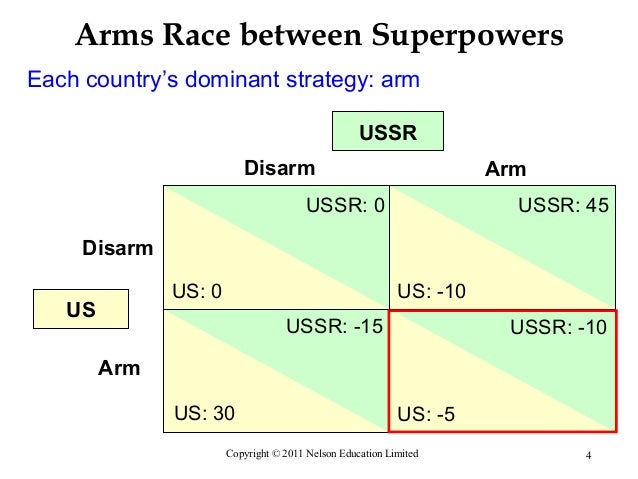
‘Game-theory’ can be used to explain ‘interdependence’ and ‘price-stickiness’, which are both characteristics of oligopolies. A game has three central components - players, outcomes and the need for a strategy.
What is game theory in microeconomics?
Afairly recent development in microeconomics has been the introduction of game theory as an analytic tool to understand the behavior of individual economic agents. This particular form of
What is the difference between oligopoly and a monopoly?
The following are the major differences between monopoly and oligopoly:
- Monopoly refers to a type of market, having a single seller dominating the whole market. ...
- In monopoly as there is a sole seller of a product or provider of service, the competition does not exist at all. ...
- In a monopoly, there is only one player in the entire market, but in oligopoly, the range of players is 2 – 10, in the market.
What role does oligopoly play on the economy?
The role of oligopolies in modern economy of Russia In most capitalist countries, the market is characterized by oligopolistic relations. Oligopoly in the economy is a middle tier that allows, on the one hand, to control all major enterprises and manage them, and create future conditions for entrance to the competitive environment.
What are the causes of monopoly in economics?
Causes of monopoly. The causes of monopoly, according to economic theory, are: The ownership of a strategic tangible or intangible resource. As key raw material or essential and secret information regarding production, or proximity of some kind to an indispensable primary supplier.
Why is game theory useful for oligopoly?
Economists often use game theory to understand oligopoly firm behavior. It helps to predict likely outcomes when firms engage in certain behaviors, such as price-fixing and collusion.
What is game theory strategy of oligopoly pricing problem?
When firms in an oligopoly must decide about quantity and pricing, they must consider what the other firms will do, since quantity and price are inversely related. If all the firms produce too much, then the price may drop below their average total costs, causing them losses.
Why is game theory useful for studying oligopolistic markets but not perfectly competitive markets?
In an oligopolistic market though, sellers have a lot of market power each and thus, game theory is incredibly useful as you must determine how to change your output given that the actions of others affect you and your actions affect them.
In which market structure is game theory?
In oligopoly markets, there is a tension between cooperation and self-interest. If all the firms limit their output, the price is high, but then firms have an incentive to expand output. The techniques of game theory are used to solve for the equilibrium of an oligopoly market.
What is oligopoly game?
The purpose of The Oligopoly Game is to demonstrate the issue of game theory that presents itself to firms operating in an oligopolistic market when they are prevented from colluding by competition law. The game, which usually takes around an hour to complete, mimics the classic conundrum of the 'prisoners' dilemma.
Which theory has numerous applications in oligopoly market?
The game theoryThe game theory has been applied not only to the oligopoly but also to other economic questions like demand when uncertainty is present.
What is the prisoner's dilemma and what does it have to do with oligopoly?
In oligopoly, prisoner's dilemma is used to illustrate the difficulty of maintaining cooperation between firms because the firms would want to cheat their rivals in order to gain at their expense. Even when it is mutually beneficial, cooperation between firms becomes very difficult.
What will happen when an oligopoly market reaches a Nash equilibrium?
When an oligopoly market reaches a Nash equilibrium, a firm will have chosen its best strategy, given the strategies chosen by other firms in the market. higher than in monopoly markets and lower than in perfectly competitive markets. The essence of an oligopolistic market is that there are only a few sellers.
How do oligopolies determine profitability?
The oligopolist maximizes profits by equating marginal revenue with marginal cost, which results in an equilibrium output of Q units and an equilibrium price of P.
What is oligopoly market structure?
An oligopoly is defined as a market structure with few firms and barriers to entry. Oligopoly = A market structure with few firms and barriers to entry. There is often a high level of competition between firms, as each firm makes decisions on prices, quantities, and advertising to maximize profits.
What are the models of oligopoly?
