
In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones
Histone
In biology, histones are highly alkaline proteins found in eukaryotic cell nuclei that package and order the DNA into structural units called nucleosomes. They are the chief protein components of chromatin, acting as spools around which DNA winds, and playing a role in ge…
How are chromosomes organized?
As the chromosomal DNA is wrapped around those histones, the DNA is organized into something that is called chromatin. Each subunit of chromatin, which is the little ball of DNA wrapped around the histone proteins, is referred to as a nucleosome. We've also talked about the functional organization of the chromosome.
What is the structure of DNA in a chromosome?
In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
How are DNA molecules packed up into chromosomes?
This animation shows how DNA molecules are packed up into chromosomes. DNA is tightly packed up to fit in the nucleus of every cell. As shown in the animation, a DNA molecule wraps around histone proteins to form tight loops called nucleosomes.
What is a chromosome?
What is a chromosome?: MedlinePlus Genetics What is a chromosome? From Genetics Home Reference. Learn more In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
How are DNA and proteins organized into chromosomes?
Chromosomes are made up of a DNA-protein complex called chromatin that is organized into subunits called nucleosomes. The way in which eukaryotes compact and arrange their chromatin not only allows a large amount of DNA to fit in a small space, but it also helps regulate gene expression.
How the DNA is organized?
Nucleotides are arranged in two long strands that form a spiral called a double helix. The structure of the double helix is somewhat like a ladder, with the base pairs forming the ladder's rungs and the sugar and phosphate molecules forming the vertical sidepieces of the ladder.
How is DNA organized in genes?
Genetic information is carried in the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA. Each molecule of DNA is a double helix formed from two complementary strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds between G-C and A-T base pairs.
How is DNA organized in a human cell quizlet?
How is DNA organized in a human cell? There are 46 strands, called chromosomes. Humans have two copies (one from our mother, one from our father) of 23 unique pieces of DNA. Adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine are the nitrogenous bases found in the DNA of which organism(s)?
How is DNA arranged GCSE?
DNA consists of 2 long strands of alternating sugar and phosphate molecules. The chains are twisted to form a double helix. There are pairs of bases holding the chains together. The 4 bases are A (adenine), T (thymine), C (cytosine) and G (guanine).
How is DNA Organised inside the cell nucleus?
To package DNA inside the nucleus, cells wrap their DNA strands around scaffolding proteins to form a coiled condensed structure called chromatin. Chromatin is further folded into higher orders of structure that form the characteristic shape of chromosomes.
How is DNA organized in the nucleus when the cell is prepared for division?
DNA is normally found as a loosely contained structure called chromatin within the nucleus, where it is wound up and associated with a variety of histone proteins. When a cell is about to divide, the chromatin coils tightly and condenses to form chromosomes.
How is the DNA organized in the cell during mitosis?
The DNA in the nucleus wraps around proteins to form chromosomes. During mitosis, the newly duplicated chromosomes are divided into two daughter nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four phases, called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
How is the DNA organized in the cell during mitosis?
The DNA in the nucleus wraps around proteins to form chromosomes. During mitosis, the newly duplicated chromosomes are divided into two daughter nuclei. Mitosis occurs in four phases, called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What is the first level of DNA organization?
In the first level of compaction, short stretches of the DNA double helix wrap around a core of eight histone proteins at regular intervals along the entire length of the chromosome ([link]). The DNA-histone complex is called chromatin.
How is DNA organized during interphase?
During interphase, the cell's DNA is not condensed and is loosely distributed. A stain for heterochromatin (which indicates the position of chromosomes) shows this broad distribution of chromatin in a mouse cell (upper left). The same stain also shows the organized, aligned structure of the chromosomes during mitosis.
What is a portrait of human chromosomes?
A portrait of human chromosomes: this process labels the chromosomes with multicolored fluorescent tags, allowing researchers to consistently distinguish between chromosomes.
