What UV radiation is and why it is harmful?
The NTP has made the following determinations:
- Solar radiation is known to be a human carcinogen.
- Exposure to sunlamps or sunbeds is known to be a human carcinogen.
- Broad-spectrum UV radiation is known to be a human carcinogen.
- UVA radiation is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen.
- UVB radiation is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen.
What damage may be caused by UV radiation?
Ultraviolet (UV) light is well known as a cause of skin cancer. This wavelength of radiation can damage your eyes too. But you can protect your eyes from the sun’s rays, guarding against potential blindness. There are three types of UV light, with UVA and UVB rays reaching the surface of the earth and causing the most damage to your eyes.
What is UV radiation and how dangerous can it be?
UV radiation is a type of radiation that is produced by the sun and some artificial sources, such as solariums. According to the Met Office, a small amount of UV radiation is essential in the production of vitamin D. But too much exposure to the sun can have serious effects on your skin and eyes. How dangerous is sunburn?
What are the dangers of UV radiation?
The strength of the UV rays reaching the ground depends on a number of factors, such as:
- Time of day: UV rays are strongest between 10 am and 4 pm.
- Season of the year: UV rays are stronger during spring and summer months. ...
- Distance from the equator (latitude): UV exposure goes down as you get farther from the equator.
- Altitude: More UV rays reach the ground at higher elevations.
What does UV radiation damage?
Cataracts and Other Eye Damage Cataracts are a form of eye damage in which a loss of transparency in the lens of the eye clouds vision. If left untreated, cataracts can lead to blindness. Research has shown that UV radiation increases the likelihood of certain cataracts.
How does UV light damage cellular DNA?
Solar ultraviolet (UV) radiation generates bulky photodimers at di-pyrimidine sites that pose stress to cells and organisms by hindering DNA replication and transcription. In addition, solar UV also induces various types of oxidative DNA lesions and single strand DNA breaks.
How does UV damage organisms?
UV-B radiation has been shown to be harmful to living organisms, damaging DNA, proteins, lipids and membranes. Plants, which use sunlight for photosynthesis and are unable to avoid exposure to enhanced levels of UV-B radiation, are at risk.
How does UV radiation cause mutations?
In fact, UV-A radiation commonly damages DNA in an oxygen-dependent manner that involves photosensitization. This leads to the production of a free radical that then interacts with and oxidizes DNA bases. These oxidized bases don't pair correctly during replication, resulting in mutations (Figure 1).
How does UV light damage the DNA strand?
Direct DNA damage can occur when DNA directly absorbs a UVB photon, or for numerous other reasons. UVB light causes thymine base pairs next to each other in genetic sequences to bond together into pyrimidine dimers, a disruption in the strand, which reproductive enzymes cannot copy.
How does ultraviolet light destroy bacterial cells quizlet?
UV causes mutation called thymine dimers which put kinks in DNA strands, rendering the molecule useless for transcription. What damage does UV cause which makes it effective in killing bacteria? bacteria can synthesize their own repair enzymes to fix the damages caused by mutagens like UV light.
How does UV radiation damage DNA quizlet?
UV light damages the DNA of exposed cells by causing bonds to form between adjacent pyrimidine bases, usually thymines, in DNA chains. The thymine dimers inhibit correct replication of the DNA during reproduction of the cell.
How does UV light damage DNA quizlet?
UV light damages the DNA of exposed cells by causing bonds to form between adjacent pyrimidine bases, usually thymines, in DNA chains. The thymine dimers inhibit correct replication of the DNA during reproduction of the cell.
How does UV light and other ionizing radiation damage DNA molecules?
How does UV light and other ionizing radiations damage DNA molecules? creating thymine dimers between adjacent thymines in the DNA chain.
What is the most common type of DNA damage caused by ultraviolet UV radiation?
UV radiation induces two of the most abundant mutagenic and cytotoxic DNA lesions such as cyclobutane-pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and 6-4 photoproducts (6-4PPs) and their Dewar valence Isomers.
Which DNA sequences would be damaged by UV radiation?
Abstract. The sequence specificity of UV-induced DNA damage was determined with a higher precision and accuracy than previously reported. UV light induces two major damage adducts: cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs) and pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts (6-4PPs).