We have now covered three models of oligopoly: Cournot, Bertrand, and Stackelberg. These three models are alternative representations of oligopolistic behavior. The Bertand model is relatively easy to identify in the real world, since it results in a price war and competitive prices.
What is the importance of game theory?
Game theory is a field of study that helps us understand decision making in strategic situations. In addition to being an important methodology within the economics discipline, it also gives insights into pricing and management strategies used by a business.
What is the pricing strategy of oligopoly market?
Pricing strategies of oligopolies Oligopolists may use predatory pricing to force rivals out of the market. This means keeping price artificially low, and often below the full cost of production. They may also operate a limit-pricing strategy to deter entrants, which is also called entry forestalling price.
How can game theory be used to explain pricing?
Game Theory is relevant to an oligopolistic firm as it influences their pricing strategy to be consistent. It is unlikely to sharply increase prices. As, if it does this, its rivals in the market can easily undercut and profit from it. If it decreases, the other firms will also follow.
What is price leadership under oligopoly market what are its importance?
Price leadership occurs when a leading firm in a given industry is able to exert enough influence in the sector that it can effectively determine the price of goods or services for the entire market. There are three primary models of price leadership: barometric, collusive, and dominant.
How do oligopolies set prices?
Understanding Oligopolies Firms in an oligopoly set prices, whether collectively—in a cartel—or under the leadership of one firm, rather than taking prices from the market. Profit margins are thus higher than they would be in a more competitive market.
What is game theory?
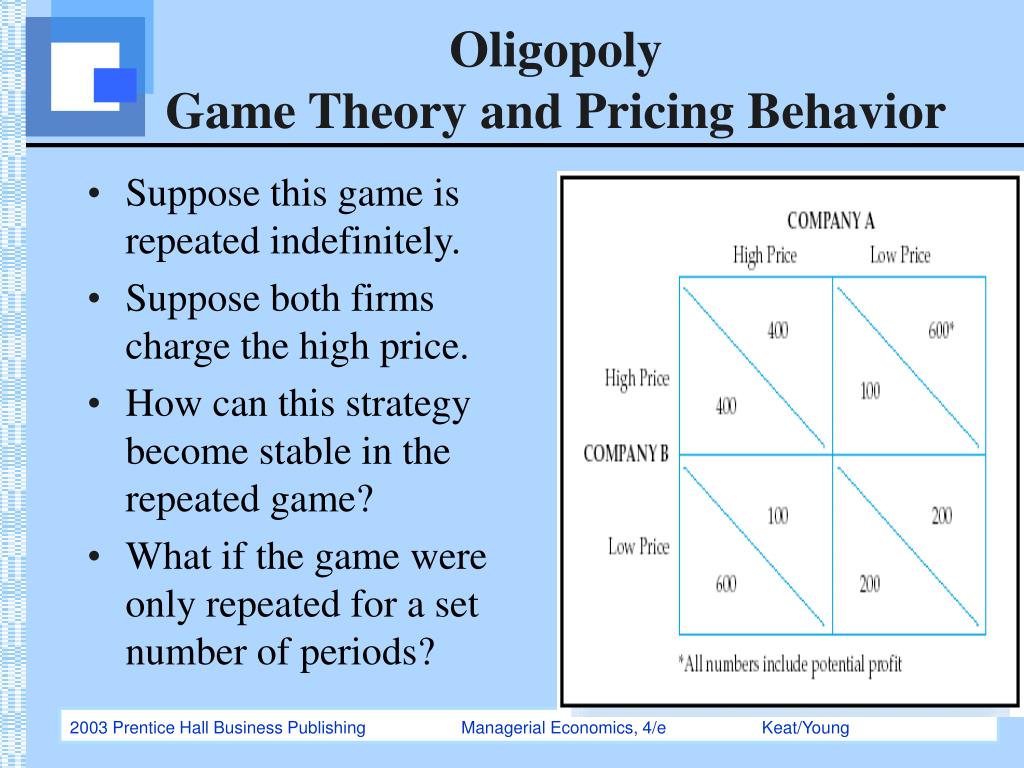
Game theory uses the same setup as regular games, including players, moves, strategies, and rewards. Below is an example of a simple game simulation, which helps to explain some oligopoly behavior.
Who won the Nobel Prize for Game Theory?
In 1994, John Nash (pictured) won the Nobel Prize for his revolutionary game theory models. He was also the subject of the 1998 biography by Sylvia Nasar and the 2001 film A Beautiful Mind, starring Russell Crowe.
What happens when firm B sets a high price and firm A sets a lower price?
The opposite happens when firm B sets a high price, and firm A sets a lower price (the green option). If both firms set a high price, then neither firm will have a market share advantage, but the high price will generate a moderately high profit for each firm (the black option).
What happens when firm B sets a high price?
