development. Thus, maternal radiation exposure had statistically significant negative impacts on the probability of seed germination (Fig.
How does UV radiation affect the environment?
Effects on the environment Ultraviolet radiation not only affects humans, but wildlife as well. Excessive UV -B inhibits the growth processes of almost all green plants. There is concern that ozone depletion may lead to a loss of plant species and reduce global food supply.
How does radiation affect photosynthesis?
Electromagnetic radiation may affect the photosynthetic phosphorylation by affecting the ATP synthase on the thylakoid cells of M. aeruginosa and thus may affect photosynthetic phosphorylation. Electromagnetic radiation may be one of the reasons that indirectly affect photosynthetic carbon sequestration.
Why is UV radiation harmful to organisms?
UV radiation has been linked to several types of skin cancer, as well as some other cancers. Even though it comes from the sun and is natural, there are behaviors that can overexpose us to sunlight, and cause skin damage. Common issues like sunburns or liver spots can develop into something more serious over time.
Do plants use UV light for photosynthesis?
Plants don't require UV light to photosynthesize their food. The reason is that UV light falls within the electromagnetic spectrum which is outside the visible or photosynthetic active radiation band.
Do plants need UVB or UVA?
Plants respond to exposure to both UVA and UVB light; different plants respond in different ways, but in general studies have shown increased production of antioxidants / flavonoids and other natural sunscreen compounds in a process called photomorphogenesis.
How does UV light affect photosynthesis?
UV-A light is known to boost the photosynthesis process in the plant. Over time, it leads to better and faster plant growth. This is further backed by studies that claim exposure to UV-A light increases the photosynthesis in plants by a whopping 12%.
What color UV light is best for plants?
What Color Light is Best for Plant Growth?Violet-blue light in the 400 – 520 nanometer range encourages chlorophyll absorption, photosynthesis, and growth.Red light in the 610 – 720 spectrum range promotes flowering and budding.
What is the effect of UV on plants?
Plants use sunlight for photosynthesis and, as a consequence, are exposed to the ultraviolet (UV) radiation that is present in sunlight. UV radiation plays both positive and negative effects on plants which are discussed brief in this article... Effect of UV Radiation on Crop Plants. Authors: Chongtham Allaylay Devi and Brij Bihari Pandey.
What is the UV radiation that plants use?
Plants use sunlight for photosynthesis and, as a consequence, are exposed to the ultraviolet (UV) radiation that is present in sunlight. UV radiation is generally divided into three classes: UV-C, UV-B, and UV-A. The UV-C region of the UV spectrum includes wavelengths below 280 nm; these highly energetic wavelengths are effectively absorbed by ...
What percentage of solar radiation is UVR?
UVR represents only about 7-9 % of total solar radiation reaching the biosphere, but unlike other types of solar radiation, UVR is highly energetic radiation. This means that UVR can cause reactions between molecules that are hit by such radiation. Introduction.
What is the wavelength of ultraviolet radiation?
Ultraviolet radiation (UVR) is a type of solar radiation with wavelengths between 100 and 400 nm. It ends where the colours of rainbow start. The atmosphere absorbs all UV-C (< 280 nm), a significant part of UV-B (280 – 315 nm) but transmits most of the UV-A radiation (315 – 400 nm).
What is the wavelength of UV light?
Like all living organisms, plants sense and respond to UV radiation, both the wavelengths present in sunlight (UV-A and UV-B) and the wavelengths below 280 nm (UV-C). AI1 types of UV radiation are known to damage various plant processes. Such damage can be classified into two categories: damage to DNA (which can cause heritable mutations) ...
How do plants attract pollinators?
They attract pollinators to their insect traps, by imitating the UV-visible patterns of flowers. Plants provide protective substances for humans. Plants also produce many important protective substances and vitamins that are indispensable for them, but also benefit us, since our bodies are not able to synthesise them.
Why is UV C used in DNA?
UV-C has been used because DNA has a strong absorption maximum in the UV-C range ( at 260 nm); UV-C photons are highly energetic, and high levels of damage can thus be created quickly. The best-studied UV radiation-induced DNA lesion is the cyclobutane-type pyrimidine dimer (CPD).
What are the three regions of UV radiation?
UV and plants. Ultraviolet radiation (UV) is arbitrarily divided into three regions A (315 nm to 400 nm), B (280 nm to 315 nm), C (280 nm to 200 nm). UV-C radiation is not present in sunlight at ground level, while UV-B and UV-A are.
Is UV B radiation harmful?
As a result of improved experimental design and methods the view of UV-B radiation as a damaging agent, has given way to a view where UV-B radiation is considered as a specific regulator of gene expression, metabolite profiles, and responses to climate change for plants growing in sunlight.
Can UVB radiation damage plants?
The case with UV-B radiation is mid way, as could be expected from the intermediate energy content of its photons. Large and/or sudden exposure of plants to UV-B radiation can cause damage, while smaller and gradual exposure normally results in regulatory processes.
Is UV B harmful to plants?
While damage can be expected to always be detrimental to plant growth and crop yield, regulatory responses can result in a wide array of different effects, both positive and negative, on growth, yield and nutritional quality of plants. Significant new understanding of UV-B mediated processes in plants has been gained during the last decade.