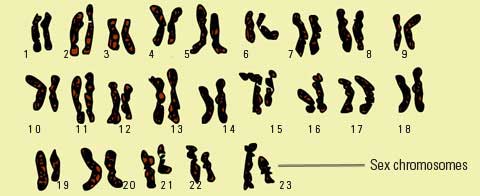
How many chromosomes are there in the human genome?
These are arranged into 22 matching pairs plus 1 pair of sex chromosomes consisting of 2 X's in women and an X and a Y in men. So humans have a total of 46 chromosomes in each cell, known collectively as a karyotype.
Where are breakpoints in the genome?
Professor David Porteous explains that breakpoints in the genome are locations on a chromosome where DNA might get deleted, inverted, or swapped around.
What is a chromosome made of?
In the nucleus of each cell, the DNA molecule is packaged into thread-like structures called chromosomes. Each chromosome is made up of DNA tightly coiled many times around proteins called histones that support its structure.
What is the DNA that makes up chromosomes?
However, the DNA that makes up chromosomes becomes more tightly packed during cell division and is then visible under a microscope. Most of what researchers know about chromosomes was learned by observing chromosomes during cell division. Each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, ...
What is the centromere on a chromosome?
The location of the centromere on each chromosome gives the chromosome its characteristic shape, and can be used to help describe the location of specific genes. DNA and histone proteins are packaged into structures called chromosomes. Credit: U.S. National Library of Medicine.
What is the constriction point on a chromosome?
Each chromosome has a constriction point called the centromere, which divides the chromosome into two sections, or “arms.” The short arm of the chromosome is labeled the “p arm.” The long arm of the chromosome is labeled the “q arm.” The location of the centromere on each chromosome gives the chromosome its characteristic shape, and can be used to help describe the location of specific genes.
Where is the genetics home reference?
Genetics Home Reference has merged with MedlinePlus. Genetics Home Reference content now can be found in the "Genetics" section of MedlinePlus. Learn more
What are the mated pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism called?
Matched pairs of chromosomes in a diploid organism are called homologous (“same knowledge”) chrom osomes. Of a pair of homologous chromosomes, one came from the egg and the second came from the sperm.
What is the region of DNA that contains the genetic material?
The region in the cell containing this genetic material is called a nucleoid (remember that prokaryotes do not have a separate membrane-bound nucleus). Some prokaryotes also have smaller loops of DNA called plasmids that are not essential for normal growth.
What are homologous chromosomes?
Homologous chromosomes are the same length and have specific nucleotide segments called genes in exactly the same location, or locus. Genes, the functional units of chromosomes, determine specific characteristics by coding for specific proteins. Traits are the variations of those characteristics.
How is DNA twisted?
The DNA is twisted by what is known as supercoiling. Supercoiled DNA is coiled more tightly than would be typically be found in a cell (more than 10 nucleotides per twist of the helix). If you visualize twisting a rope until it twists back on itself, you have a pretty good visual of supercoiled DNA.
What is the DNA of a prokaryote?
DNA Organization in Prokaryotes. A cell’s DNA, packaged as a double-stranded DNA molecule, is called its genome. In prokaryotes, the genome is composed of a single, double-stranded DNA molecule in the form of a loop or circle (Figure 1). The region in the cell containing this genetic material is called a nucleoid ...
Why are there variations in a gene?
The variation of individuals within a species is due to the specific combination of the genes inherited from both parents. Even a slightly altered sequence of nucleotides within a gene can result in an alternative trait. For example, there are three possible gene sequences (alleles) on the human chromosome that code for blood type: sequence A, sequence B, and sequence O. Because all diploid human cells have two copies of the chromosome that determines blood type, the blood type (the trait) is determined by which two versions of the marker gene are inherited. It is possible to have two copies of the same allele on both homologous chromosomes, with one on each (for example, AA, BB, or OO), or two different alleles, such as AB.
How many base pairs are in a bacteria genome?