When firm A sets a high price, but firm B sets a lower price (the blue option in the table), then most consumers will purchase firm’s B’s products, and firm B will make a much higher profit than firm A. The opposite happens when firm B sets a high price, and firm A sets a lower price (the green option).
Which countries are in disagreement with OPEC?
This makes it very hard to reach an agreement between members, especially if there are a lot of members. OPEC countries Saudi Arabia, Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, and Venezuela have had many disagreements about how much to produce and what price to charge.
Is OPEC a cartel?
In most industrialized countries, anti-trust laws prohibit explicit cooperation. OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries) is a cartel and operates outside of countries’ boundaries. Therefore, OPEC is not illegal.
Is it difficult for a non-monopoly firm to earn excessively high profits even in the long run?
This is often the case, even when firms attempt to collude and form cartels. Usually, in the long run, competitive market forces prevail and keep prices in check for consumers.
What is an oligopoly?
An oligopoly consists of a small number of firms producing for the same market. Defining characteristics include barriers to entry (which protect any resulting profits) and patterns of strategic interaction among the firms. To identify “strategic interactions,” it helps to understand why perfectly competitive firms are not interacting strategically.
Why are prices sticky in oligopoly?
The “kinked demand curve” model of oligopoly can explain why prices of some goods tend to be “sticky:” any decrease in price is met by competitors but any increase in price is not , so changing price in either direction lowers profits. Game theory.
What is a monopolistically competitive market?
Monopolistically competitive markets are made up of a large number of firms producing differentiated products. (The market for t-shirts might fall into this category, because t-shirts from different companies are substitutes for each other but not identical – the definition of “differentiated”).
What is the goal of market competition?
In market competition, the goal is generally profit-maximization (at least in the long run; short run losses might strategically lead to long run gains). Finally, the competing firms have various strategies available to them (which could involve price, product innovation, location, etc.).
What do firms do in a perfectly competitive market?
In a perfectly competitive market, firms do one thing: equate the market-generated price (determined through interactions of many buyers and sellers) to their own marginal cost of production to find their profit-maximizing level of output. That’s it.
Is there a rule of thumb for oligopoly?
There isn’t a simple rule of thumb (such as “set marginal revenue equal to marginal cost”) that will predict prices, output levels or profits for oligopolies. Microeconomic theorists have created a variety of models to depict specific types of interactions that may be present in oligopolies. For example, the model of Bertrand competition ...
Who developed game theory?
First developed by mathematician John von Neumann, it provides a way to think logically about the choices players should make to bring about the best possible outcomes. Game theory emphasizes the interdependence of the players: the outcome of any game depends on your own choices AND the choices made by your competitors.
Key Terms Regarding Oligopolies
Collusion: a secret agreement to cooperate and work together in order to accomplish a common goal. This is similar to when two individuals who are suspected and arrested for a particular crime agree to both remain silent.
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of how people behave in strategic situations. With the oligopoly market structure, we use a matrix to apply this concept.
How is game theory applied to politics?from en.wikipedia.org
Early examples of game theory applied to political science are provided by Anthony Downs. In his 1957 book An Economic Theory of Democracy, he applies the Hotelling firm location model to the political process. In the Downsian model, political candidates commit to ideologies on a one-dimensional policy space. Downs first shows how the political candidates will converge to the ideology preferred by the median voter if voters are fully informed, but then argues that voters choose to remain rationally ignorant which allows for candidate divergence. Game theory was applied in 1962 to the Cuban Missile Crisis during the presidency of John F. Kennedy.
How did game theory change economics?from investopedia.com
Game theory brought about a revolution in economics by addressing crucial problems in prior mathematical economic models. For instance, neoclassical economics struggled to understand entrepreneurial anticipation and could not handle the imperfect competition. Game theory turned attention away from steady-state equilibrium toward the market process.
What Is Game Theory?from investopedia.com
Game theory is a theoretical framework for conceiving social situations among competing players. In some respects, game theory is the science of strategy, or at least the optimal decision-making of independent and competing actors in a strategic setting.
Who came up with game theory?from investopedia.com
Game theory is largely attributed to the work of mathematician John von Neumann and economist Oskar Morgenstern in the 1940s and was developed extensively by many other researchers and scholars in the 1950s. It remains an area of active research and applied science to this day.
What are some of the assumptions about these games?from investopedia.com
Like many economic models, game theory also contains a set of strict assumptions that must hold for the theory to make good predictions in practice. First, all players are utility-maximizing rational actors that have full information about the game, the rules, and the consequences. Players are not allowed to communicate or interact with one another. Possible outcomes are not only known in advance but also cannot be changed. The number of players in a game can theoretically be infinite, but most games will be put into the context of only two players.