Do UVA and UVB affect the body in different ways?
The skin UVA activates melanin pigment already present in the upper skin cells. It creates a tan that appears quickly but is also lost quickly. Fur...
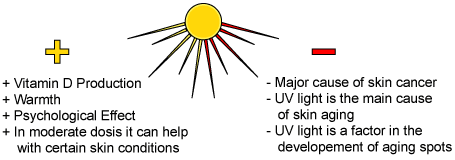
Are there beneficial effects of UV radiation?
The sun's rays provide warmth and light that enhance your general feeling of well-being and stimulate blood circulation. Some UV radiation is essen...
What are the effects of UV on the skin?
The truth about a suntan There is no such thing as a healthy tan! The skin produces a dark-coloured pigment, melanin, as a shield against further d...
What are the effects of UV on the eye?
The eye occupies less than 2 per cent of the whole body surface area, but it represents the sole organ system to allow the penetration of visible l...
Does UV interact with the immune system?
Sunlight exposure can precede the onset of recurrent eruptions of cold sores. UVB radiation appears to reduce the effectiveness of the immune syste...
I am dark-skinned – do I still need to be careful?
Yes, you do. Compared to fair-skinned people, dark-skinned people have a much lower risk of developing melanoma or non-melanoma skin cancers. They...
What does UV radiation do to cells?
Kornblihtt, a Howard Hughes Medical Institute international research scholar at the University of Buenos Aires and the National Research Council of Argentina, has found that UV radiation causes human cells to create proteins that trigger cell death. It’s a built-in safety pathway whose precise mechanism had never been seen before.
How many genes are switched in response to UV C?
Using special chips that analyzed the mRNA of about 500 genes, Kornblihtt found that 14 percent of the genes switched forms in response to UV-C. “We found that UV radiation causes changes in alternative splicing, but only in a certain subset of genes,” Kornblihtt says.
What are the effects of apoptosis on cancer?
Defects in apoptosis can be harmful—leading to extended cell survival and the potential for the uncontrolled growth characteristic of cancer. The Bcl-X and caspase-9 genes can produce two different proteins via alternative splicing. For each gene, one version prevents cell death, while the other version encourages it.
Is it better for a cell to die or spread?
It's better for the cell to die than to spread the mutations. Alberto R. Kornblihtt. “It's better for the cell to die than to spread the mutations,” Kornblihtt says. The findings were published in the May 15, 2009 issue of the journal Cell.
Does UV radiation cause cancer?
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun can zap DNA, damage cells, and set the stage for the subsequent development of cancer. Scientists have now identified the built-in safety mechanism that forces some cells damaged by UV radiation to commit suicide so they do not perpetuate harmful mutations.
What are the diseases caused by UV light?
Other UV-related skin disorders include actinic keratoses and premature aging of the skin. Actinic keratoses are skin growths that occur on body areas exposed to the sun. The face, hands, forearms, and the “V” of the neck are especially susceptible to this type of lesion.
What are the risks of sun exposure?
Understanding these risks and taking sensible precautions will help you enjoy the sun while reducing your chances of sun-related health problems. Skin cancer (melanoma and nonmelanoma) Premature aging and other skin damage. Cataracts and other eye damage.
How many people die from skin cancer every hour?
One in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. One American dies from skin cancer every hour. Unprotected exposure to UV radiation is the most preventable risk factor for skin cancer.
Why is skin thick and wrinkled?
Chronic exposure to the sun also causes premature aging, which over time can make the skin become thick, wrinkled, and leathery. Since it occurs gradually, often manifesting itself many years after the majority of a person’s sun exposure, premature aging is often regarded as an unavoidable, normal part of growing older.
Does UV light affect the immune system?
But overexposure to UV radiation can weaken the immune system, reducing the skin’s ability to protect against these invaders.
Does basal cell carcinoma spread to other parts of the body?
Basal cell carcinoma grows slowly, and it rarely spreads to other parts of the body . It can, however, penetrate to the bone and cause considerable damage. Squamous cell carcinomas are tumors that may appear as nodules or as red, scaly patches.