The size of the genome in one of the most well-studied prokaryotes, E.coli, is 4.6 million base pairs (which would be approximately 1.1 mm in length, if cut and stretched out). So how does this fit inside a small bacterial cell? The DNA is twisted by what is known as supercoiling. Supercoiled DNA is coiled more tightly than would be typically be found in a cell (more than 10 nucleotides per twist of the helix). If you visualize twisting a rope until it twists back on itself, you have a pretty good visual of supercoiled DNA. This process allows the DNA to be compacted into the small space inside a bacteria.
What is the storehouse of information in a cell?
So as you recall, DNA is the storehouse of information in the cell. DNA is organized into chromosomes and all of the DNA in the cell is referred to as the genome. DNA is a linear molecule; it's kind of like a string, kind of like our light strings that we're talking about.
Why is DNA important to the cell?
I said that it's going to be important not only to package the DNA into the cell, which organizing it into chromatin has helped us do, but I also said it's going to be important to be able to actually find information in the DNA. We said that DNA is a storehouse of information, and DNA is basically providing information to create different things that the cell's going to need. So if the cell needs microtubules, DNA is going to code for that. If the cell needs to make mitochondria, DNA is going to code for that.
What is the function of a gene?
A gene is a distinct unit of DNA that can code for RNA, and in turn, that RNA can make protein. Then the proteins can provide the functionality that the cell needs. Definition of genes. You might think of chromosomes then as just being jam packed with genes one after another.
What is the information that a cell needs to function?
It's providing all the information the cell needs to be able to provide function not only for itself, but also for you as an organism. Genes. The information that's stored in chromosomes is referred to as a gene . A gene is a distinct unit of DNA that can code for RNA, and in turn, that RNA can make protein.
What is DNA coded for?
So the DNA is going to code for things that the cell needs to be able to make all the structures that it needs to be a cell. It's also going to code for things to tell that cell what to do - telling that cell if it's going to be a red blood cell or a muscle cell.
What is the role of histones in DNA?
Histones, which are proteins that help package the DNA, play a central role in that process. As the chromosomal DNA is wrapped around those histones, the DNA is organized into something that is called chromatin. Each subunit of chromatin, which is the little ball of DNA wrapped around the histone proteins, is referred to as a nucleosome.
Why is DNA called junk DNA?
Historically, scientists actually referred to this as ' junk DNA ' because they couldn't imagine that this DNA served any purpose if it wasn't producing any proteins. We actually now know that that's wrong, and actually, non-coding DNA serves a number of purposes both structurally and functionally. Lesson Summary.
How many chromosomes are there in a human body?
Different organisms have different numbers of chromosomes. Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes--22 pairs of numbered chromosomes, called autosomes, and one pair of sex chromosomes, X and Y. Each parent contributes one chromosome to each pair so that offspring get half ...
What is the chromosome in a cell?
Narration. A chromosome is the structure housing DNA in a cell. Chromosomes are structurally quite sophisticated, containing elements necessary for processes such as replication and segregation. Each species has a characteristic set of chromosomes with respect to number and organization. For example, humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes--22 pairs ...
Can you add videos to your watch history?
Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations. To avoid this, cancel and sign in to YouTube on your computer.
What is the concept of 29?
Concept 29 DNA is packaged in a chromosome. DNA is packaged in a chromosome. Work on cytology in the late 1800s had shown that each living thing has a characteristic set of chromosomes in the nucleus of each cell. During the same period, biochemical studies indicated that the nuclear materials that make up the chromosomes are composed ...
Where is DNA wound?
The DNA strand is wound around histone cores, which, in turn, are looped and fixed to specific regions of the chromosome.
Is DNA a genetic code?
In the first four decades of the 20th century, many scientists believed that protein carried the genetic code, and DNA was merely a supporting "scaffold.". Just the opposite proved to be true. Work by Avery and Hershey, in the 1940s and 1950s, proved that DNA is the genetic molecule.