Is UV C radiation a regulatory function?
Responses to UV-C radiation are most frequently the result of direct or indirect damage to plant cells and their components, UV-C radiation is not considered to have a regulatory function.
Why is UV B reducing the height of plants?
Reduction in plant height from exposure to UV-B is due in part to decreased levels of a growth hormone (indole acetic acid) in plants. The smaller and more compact canopy reduces the amount of UV-B intercepted by the plant, but also reduces the potential or total photosynthetic area essential for growth.
How does UV B affect insects?
However, the impact of UV-B radiation on mechanisms of other behavior of adult insects, such as oviposition and breeding, that are more relevant under natural conditions are not well understood and need investigation. Ultraviolet-B radiation changes the chemistry, morphology, and physiology of plants.
What is UV B damage?
In plants, UV-B radiation damages cell membranes and all organelles within the cell, including the chloroplasts, mitochondria, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) within the nucleus. Damage to these cell organelles directly or indirectly affects basic plant metabolic processes, such as photosynthesis, respiration, growth, and reproduction. ...
How do insects protect themselves from UV radiation?
Some insects protect themselves from UV-B radiation by feeding on the underside of the leaves where UV-B penetration is lower (Paul et al., 1997) and avoiding areas of plants where defensive chemicals accumulate (McCloud et al., 1992).
What is the rate of increase in weight and size of plant organs?
Growth is the rate of increase in weight and size of plant organs, such as leaf, stem, or root. Dry matter is the total weight of all plant organs. Exposure to UV-B radiation caused decreases in growth of leaves and stems in many plant species in both controlled environment and field studies (Kakani et al., 2003a).
Why are cotton flowers smaller?
Cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) flowers produced on plants exposed to elevated UV-B were smaller due to reduced petal and bract size, and had fewer anthers (Kakani et al., 2003b). In general, reproductive organs of most plant species (pollen and ovules) are highly protected by sepals, petals, and ovary walls.
Does pollen tube affect the fertilization process?
Consequently, it affects the fertilization process, which results in fewer seeds in sensitive plants. However, once the pollen tube penetrates the stigma surface, the walls of the style and ovary may provide some protection against UV-B radiation.
How does UV light affect plants?
Plants can produce up to 15 different variant defense proteins as soon as they are exposed to UV light. UV light has the ability to destroy harmful microorganisms, particularly when the wavelengths are shorter than 300 nm. Not only that, but UV light can increase your plants’ resistance to bacteria, insects, and fungus.
Why do tomatoes grow with UV?
This is great for those growing flower, because it means the taste and aroma of your flower will be increased.
What do you need to know about UV light?
Some growers even wonder whether ultraviolet light has a place in plant cultivation of any kind at all. The fact of the matter is that if you are growing plants indoors, you should be supplementing your plants with some form of it.
What is the wavelength of ultraviolet light?
Ultraviolet B (UVB) The next type of ultraviolet light is UVB, or ultraviolet B. this kind of light has wavelengths between 29 nm and 320 nm. It contains about a fifth of 1% of overall natural sunlight. In contrast to UVA, it can damage DNA and has been known to have cancerous effects on humans and animals.
How many terpenes are in a flower without UV light?
But to take things a step further, consider the fact that one study found that flower grown without UV light will be missing up to 6 key terpenes! And as we are coming to realize, terpenes affect the way flower makes you feel, as well as that taste and aroma.
What is UV light?
Often referred to as UV light for short, ultraviolet light is technically a type of electromagnetic radiation garnered from natural sunlight. Every time you are out in the sun, you are exposed to UV light. It is broken up into three different categories of wavelengths - UVA, UVB, and UVC.
How many watts of UV light should I use for a 4x4 tent?
You can get great results with just 2-3 watts of UV light per square foot of growing space. This means for a 4'x4' tent, for example, you would be just fine with around 32-48 watts of UV lighting to yield the benefits.
How does UV B affect the biosphere?
Because UV-B affects organisms that move nutrients and energy through the biosphere, we can expect changes in their activities to alter biogeochemical cycles. For example, reducing populations of phytoplankton would significantly impact the world’s carbon cycle, because phytoplankton store huge amounts of carbon in the ocean. ...
What are the effects of UV B?
We know that increased exposure to UV-B radiation has specific effects on human health, crops, terrestrial ecosystems, aquatic ecosystems, and biogeochemical cycles. (“Biogeochemical cycles” refers to the cycling of chemicals such as carbon and energy throughout the Earth system.)
How does UV B affect skin?
UV-B induces skin cancer by causing mutation in DNA and suppressing certain activities of the immune system. The United Nations Environment Program estimates that a sustained 1 percent depletion of ozone will ultimately lead to a 2-3 percent increase in the incidence of non-melanoma skin cancer.
What is the highest radiation in Antarctica?
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation in Antarctica is commonly highest in spring. (Image courtesy of NOAA) In the Antarctic, increased exposure to UV-B radiation due to the appearance of the ozone hole commonly results in at least a 6-12 percent reduction in photosynthesis by phytoplankton in surface waters.