What is profit maximization in economics?from thismatter.com
In competitive, monopolistically competitive, and monopolistic markets, the profit maximizing strategy is to produce that quantity of product where marginal revenue = marginal cost. This is also true of oligopolistic markets — the problem is, it is difficult for a firm in an oligopoly to determine its marginal revenue because the quantity of product that can be sold for a given price will depend on the prices charged by the other firms in the oligopoly and the quantity that they produce. Economists have examined this interdependence by using game theory, which analyzes strategies used by individual players that account for what the other players will do. What distinguishes game theory from other types of economic decisions is that decisions in game theory are based on what other people in the game will do or would be expected to do. Most other economic decisions are not based on the reaction or expected reactions of others but are based on details of the thing being decided.
What happens if you repeat a game?from economicshelp.org
If games are repeated then there is the possibility of punishing people for cheating, this will provide an incentive for sticking to the Pareto optimal approach.
How do firms in an oligopoly decide on quantity and pricing?
When firms in an oligopoly must decide about quantity and pricing, they must consider what the other firms will do, since quantity and price are invers ely related. If all the firms produce too much, then the price may drop below their average total costs, causing them losses. If they can restrict quantity to that which corresponds to where marginal cost = marginal revenue for the oligopoly as a whole, then they can maximize their profits. However, they do have one advantage over the prisoner's dilemma scenario — they usually know what the other firms did in the past, so they can decide on quantity and pricing based on the assumption that they will act in the same way in the future. But if the firm is wrong in its anticipation, then they can make corrections in its production schedule.
What is game theory?
Economists have examined this interdependence by using game theory, which analyzes strategies used by individual players that account for what the other players will do. What distinguishes game theory from other types of economic decisions is that decisions in game theory are based on what other people in the game will do or would be expected to do.
How do cartels work?
When firms in a cartel cooperate by restricting quantity for higher prices , then each firm gets Po for its product by restricting its quantity to the agreed amount Qo (it is assumed that Qo = each firm's MR = MC output), and each firm earns the revenue above its marginal cost represented by the areas 1 + 3 in the diagram on the left. Hence, the oligopoly earns what a monopoly would earn. (Note that the quantity Qo would probably be different for the different firms, but the graph still represents each firm's revenue, but the quantity axis would be adjusted, depending on the firm's market share, which is usually commensurate with its size.)
What happens when none of the cartel members cooperate?
When none of the cartel members cooperate, then the quantity increases to Qc and the market price declines to the competitive price Pc, and each firm in the oligopoly earns 3 + 4 above their marginal cost. (Again, the size of the 2 areas will be commensurate with the size of the firms and their corresponding market share.)
Why do cartels fail?
Cartels often fail because one or more firms will be tempted to cheat, since this will allow them to earn outsized profits , especially if they are a smaller firm that contributes only a small share of the total output of the oligopoly. For that would allow the firm to sell a greater quantity at the profit maximizing price without lowering demand, and therefore, the price. It would also improve the firm's economy of scale.
What is the common scenario for applying game theory to decision making?
A common scenario for applying game theory to decision-making is the prisoners' dilemma. Bennie and Stella were arrested for robbing banks. Each was interrogated in separate rooms, where the interrogators offered them a choice: if neither confessed, then they would each get 2 years.
How many possibilities are there in the payoff matrix?
There are 4 possibilities, represented by the following payoff matrix:
What is game theory in oligopoly?
Below is a game theory example that models collusion in a two-firm oligopoly: It is important to note that in real-life oligopolies, the games (instances of collusion) are sequential; meaning that one firm’s behavior in one game may influence the game’s outcome in future periods.
What is an oligopoly?
The term “oligopoly” refers to an industry where there are only a small number of firms operating. In an oligopoly, no single firm enjoys a large amount of market power. Economies of Scope Economies of scope is an economic concept that refers to the decrease in the total cost of production when a range of products are produced together rather ...
How to protect consumers from oligopolies?
While some oligopolies do not significantly harm consumers, others do. In such cases, governments can take a range of actions to protect consumers, such as:
Why do firms need to collude in an oligopoly?
In an oligopoly, all firms would need to collude in order to raise prices and realize a higher economic profit. Most oligopolies exist in industries where goods are relatively undifferentiated and broadly provide the same benefit to consumers.
Why do oligopolies exist?
The biggest reason why oligopolies exist is collaboration. Firms see more economic benefits in collaborating on a specific price than in trying to compete with their competitors. By controlling prices, oligopolies are able to raise their barriers to entry.
What is the new equilibrium?
Therefore, the new equilibrium would be the one where neither firms collude and achieve profits that would occur under perfect competition (which is significantly less profitable than colluding). Thus, to realize the best long-run profits, firms in an oligopoly choose to collude.
What is utility theory?
Utility Theory In the field of economics, utility (u) is a measure of how much benefit consumers derive from certain goods or services. From a finance