Does sun damage skin?
However, up to 90 percent of the visible skin changes commonly attributed to aging are caused by the sun. With proper protection from UV radiation, most premature aging of the skin can be avoided.
What is UV B radiation?
Ultraviolet B radiation, harmful to living organisms, represents a small portion of the spectrum, from 290 to 320 nanometer wavelengths. (Illustration by Robert Simmon) DNA readily absorbs UV-B radiation, which commonly changes the shape of the molecule in one of several ways.
What is the chemical that protects cells from UV radiation?
In addition to their own resiliency, living things and the cells they are made of are protected from excessive amounts of UV radiation by a chemical called ozone. A layer of ozone in the upper atmosphere absorbs UV radiation and prevents most of it from reaching the Earth.
What is the wavelength of ultraviolet radiation?
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface is in wavelengths between 290 and 400 nm (nanometers, or billionths of a meter). This is shorter than wavelengths of visible light, which are 400 to 700 nm.
What is the wavelength of light in the electromagnetic spectrum?
The incoming radiation at shorter wavelengths, 290-320 nm, falls within the UV-B part of the electromagnetic spectrum. (UV-B includes light with wavelengths down to 280 nm, but little to no radiation below 290 nm reaches the Earth’s surface).
How does the Sun's energy work?
The sun radiates energy in a wide range of wavelengths, most of which are invisible to human eyes. The shorter the wavelength, the more energetic the radiation, and the greater the potential for harm. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation that reaches the Earth’s surface is in wavelengths between 290 and 400 nm (nanometers, or billionths of a meter). ...
What is UV A?
Radiation at the longer UV wavelengths of 320-400 nm, called UV-A, plays a helpful and essential role in formation of Vitamin D by the skin, and plays a harmful role in that it causes sunburn on human skin and cataracts in our eyes.
Can UV light damage DNA?
As a result, distorted proteins can be made, or cells can die. Ultraviolet (UV) photons harm the DNA molecules of living organisms in different ways. In one common damage event, adjacent bases bond with each other, instead of across the “ladder.”.
What is DNA damaged by UV radiation?
DNA Damage by UV Radiation. DNA is composed of two complementary strands that are wound into a double helix. The hereditary message is chemically coded and made up of the four nucleotides adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G) and cytosine (C). UVB light interferes directly with the bonding between the nucleotides in the DNA.
What is the effect of UVB light on DNA?
UVB light interferes directly with the bonding between the nucleotides in the DNA. The two main DNA lesions formed by exposure to UVB are cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPD) and 6-4 pyrimidine pyrimidone photoproducts (6-4PPs), and its Dewar isomers.
How does UVA damage DNA?
UVA (and also UVB) radiation cause indirect damage to DNA via absorption of photons by non-DNA chromophores. This generates reactive oxygen species like singlet oxygen or hydrogen peroxide that oxidize the DNA bases causing mutations.
Which rays are the most damaging?
UVC rays (100-280 nm) are the most energetic and damaging of the three rays. Fortunately, UVC is absorbed by the ozone layer before reaching the earth’s surface. UVA rays (315-400 nm) possess the lowest energy and is able to penetrate deep into the skin. Prolonged exposure has been linked to ageing and wrinkling of the skin.
What is the cause of melanomas?
Prolonged exposure has been linked to ageing and wrinkling of the skin. UVA is also the main cause of melanomas. UVB rays (280-315 nm) possess higher energy than UVA rays and affect the outer layer of the skin leading to sunburns and tans. Basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma are caused by UVB radiation.
What are the effects of ultraviolet radiation on plant cells?
Recent measurements of ozone levels have led to concern that the stratospheric ozone layer is being depleted as a result of contamination with man-made chlorofluorocarbons.
Is UV B harmful to plants?
UV-B radiation has been shown to be harmful to living organisms, damaging DNA, proteins, lipids and membranes. Plants, which use sunlight for photosynthesis and are unable to avoid exposure to enhanced levels of UV-B radiation, are at risk.
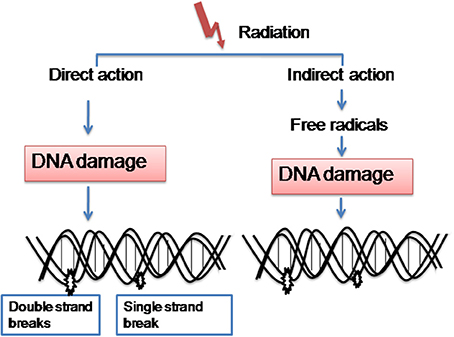
How does radiation affect cells?
It can affect cells through direct and indirect action, causing DNA damage as well as mutations. This can be especially harmful to cells that divide very quickly. But sometimes this can be a good thing, like when doctors use radiation to fight cancer. Let's Talk Science needs your input!
Why does radiation kill cells?
The radiation could prevent the DNA from replicating correctly. The radiation could damage the DNA so badly that the cell dies. This is called apoptosis. One dead cell is not a big problem. After all, millions of your cells die every day. But if too many cells die at once, the organism could also die.
What happens when ionizing radiation is used in a cell?
When ionizing radiation interacts with a cell, several things can happen: The radiation could pass through the cell without damaging the DNA. The radiation could damage the cell’s DNA , but the DNA repairs itself. The radiation could prevent the DNA from replicating correctly.
What can hydroxyl ions react with?
For example, hydroxyl ions (OH -) can react with hydrogen atoms inside a DNA molecule to form hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ). This can cause the types of DNA damage we talked about earlier. Over time, damage from free radicals can build up.
What is ionizing radiation?
Ionizing radiation is radiation that can remove electrons from an atom. Losing an electron charges, or ionizes, the atom. Sometimes, ionizing radiation takes the form of a wave, like gamma rays or X-rays. But it can also take the form of a particle, like neutrons or alpha and beta particles. Natural sources of radiation (© 2019 Let’s Talk Science).
What happens if DNA is not repaired?
DNA mutations involve changes to the sequence of base pairs (number 1 on the list and diagram). If DNA damage is not repaired, it can lead to mutations. Mutations can prevent genes from making correct proteins. This can be very harmful to an organism.
How does direct action affect DNA?
Direct action can also damage critical cellular systems. Sometimes, it can even lead to cancer. Alpha particles, beta particles and X-rays can directly affect a DNA molecule in one of three ways: Changing the chemical structure of the bases;
What happens when a cell is bombarded by radiation?
Radiation and electrons bombarded by radiation move haphazardly inside the cell, resulting in damage to the various molecules forming the cell. Chromosomal DNA inside the cell nucleus can also be damaged.
Why is radiation harmful to DNA?
When part of a DNA break is repaired incorrectly, chromosome aberrations occur. Radiation is harmful to health because radiation exposure can damage cellular DNA ( mostly in the form of DNA breaks).
Skin Cancer
- Each year, more new cases of skin cancer are diagnosed in the U.S. than new cases of breast, prostate, lung, and colon cancer combined. One in five Americans will develop skin cancer in their lifetime. One American dies from skin cancer every hour. Unprotected exposure to UV radiation is the most preventable risk factor for skin cancer.
Premature Aging and Other Skin Damage
- Other UV-related skin disorders include actinic keratoses and premature aging of the skin. Actinic keratoses are skin growths that occur on body areas exposed to the sun. The face, hands, forearms, and the “V” of the neck are especially susceptible to this type of lesion. Although premalignant, actinic keratoses are a risk factor for squamous cell carcinoma. Look for raised, r…
Cataracts and Other Eye Damage
- Cataracts are a form of eye damage in which a loss of transparency in the lens of the eye clouds vision. If left untreated, cataracts can lead to blindness. Research has shown that UV radiation increases the likelihood of certain cataracts. Although curable with modern eye surgery, cataracts diminish the eyesight of millions of Americans and cost billions of dollars in medical care each y…
Immune Suppression
- Scientists have found that overexposure to UV radiation may suppress proper functioning of the body’s immune system and the skin’s natural defenses. For example, the skin normally mounts a defense against foreign invaders such as cancers and infections. But overexposure to UV radiation can weaken the immune system, reducing the skin’s ability to pr...